File
... It was once believed that conditioning occurred the same in all animals (and therefore you could study human behavior by studying any animal) and that you could associate any neutral stimulus with a response. Not so. Animals have biological predispositions to ...
... It was once believed that conditioning occurred the same in all animals (and therefore you could study human behavior by studying any animal) and that you could associate any neutral stimulus with a response. Not so. Animals have biological predispositions to ...
CHAPTER 6: LEARNING
... Section 1: Classical Conditioning Section 2: Operant Conditioning Section 3: Cognitive Factors in Learning Section 4: The PQ4R Method: Learning to Learn ...
... Section 1: Classical Conditioning Section 2: Operant Conditioning Section 3: Cognitive Factors in Learning Section 4: The PQ4R Method: Learning to Learn ...
Chapter 5 - IPFW.edu
... B. Tolerance may be a biological phenomenon, but it also may be a classically conditioned response. 1. Aspects of the environment become stimuli that produce a classicallyconditioned reaction that leads to tolerance. 2. In a new environment the same amount of drug—without the conditioned tolerance c ...
... B. Tolerance may be a biological phenomenon, but it also may be a classically conditioned response. 1. Aspects of the environment become stimuli that produce a classicallyconditioned reaction that leads to tolerance. 2. In a new environment the same amount of drug—without the conditioned tolerance c ...
What is learned?
... spontaneous recovery: after rest interval, extinguished CR reappears at almost previous strength, and extinguishes faster next time ...
... spontaneous recovery: after rest interval, extinguished CR reappears at almost previous strength, and extinguishes faster next time ...
Learning - Forensic Consultation
... map (a mental image of a threedimensional space). They also displayed latent learning (hidden learning that exists without behavioral signs). ...
... map (a mental image of a threedimensional space). They also displayed latent learning (hidden learning that exists without behavioral signs). ...
presentation source
... subjective awareness of themselves & their situations • Human choices, creativity, & selfactualization are important areas to study • It is better to study an important problem with a less refined methodology than a trivial problem with a complex methodology ...
... subjective awareness of themselves & their situations • Human choices, creativity, & selfactualization are important areas to study • It is better to study an important problem with a less refined methodology than a trivial problem with a complex methodology ...
leadership
... Extinction: The condition stimulus looses the power to evoke a conditioned response No reinforcement: Disconnect the link between the CS and the US, the link between the bell and the food. i.e Bell but no food. Response looses strength ...
... Extinction: The condition stimulus looses the power to evoke a conditioned response No reinforcement: Disconnect the link between the CS and the US, the link between the bell and the food. i.e Bell but no food. Response looses strength ...
Psychology HW pg. 313-325
... better than group A) Conclusions – Rats in group C were learning all along but didn’t show it. Two big things from this study 1. Latent Learning: Learning is hidden until it is used. 2. Cognitive Map: A mental representation of the spatial layout Rescorla – Predictive power of US/CS. • Group A – 20 ...
... better than group A) Conclusions – Rats in group C were learning all along but didn’t show it. Two big things from this study 1. Latent Learning: Learning is hidden until it is used. 2. Cognitive Map: A mental representation of the spatial layout Rescorla – Predictive power of US/CS. • Group A – 20 ...
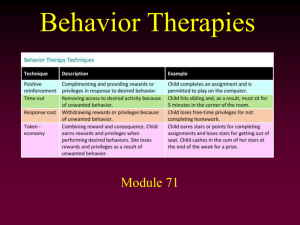
Module 71 - Behavioral Therapy
... • Eventually bladder tension (CR) causes the child to awaken (CR). • It is effective in about 75 percent of school-age children who have difficulties with bedwetting. ...
... • Eventually bladder tension (CR) causes the child to awaken (CR). • It is effective in about 75 percent of school-age children who have difficulties with bedwetting. ...
chapter 6 review with answers
... unnatural response towards. - Example bell 3. Unconditioned response - Natural response - Example salivation towards food 4. Conditioned response - Unnatural response - Salivation towards bell 5. Trial - Pairing of Unconditioned stimulus to Conditioned Stimulus 6. Acquisition - Initial stage of lear ...
... unnatural response towards. - Example bell 3. Unconditioned response - Natural response - Example salivation towards food 4. Conditioned response - Unnatural response - Salivation towards bell 5. Trial - Pairing of Unconditioned stimulus to Conditioned Stimulus 6. Acquisition - Initial stage of lear ...
Behavioral Theory rev 2012
... Stimulus generalization – somewhat like over generalization in language, people may over generalize a response CER’s – conditioned emotional responses often compound generalization and create problems for discrimination (classically conditioned) Stimulus discrimination – Identifying key elements ...
... Stimulus generalization – somewhat like over generalization in language, people may over generalize a response CER’s – conditioned emotional responses often compound generalization and create problems for discrimination (classically conditioned) Stimulus discrimination – Identifying key elements ...
learning behavior
... Habituation is the simplest form of learning. Habituation like phenomena is found in every group of animals from Weevil to Whales. By habituation animals learn to conserve energy and time by not responding to an irrelevant stimulus. If a neutral stimulus that has neither noxious nor beneficial ...
... Habituation is the simplest form of learning. Habituation like phenomena is found in every group of animals from Weevil to Whales. By habituation animals learn to conserve energy and time by not responding to an irrelevant stimulus. If a neutral stimulus that has neither noxious nor beneficial ...
Chapter 5 - Learning
... for a correct response made after a fixed amount of time has elapsed since the last reinforcement. Whereas, in a variable-interval schedule, the amount of time that must elapse before reinforcement can be given for a correct response is variable rather than fixed. Escape learning is learning of be ...
... for a correct response made after a fixed amount of time has elapsed since the last reinforcement. Whereas, in a variable-interval schedule, the amount of time that must elapse before reinforcement can be given for a correct response is variable rather than fixed. Escape learning is learning of be ...
Behaviorist Perspective - West Point Public Schools
... What was the UCR, UCS, CR, and CS of one of your activities ...
... What was the UCR, UCS, CR, and CS of one of your activities ...
Theorists Ivan Pavlov John B. Watson Edward L.Thorndike
... I found it interesting that the theorist seemed to connect with the fact that the environment plays a role in the theory. The environment has to be set up favorably for the student to react favorably. If the environment is unsatisfactory the student will react accordingly. I have tried to create a v ...
... I found it interesting that the theorist seemed to connect with the fact that the environment plays a role in the theory. The environment has to be set up favorably for the student to react favorably. If the environment is unsatisfactory the student will react accordingly. I have tried to create a v ...
20 IVAN PAVLOV AND CLASSICAL CONDITIONING
... had become connected in the brain with the arrival of the food itself. Salivation occurred in anticipation of that food. Pavlov set out to study the formation of such connections. But the assistant was an unnecessary complication, and the dog had had experience with him before. Pavlov wanted to stud ...
... had become connected in the brain with the arrival of the food itself. Salivation occurred in anticipation of that food. Pavlov set out to study the formation of such connections. But the assistant was an unnecessary complication, and the dog had had experience with him before. Pavlov wanted to stud ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... 19. It is easier to train a dog to bark for food than to train it to stand on its hind legs for food. This best illustrates the importance of ______ in learning. ...
... 19. It is easier to train a dog to bark for food than to train it to stand on its hind legs for food. This best illustrates the importance of ______ in learning. ...
Classical Conditioning
... Learning and Conditioning Experiment Analysis With a partner, you are going to look at a number of psychologists that show each type of learning. You need to research 3 of the 4 Learning psychologists that test Classical Conditioning, Operant Conditioning, and Observational Learning. ...
... Learning and Conditioning Experiment Analysis With a partner, you are going to look at a number of psychologists that show each type of learning. You need to research 3 of the 4 Learning psychologists that test Classical Conditioning, Operant Conditioning, and Observational Learning. ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... 19. It is easier to train a dog to bark for food than to train it to stand on its hind legs for food. This best illustrates the importance of ______ in learning. ...
... 19. It is easier to train a dog to bark for food than to train it to stand on its hind legs for food. This best illustrates the importance of ______ in learning. ...
Learning a - landman
... Stimulus Discrimination Learners can be trained not to generalize, but rather to make a conditioned response only to a single stimulus. Classical • CR is specific to a certain CS-US pairing Operant • Reinforcing only specific responses ...
... Stimulus Discrimination Learners can be trained not to generalize, but rather to make a conditioned response only to a single stimulus. Classical • CR is specific to a certain CS-US pairing Operant • Reinforcing only specific responses ...
Chapter 5: Learning - College of the Canyons
... The first question is the easiest way to break down the information. If an event is a stimulus, it will cause something else to happen. A stimulus is any event that causes a response. Once you determine if your event is a stimulus or response, the second question is fairly easy. Is the stimulus some ...
... The first question is the easiest way to break down the information. If an event is a stimulus, it will cause something else to happen. A stimulus is any event that causes a response. Once you determine if your event is a stimulus or response, the second question is fairly easy. Is the stimulus some ...
Homework Review
... think of a particular romantic partner. a particular cologne is smelled and you immediately think of a romantic partner. ...
... think of a particular romantic partner. a particular cologne is smelled and you immediately think of a romantic partner. ...
Isabella E - BDoughertyAmSchool
... Classical conditioning is generally used with low-involvement products. This is because classical conditioning is most effective when emotion is involved (Classical Conditioning.) Advertising for low-involvement products usually attacks the consumer through affective means because nobody wants to t ...
... Classical conditioning is generally used with low-involvement products. This is because classical conditioning is most effective when emotion is involved (Classical Conditioning.) Advertising for low-involvement products usually attacks the consumer through affective means because nobody wants to t ...
Classical conditioning

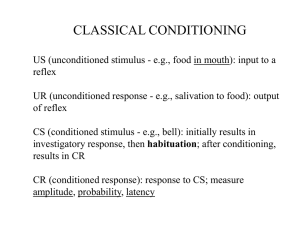
Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a learning process in which an innate response to a potent stimulus comes to be elicited in response to a previously neutral stimulus; this is achieved by repeated pairings of the neutral stimulus with the potent stimulus. The basic facts about classical conditioning were discovered by Ivan Pavlov through his famous experiments with dogs. Together with operant conditioning, classical conditioning became the foundation of Behaviorism, a school of psychology that dominated psychology in the mid-20th century and is still an important influence on the practice of psychological therapy and the study of animal behaviour (ethology). Classical conditioning is now the best understood of the basic learning processes, and its neural substrates are beginning to be understood.