A17 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... Sensory receptors - transducers that convert various forms of energy in environment into action potentials in neurons. sensory receptors may be: a) neurons (distal tip of peripheral axon of sensory neuron) – e.g. in skin receptors. b) specialized cells (that release neurotransmitter and generate a ...
... Sensory receptors - transducers that convert various forms of energy in environment into action potentials in neurons. sensory receptors may be: a) neurons (distal tip of peripheral axon of sensory neuron) – e.g. in skin receptors. b) specialized cells (that release neurotransmitter and generate a ...
Conditioning and Learning
... Garcia and Koelling (1966) demonstrated that some stimulus-response associations are much easier to condition than others. (a) Their procedure allowed them to pair a taste stimulus (saccharin-flavored water) with visual and auditory stimuli (a bright light and noisy buzzer), and/or pain-inducing sho ...
... Garcia and Koelling (1966) demonstrated that some stimulus-response associations are much easier to condition than others. (a) Their procedure allowed them to pair a taste stimulus (saccharin-flavored water) with visual and auditory stimuli (a bright light and noisy buzzer), and/or pain-inducing sho ...
PSYC 2500-02 LEARNING: QUIZ 2 NAME: Spring 2016 Read each
... He accepted the "S-O-R" psychology of Hull and other classical behaviorists that made an appeal to physiological responses, though implicit and unobservable. b) He wanted psychology to be a technology of behavior, and therefore had the goal of being able to perfectly control and predict behavior usi ...
... He accepted the "S-O-R" psychology of Hull and other classical behaviorists that made an appeal to physiological responses, though implicit and unobservable. b) He wanted psychology to be a technology of behavior, and therefore had the goal of being able to perfectly control and predict behavior usi ...
Document
... • Third-order neurons • Conduct impulses from the thalamus to the somatosensory cortex (perceptual level) ...
... • Third-order neurons • Conduct impulses from the thalamus to the somatosensory cortex (perceptual level) ...
Do Stimuli Elicit Behavior?—A Study in the Logical Foundations of
... quite different from, and much more serious than, the grammatical refinements of behaviorese. Traditional S-R jargon, in which a stimulus is spoken of as though it were in itself the elicitor of the response, plus failure to recognize explicitly that the imminent external cause of a behavioral event ...
... quite different from, and much more serious than, the grammatical refinements of behaviorese. Traditional S-R jargon, in which a stimulus is spoken of as though it were in itself the elicitor of the response, plus failure to recognize explicitly that the imminent external cause of a behavioral event ...
IA_CogCore
... responses in V1, V2, and V3 to a bar on a background grid of lower contrast. • Cooling typically produces a reversible reduction in firing rate to the cell’s optimal stimulus. • Top down effect is greatest for stimuli of low contrast. If the stimulus is easy to see when it is not moving, top-down in ...
... responses in V1, V2, and V3 to a bar on a background grid of lower contrast. • Cooling typically produces a reversible reduction in firing rate to the cell’s optimal stimulus. • Top down effect is greatest for stimuli of low contrast. If the stimulus is easy to see when it is not moving, top-down in ...
Learning theory
... Learning theory essay 4) These infants had remained bonded to their biological mothers, who were not their primary caregivers. This rejects the concept that food is the primary driver for attachment as predicted by the learning theory. 5) This shows that although it is logical to suggest that a bab ...
... Learning theory essay 4) These infants had remained bonded to their biological mothers, who were not their primary caregivers. This rejects the concept that food is the primary driver for attachment as predicted by the learning theory. 5) This shows that although it is logical to suggest that a bab ...
Describe and evaluate the historical and cultural conditions that
... opened the first fully functioning psychology laboratory in 1879 as well (We Didn’t Start the Fire, 2008). These achievements, amongst others are what leave Wundt’s mark on the world of psychology today. Known best for his theory of evolution, Charles Darwin (1809-1880) is another important and wid ...
... opened the first fully functioning psychology laboratory in 1879 as well (We Didn’t Start the Fire, 2008). These achievements, amongst others are what leave Wundt’s mark on the world of psychology today. Known best for his theory of evolution, Charles Darwin (1809-1880) is another important and wid ...
Slide ()
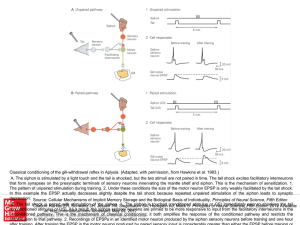
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
Time-55 minutes, 100 Questions - Bremen High School District 228
... A) difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution. B) average squared deviation of scores from a sample mean. C) direction and strength of the relationship between two variables. D) statistical significance of a difference between two sample means. E) frequency of scores at each ...
... A) difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution. B) average squared deviation of scores from a sample mean. C) direction and strength of the relationship between two variables. D) statistical significance of a difference between two sample means. E) frequency of scores at each ...
Myer Chapter 8 Learning - sls
... baby sees any man, the baby calls out “Dada.”) Discrimination is the reverse of generalization. Some stimuli have pleasant consequences and some do not. (A baby gradually learns that only one person responds with a smile when called “Dada.”) ...
... baby sees any man, the baby calls out “Dada.”) Discrimination is the reverse of generalization. Some stimuli have pleasant consequences and some do not. (A baby gradually learns that only one person responds with a smile when called “Dada.”) ...
Chapter 6: Learning - Doral Academy Preparatory
... Q1. A group of ranchers attempts to discourage coyotes from attacking their sheep by placing a substance on the wool of the sheep that makes coyotes violently ill if they eat it.Very quickly, the coyotes avoid the sheep entirely. In this scenario, what are the UCS, CS, and CR, respectively? (A) The ...
... Q1. A group of ranchers attempts to discourage coyotes from attacking their sheep by placing a substance on the wool of the sheep that makes coyotes violently ill if they eat it.Very quickly, the coyotes avoid the sheep entirely. In this scenario, what are the UCS, CS, and CR, respectively? (A) The ...
Chapter05 Power Point - Marie-Murphy-WIN13
... delayed – Short-term consequences are more of incentive than long-term ...
... delayed – Short-term consequences are more of incentive than long-term ...
Chapter 6: Behaviour
... Honeybees can be conditioned to seek food on a piece of blue cardboard By offering other colors to a blue-conditioned bee, Karl von Frisch found that honeybees can discriminate between yellow-green, blue-green, blue-violet, and UV •After a period of feeding from a dish placed on blue cardboard, the ...
... Honeybees can be conditioned to seek food on a piece of blue cardboard By offering other colors to a blue-conditioned bee, Karl von Frisch found that honeybees can discriminate between yellow-green, blue-green, blue-violet, and UV •After a period of feeding from a dish placed on blue cardboard, the ...
File
... Stimulus discrimination involves responding to one stimulus but not to stimuli that are similar Confusing stimuli may cause experimental neurosis ...
... Stimulus discrimination involves responding to one stimulus but not to stimuli that are similar Confusing stimuli may cause experimental neurosis ...
Rat Maze - FTHS Wiki
... completed if you beat your previous time • Try again—you can complete as many mazes as possible in the time allotted ...
... completed if you beat your previous time • Try again—you can complete as many mazes as possible in the time allotted ...
PSY 402
... Fixity of cat flank-rubbing supported Guthrie but was later shown to be related to the presence of the experimenter instead. ...
... Fixity of cat flank-rubbing supported Guthrie but was later shown to be related to the presence of the experimenter instead. ...
Operant Conditioning
... – Increases frequency of behavior by removing an unpleasant (aversive) stimulus • Ex: Aspirin, giving in to tantrum, faking sick, drugs to avoid withdrawal ...
... – Increases frequency of behavior by removing an unpleasant (aversive) stimulus • Ex: Aspirin, giving in to tantrum, faking sick, drugs to avoid withdrawal ...
Sensory perception
... • Information from other receptors, especially odor • Temperature and texture of food ...
... • Information from other receptors, especially odor • Temperature and texture of food ...
chapter3 (new window)
... Selective Rearing • Animals are reared in environments that contain only certain types of stimuli – Neurons that respond to these stimuli will become more predominate due to neural plasticity. – Blakemore and Cooper (1970) showed this by rearing kittens in tubes with either horizontal for vertical ...
... Selective Rearing • Animals are reared in environments that contain only certain types of stimuli – Neurons that respond to these stimuli will become more predominate due to neural plasticity. – Blakemore and Cooper (1970) showed this by rearing kittens in tubes with either horizontal for vertical ...
Chapter 2: Research Methodology
... A. After extinction of the association, the animal shows the conditioned response again. B. An animal can easily learn to associate a conditioned stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus. C. If an animal is sick, it remembers the learned association after it ...
... A. After extinction of the association, the animal shows the conditioned response again. B. An animal can easily learn to associate a conditioned stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus. C. If an animal is sick, it remembers the learned association after it ...
Neural Correlates of Selection
... • Opportunity to participate in Cognitive Neuroscience and Perception experiment - sign up for Tuesday, Wednesday or Thursday afternoons by emailing [email protected] ...
... • Opportunity to participate in Cognitive Neuroscience and Perception experiment - sign up for Tuesday, Wednesday or Thursday afternoons by emailing [email protected] ...
Conditioning
... Evidence of cognitive processes during operant learning comes from rats during a maze exploration in which they navigate the maze without an obvious reward. Rats seem to develop cognitive maps, or mental representations, of the layout of the maze ...
... Evidence of cognitive processes during operant learning comes from rats during a maze exploration in which they navigate the maze without an obvious reward. Rats seem to develop cognitive maps, or mental representations, of the layout of the maze ...
Introduction to Psychology
... when a UCS does not follow a CS in operant conditioning, when a response is no ...
... when a UCS does not follow a CS in operant conditioning, when a response is no ...