Replication vs. Transcription vs. Translation
... How is RNA different from DNA? (Hint: 3 ways) 1. Their structures are different- RNA is single stranded (DNA is double stranded), 2. The sugar in RNA is ribose (DNA’s sugar is deoxyribose), 3. RNA contains different nitrogenous bases- AGCU (DNA contains AGCT) ...
... How is RNA different from DNA? (Hint: 3 ways) 1. Their structures are different- RNA is single stranded (DNA is double stranded), 2. The sugar in RNA is ribose (DNA’s sugar is deoxyribose), 3. RNA contains different nitrogenous bases- AGCU (DNA contains AGCT) ...
Biochemistry Lecture 23 THE LAST ONE!
... – Shine-Dalgarno sequence helps w/ proper placement of mRNA into P site (27-23) • Specific seq along mRNA @ partic site relative to intitiation codon • Recognized by rRNA of 30S ribosome • Helps “line up” mRNA initiation codon @ P site on 30S ...
... – Shine-Dalgarno sequence helps w/ proper placement of mRNA into P site (27-23) • Specific seq along mRNA @ partic site relative to intitiation codon • Recognized by rRNA of 30S ribosome • Helps “line up” mRNA initiation codon @ P site on 30S ...
Plant Biotechnology
... The long history of plant breeding provides plant geneticists with a wealth of strains that can be exploited at the molecular level Plants produce large no.s of progeny; so rare mutations and recombinations can be found more easily Plants have been regenerative capabilities, even from one cell Speci ...
... The long history of plant breeding provides plant geneticists with a wealth of strains that can be exploited at the molecular level Plants produce large no.s of progeny; so rare mutations and recombinations can be found more easily Plants have been regenerative capabilities, even from one cell Speci ...
Transcription and Translation Review Lesson Plan
... Explain how messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA are involved in the transcription and translation of genes. Describe how the code of DNA is translated into messenger RNA and is utilized to synthesize a particular protein. Content Standards: Illinois State Science Standard 12.A.4a Ex ...
... Explain how messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA are involved in the transcription and translation of genes. Describe how the code of DNA is translated into messenger RNA and is utilized to synthesize a particular protein. Content Standards: Illinois State Science Standard 12.A.4a Ex ...
Protein-coding genes
... RNA editing RNA editing is a rare form of post-transcriptional processing whereby base-specific changes are enzymatically introduced at the RNA level. Types of RNA editing in humans: (i) C---> U, occurs in humans by a specific cytosine deaminase e.g. The expression of the human apolipoprotein B ...
... RNA editing RNA editing is a rare form of post-transcriptional processing whereby base-specific changes are enzymatically introduced at the RNA level. Types of RNA editing in humans: (i) C---> U, occurs in humans by a specific cytosine deaminase e.g. The expression of the human apolipoprotein B ...
Ch. 10 Vocabs
... -Transformation: the transfer of genetic material in the form of DNA fragments from one cell to another or from one organism to another. -Bacteriophage a virus that infects bacteria. Section 2: -Nucleotide: in a nucleic-acid chain, a subunit that consists of a sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous base. ...
... -Transformation: the transfer of genetic material in the form of DNA fragments from one cell to another or from one organism to another. -Bacteriophage a virus that infects bacteria. Section 2: -Nucleotide: in a nucleic-acid chain, a subunit that consists of a sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous base. ...
Nucleic Acids - Biology Innovation
... Choice of four organic bases, adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil (mainpoint: not thymine). They also pair up, cytosine with guanine and adenine with uracil. Three types of RNA, ribosomal (rRNA), transfer (tRNA) and messenger (mRNA). ...
... Choice of four organic bases, adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil (mainpoint: not thymine). They also pair up, cytosine with guanine and adenine with uracil. Three types of RNA, ribosomal (rRNA), transfer (tRNA) and messenger (mRNA). ...
Controllable genes
... 1- Are expressed only as needed. Their amount may increase or decrease with respect to their basal level in different condition. 2- Their structure is relatively complicated with some response elements ...
... 1- Are expressed only as needed. Their amount may increase or decrease with respect to their basal level in different condition. 2- Their structure is relatively complicated with some response elements ...
Regulation of gene expression
... 1- Are expressed only as needed. Their amount may increase or decrease with respect to their basal level in different condition. 2- Their structure is relatively complicated with some response elements ...
... 1- Are expressed only as needed. Their amount may increase or decrease with respect to their basal level in different condition. 2- Their structure is relatively complicated with some response elements ...
So You Think
... won the Nobel Prize for discovering the shape of DNA. ________________ 5. DNA is said to have a ___________ ___________ ________________ shape. ________________ 6. Weak _________________ bonds allow the DNA ________________ molecule to “unzip”. ________________ 7. RNA contains three of the same nucl ...
... won the Nobel Prize for discovering the shape of DNA. ________________ 5. DNA is said to have a ___________ ___________ ________________ shape. ________________ 6. Weak _________________ bonds allow the DNA ________________ molecule to “unzip”. ________________ 7. RNA contains three of the same nucl ...
Exam 3/Final Exam Study Guide
... 2. In 1987, Genentech was the first company to create a biologic through genetic engineering of E. coli. They inserted the human eukaryotic gene for insulin production into the prokaryote, which caused the bacteria to produce insulin. They then purified the insulin, packaged it, and sold it as a dru ...
... 2. In 1987, Genentech was the first company to create a biologic through genetic engineering of E. coli. They inserted the human eukaryotic gene for insulin production into the prokaryote, which caused the bacteria to produce insulin. They then purified the insulin, packaged it, and sold it as a dru ...
amino acid - Humble ISD
... Codon = a group of 3 nucleotides on mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid. A codon can be made up of any combination of the 4 nucleotides (A, U, G, C), therefore there are up to 64 possible codons. (b/c 4 x 4 x 4 = 64) Ex: AAA, AAU, AAG, AAC Many different codons represent the same amino a ...
... Codon = a group of 3 nucleotides on mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid. A codon can be made up of any combination of the 4 nucleotides (A, U, G, C), therefore there are up to 64 possible codons. (b/c 4 x 4 x 4 = 64) Ex: AAA, AAU, AAG, AAC Many different codons represent the same amino a ...
Biology 303 EXAM III
... DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation in eukaryotes. Methylation refers to 1. altering RNA polymerase activity by methylation of RNA polymerase 2. altering translational activity especially of highly methylated tRNAs. 3. alteration of DNA polymerase activity by addition of ...
... DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation in eukaryotes. Methylation refers to 1. altering RNA polymerase activity by methylation of RNA polymerase 2. altering translational activity especially of highly methylated tRNAs. 3. alteration of DNA polymerase activity by addition of ...
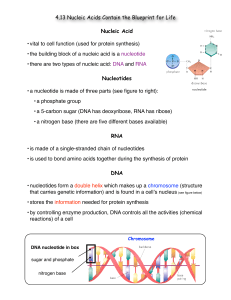
4.13 notes
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... a template to synthesise a molecule of RNA, is called transcription, and occurs in the cell nucleus. The second step is called translation and occurs in the cytoplasm, in particular in the ribosomes. During this stage ...
... a template to synthesise a molecule of RNA, is called transcription, and occurs in the cell nucleus. The second step is called translation and occurs in the cytoplasm, in particular in the ribosomes. During this stage ...
Biology 303 EXAM III
... DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation in eukaryotes. Methylation refers to 1. altering RNA polymerase activity by methylation of RNA polymerase 2. altering translational activity especially of highly methylated tRNAs. 3. alteration of DNA polymerase activity by addition of ...
... DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation in eukaryotes. Methylation refers to 1. altering RNA polymerase activity by methylation of RNA polymerase 2. altering translational activity especially of highly methylated tRNAs. 3. alteration of DNA polymerase activity by addition of ...
Slide 1
... After the RNA has been made during translation, what has to occur to finalize the RNA before it leaves the nucleus? A) Removal of the introns and exons leave the nucleus and go into the cytoplasm. B) Removal of the exons and introns leave the nucleus and go into the cytoplasm. C) Nothing has to be d ...
... After the RNA has been made during translation, what has to occur to finalize the RNA before it leaves the nucleus? A) Removal of the introns and exons leave the nucleus and go into the cytoplasm. B) Removal of the exons and introns leave the nucleus and go into the cytoplasm. C) Nothing has to be d ...
Protein Synthesis
... 7. Summarize the genetic code. Include the connection between codons and amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids that assemble into polypeptides and eventually proteins. Three consecutive nucleotides of mRNA that code for a particular amino acid is a codon. 8. Describe the relationship betwe ...
... 7. Summarize the genetic code. Include the connection between codons and amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids that assemble into polypeptides and eventually proteins. Three consecutive nucleotides of mRNA that code for a particular amino acid is a codon. 8. Describe the relationship betwe ...
More Exam Practice - Iowa State University
... tRNA whose anticodon corresponds to the codon in the A site will bind in the A site. The amino acid on the tRNA in the P site is then transferred to the amino acid on the tRNA in the A site ( they bind together in a covalent peptide bond formed by a dehydration reaction). Then, the mRNA with be “rat ...
... tRNA whose anticodon corresponds to the codon in the A site will bind in the A site. The amino acid on the tRNA in the P site is then transferred to the amino acid on the tRNA in the A site ( they bind together in a covalent peptide bond formed by a dehydration reaction). Then, the mRNA with be “rat ...
Chapter 10 (Sample questions)
... a. No sugar is present in either molecule b. Hydrogen bonding is important only in DNA c. Only DNA has a backbone of sugars and phosphates d. Adenine pairs with different bases in DNA and RNA e. Thymine pairs with different bases in DNA and RNA Which of these is found in RNA but not in DNA? a. Adeni ...
... a. No sugar is present in either molecule b. Hydrogen bonding is important only in DNA c. Only DNA has a backbone of sugars and phosphates d. Adenine pairs with different bases in DNA and RNA e. Thymine pairs with different bases in DNA and RNA Which of these is found in RNA but not in DNA? a. Adeni ...
Open-ended Review
... to the ribosomes where rRNA and tRNA translate the mRNA to obtain amino acids and build proteins ...
... to the ribosomes where rRNA and tRNA translate the mRNA to obtain amino acids and build proteins ...