Self Instructional: Cognitive Behavioral
... A way for people to teach themselves how to deal effectively with situations that had previously caused difficulties – the therapist models the appropriate behavior, the clients models the therapist’s behavior & repeats / practice ...
... A way for people to teach themselves how to deal effectively with situations that had previously caused difficulties – the therapist models the appropriate behavior, the clients models the therapist’s behavior & repeats / practice ...
Observational Learning
... Research shows that viewing media violence leads to an increased expression of aggression. ...
... Research shows that viewing media violence leads to an increased expression of aggression. ...
Strengths
... - Extinction: lack of any consequence following a behavior; decreases behavior - The Law of Effect: basically the pleasure principal - Edward Thorndike, 1901: put cats in “puzzle boxes”…with experience, they got out faster; this led to the Law of Effect - Social Learning Theory: Albert Bandura; peop ...
... - Extinction: lack of any consequence following a behavior; decreases behavior - The Law of Effect: basically the pleasure principal - Edward Thorndike, 1901: put cats in “puzzle boxes”…with experience, they got out faster; this led to the Law of Effect - Social Learning Theory: Albert Bandura; peop ...
A.P. Psychology 6 (F) - Learning By Observation
... Research shows that viewing media violence leads to an increased expression of aggression. ...
... Research shows that viewing media violence leads to an increased expression of aggression. ...
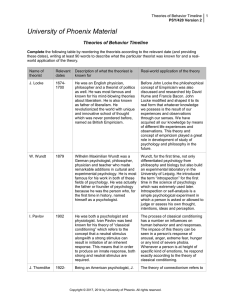
psy420r2_theories_of_behavior_timeline_1
... He has done a lot in th field of psychology that has to be remember but he is best and most known for his social cognitive theory. ...
... He has done a lot in th field of psychology that has to be remember but he is best and most known for his social cognitive theory. ...
Principles of Learning: Classical and Operant Conditioning, and
... Operant Conditioning, and Social Learning ...
... Operant Conditioning, and Social Learning ...
New Directions in Conditioning
... – Condition 1: reinforced – Condition 2: reinforced – Condition 3: not reinforced ...
... – Condition 1: reinforced – Condition 2: reinforced – Condition 3: not reinforced ...
Current Paradigms in Psychopathology and Therapy
... Presented infant with cute white rat—child showed interest in rat, was then presented with a loud noise (startle response). ...
... Presented infant with cute white rat—child showed interest in rat, was then presented with a loud noise (startle response). ...
Chapter 7 Learning Goals File
... 7. What did Mary Cover Jones discover? 8. What is the difference between classical and operant conditioning? 9. According to B.F. Skinner, why do we perform certain behaviors? 10. How do reinforcements affect behavior? 11. What is the difference between a primary and a secondary reinforcer? ...
... 7. What did Mary Cover Jones discover? 8. What is the difference between classical and operant conditioning? 9. According to B.F. Skinner, why do we perform certain behaviors? 10. How do reinforcements affect behavior? 11. What is the difference between a primary and a secondary reinforcer? ...
Learning Theories Power Point
... behavior, and that behavior could be shaped gradually. Also believed that changes in behavior are the result of an individual’s response to events that occur in the environment. Behaviorist and a Social Philosopher. Moonlights as a Poet/Author/Inventor. ...
... behavior, and that behavior could be shaped gradually. Also believed that changes in behavior are the result of an individual’s response to events that occur in the environment. Behaviorist and a Social Philosopher. Moonlights as a Poet/Author/Inventor. ...
Module 22 Powerpoint
... are harmful to individuals and society? Children who witness violence in their homes, but are not physically harmed themselves, may hate violence but still may become violent more often than the average child. Perhaps this is a result of “the Bobo doll effect”? Under stress, we do what has been ...
... are harmful to individuals and society? Children who witness violence in their homes, but are not physically harmed themselves, may hate violence but still may become violent more often than the average child. Perhaps this is a result of “the Bobo doll effect”? Under stress, we do what has been ...
Chapter 1
... – Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers – Free will of individuals – Help use inner resources to make healthier choices Cognitive Psychology – Experimental research on mental processes or cognition Modern Perspective and the Eclectic Approach Seven orientations/views – Biological/physiological, evolutionar ...
... – Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers – Free will of individuals – Help use inner resources to make healthier choices Cognitive Psychology – Experimental research on mental processes or cognition Modern Perspective and the Eclectic Approach Seven orientations/views – Biological/physiological, evolutionar ...
Down and Dirty Study Sheet
... 2. Bystander effect-people are less likely to help when several people witness an emergency due to diffusion of responsibility, thinking that someone else can be responsible 3. Social facilitation-tendency to do better on well-learned tasks when another person is present 4. Social loafing-reduction ...
... 2. Bystander effect-people are less likely to help when several people witness an emergency due to diffusion of responsibility, thinking that someone else can be responsible 3. Social facilitation-tendency to do better on well-learned tasks when another person is present 4. Social loafing-reduction ...
Name two scientists famous for their studies of classical conditioning 2
... 6 – Bill once had a blue car that was in the shop more than it was out. Since then he will not even consider owning blur or green cars. Bill’s aversion to green cars is an example of ___________. 7 – In Garcia and Koelling’s studies of taste-aversion learning, rats learned to associate taste with si ...
... 6 – Bill once had a blue car that was in the shop more than it was out. Since then he will not even consider owning blur or green cars. Bill’s aversion to green cars is an example of ___________. 7 – In Garcia and Koelling’s studies of taste-aversion learning, rats learned to associate taste with si ...
File - SSHS AP Psychology
... knowledge important to create new ideas--language, culture and social interactions important) 2) Theory of Knowledge: how is knowledge different from belief? (intellectual abilities are specific to the culture in which the child was reared) ...
... knowledge important to create new ideas--language, culture and social interactions important) 2) Theory of Knowledge: how is knowledge different from belief? (intellectual abilities are specific to the culture in which the child was reared) ...
M. Borland- Behaviorists - UHS-CD3
... Conditioned dogs to salivate at the sound of a bell, using meat powder as a stimulus ...
... Conditioned dogs to salivate at the sound of a bell, using meat powder as a stimulus ...
Grading
... Emphasis on social cognition = how people make sense of their social world— i.e., how they perceive, represent, interpret, and remember information about themselves and about other individuals and groups. - methodology and ideology from Developmental, Social, and Cognitive - comparative cognition (i ...
... Emphasis on social cognition = how people make sense of their social world— i.e., how they perceive, represent, interpret, and remember information about themselves and about other individuals and groups. - methodology and ideology from Developmental, Social, and Cognitive - comparative cognition (i ...
B. Organismic Model
... A. Learning Theory 1: Behaviorism: a mechanistic theory that describes observed behavior as a predictable response to experience. 1) Classical Conditioning: Learning based on association of a stimulus that does not ordinarily elicit a particular response with another stimulus that does elicit the re ...
... A. Learning Theory 1: Behaviorism: a mechanistic theory that describes observed behavior as a predictable response to experience. 1) Classical Conditioning: Learning based on association of a stimulus that does not ordinarily elicit a particular response with another stimulus that does elicit the re ...
Kye Paradise EDU 511 Summer 2014 GLOSSARY OF TERMS
... Constructivism: (p. 154) Learners do not passively acquire information; instead they actively try to organize it in unique ways, or construct knowledge. Individual constructivism involves an individual constructing learning separately while social constructivism involves a group of people working to ...
... Constructivism: (p. 154) Learners do not passively acquire information; instead they actively try to organize it in unique ways, or construct knowledge. Individual constructivism involves an individual constructing learning separately while social constructivism involves a group of people working to ...