molecular genetics unit review
... iii. DNA mRNA polypeptide/protein (know how to transcribe DNA and translate mRNA if given a sequence) What are the four ways gene expression is controlled? What is an operon? Describe/explain the 2 main operons (lac, trp) in prokaryotic cells. a) What are mutations? b) What are the different typ ...
... iii. DNA mRNA polypeptide/protein (know how to transcribe DNA and translate mRNA if given a sequence) What are the four ways gene expression is controlled? What is an operon? Describe/explain the 2 main operons (lac, trp) in prokaryotic cells. a) What are mutations? b) What are the different typ ...
Organization of Genetic Information Within a Cell Nucleus
... Nucleus Chromosomes are structures which contain DNA. DNA is composed of genes. ...
... Nucleus Chromosomes are structures which contain DNA. DNA is composed of genes. ...
4.13 notes
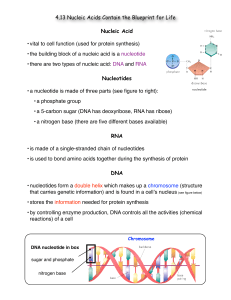
... Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded chain of nucleotides • is used to bond amino acids tog ...
... Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded chain of nucleotides • is used to bond amino acids tog ...
DISCOVERY OF DNAhandout
... Read the Nature article by Watson & Crick Discuss how they used the work of others to come up with the structure of DNA. How does the structure account for identical replication of DNA to be the conveyer of inheritance? ...
... Read the Nature article by Watson & Crick Discuss how they used the work of others to come up with the structure of DNA. How does the structure account for identical replication of DNA to be the conveyer of inheritance? ...
5echap12guidedreading
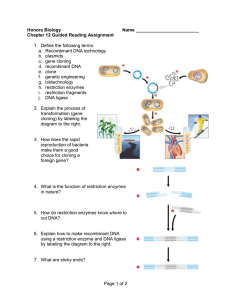
... 3. How does the rapid reproduction of bacteria make them a good choice for cloning a foreign gene? ...
... 3. How does the rapid reproduction of bacteria make them a good choice for cloning a foreign gene? ...
Lecture 10
... Crossing lox plant with cre-expressing plant to obtain F1, which will be expected to undergo Crelox recombination Retransform the lox plant with cre gene. Use inducible cre gene embedded into the lox construct. The Cre activity can be induced by applying inducer to initiate the recombination which w ...
... Crossing lox plant with cre-expressing plant to obtain F1, which will be expected to undergo Crelox recombination Retransform the lox plant with cre gene. Use inducible cre gene embedded into the lox construct. The Cre activity can be induced by applying inducer to initiate the recombination which w ...
Feb 21 Bacteria, DNA Technology, and Cell Communication
... Review Plasmids Conjugation Hfr Viral structure and types Single vs. double recombination Body Transposons Operons Negative vs. positive regulation (repressors vs. enhancers) Eukaryotic gene regulation—transcription factors Difference btw prokaryote and eukaryote gene regulation DNA technology DNA i ...
... Review Plasmids Conjugation Hfr Viral structure and types Single vs. double recombination Body Transposons Operons Negative vs. positive regulation (repressors vs. enhancers) Eukaryotic gene regulation—transcription factors Difference btw prokaryote and eukaryote gene regulation DNA technology DNA i ...
Document
... 5. Suppose individuals 1 and 5 married. Assuming no recombination occurs within the region in question, how many potentially different patterns would be observed among their progeny on Southern blot analysis? a) only 1; b) 2; c) 3; d) 4 e) 6. ...
... 5. Suppose individuals 1 and 5 married. Assuming no recombination occurs within the region in question, how many potentially different patterns would be observed among their progeny on Southern blot analysis? a) only 1; b) 2; c) 3; d) 4 e) 6. ...
Name - EdWeb
... 9. Blood cells use a protein called _______________________ to capture and carry oxygen. 10. When a gene is changed, it is said to be ______________________________________________ 11. A mutation in the hemoglobin gene cause what disorder? __________________________________ What is a Chromosome? 12. ...
... 9. Blood cells use a protein called _______________________ to capture and carry oxygen. 10. When a gene is changed, it is said to be ______________________________________________ 11. A mutation in the hemoglobin gene cause what disorder? __________________________________ What is a Chromosome? 12. ...
Genetic Engineering
... Making a cloning vector A bacterial plasmid (circular DNA) is used as one source of DNA and the second source can be from any other organism. 2. The 2 DNAs are cut at the palindromes. Both molecules become linear DNA with “sticky ends” 2. The two are mixed and the complementary sticky ends base pai ...
... Making a cloning vector A bacterial plasmid (circular DNA) is used as one source of DNA and the second source can be from any other organism. 2. The 2 DNAs are cut at the palindromes. Both molecules become linear DNA with “sticky ends” 2. The two are mixed and the complementary sticky ends base pai ...
Allele: One of the variant forms of the DNA sequence at a particular
... genome comprises of about 30000 genes. Enzyme: A protein produced by a living organism, capable of catalyzing a chemical reaction. Almost all processes in a living organism require some form of enzyme to cause the reactions to happen at a sufficient rate to support life. Risk factor: A factor in an ...
... genome comprises of about 30000 genes. Enzyme: A protein produced by a living organism, capable of catalyzing a chemical reaction. Almost all processes in a living organism require some form of enzyme to cause the reactions to happen at a sufficient rate to support life. Risk factor: A factor in an ...
Recombinant DNA - Richmond School District
... NB: The gene that is inserted into the plasmid will only work if it DOESN’T have any introns. One way to do this is to synthesize the gene in a machine. Another method is to isolate the mRNA for the gene and use “REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE” to make a DNA copy of it. (= complementary DNA ...
... NB: The gene that is inserted into the plasmid will only work if it DOESN’T have any introns. One way to do this is to synthesize the gene in a machine. Another method is to isolate the mRNA for the gene and use “REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE” to make a DNA copy of it. (= complementary DNA ...
Researchers ACT on DNA Storage
... Unlike many forms of information storage, DNA is extremely long-lasting and does not require constant electrical power. Plus, it's tiny—a small cup of DNA can store one hundred million hours of high-quality video. But until now, this storage method has faced too many obstacles: DNA synthesis is expe ...
... Unlike many forms of information storage, DNA is extremely long-lasting and does not require constant electrical power. Plus, it's tiny—a small cup of DNA can store one hundred million hours of high-quality video. But until now, this storage method has faced too many obstacles: DNA synthesis is expe ...
DNA!
... tech to create a karyotype (a map of chromosomes) to determine if trisomy 21 (3 chromosomes at 21 instead of 2) occurs. 2. PKU – tested using a blood sample to look for the presence or absence of certain proteins. This indicated whether a person’s genes are functioning normally. PKU is when a person ...
... tech to create a karyotype (a map of chromosomes) to determine if trisomy 21 (3 chromosomes at 21 instead of 2) occurs. 2. PKU – tested using a blood sample to look for the presence or absence of certain proteins. This indicated whether a person’s genes are functioning normally. PKU is when a person ...
2D Barcode Quiz
... Proteins are polymers consisting of building blocks called amino acids All proteins begin with the amino acid Methionine A codon is a series of four sequential nucleotides which codes for an amino acid Polymerase is an enzyme which breaks down DNA molecules Transcription is the process of making an ...
... Proteins are polymers consisting of building blocks called amino acids All proteins begin with the amino acid Methionine A codon is a series of four sequential nucleotides which codes for an amino acid Polymerase is an enzyme which breaks down DNA molecules Transcription is the process of making an ...
DNA Technology
... For each of these TWO technologies (Gene splicing and DNA Fingerprinting) 1. Explain the technique. Be specific and brief (one paragraph) List your source. 2. Research an example of how the technique has been used by humans. You can use one of the examples listed above or find your own. Be specific ...
... For each of these TWO technologies (Gene splicing and DNA Fingerprinting) 1. Explain the technique. Be specific and brief (one paragraph) List your source. 2. Research an example of how the technique has been used by humans. You can use one of the examples listed above or find your own. Be specific ...
The Chemistry of Life
... • The endpoint of drug molecule-receptor complexes: activation or repression of DNA replication or transcription.- Drug ...
... • The endpoint of drug molecule-receptor complexes: activation or repression of DNA replication or transcription.- Drug ...
Study Guide to Chapter 5 Ð DNA
... ______________________ a) transcription b) translation, in which a DNA serves as a template to make a strand of ___________________ a) mRNA b) tRNA. This occurs in __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is cal ...
... ______________________ a) transcription b) translation, in which a DNA serves as a template to make a strand of ___________________ a) mRNA b) tRNA. This occurs in __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is cal ...
Biology Molecular Genetic Review
... 13. Draw a piece of mRNA 5 codons long. Draw the pieces of tRNA that would match up. ...
... 13. Draw a piece of mRNA 5 codons long. Draw the pieces of tRNA that would match up. ...
which together form the gene "stories" NOTE
... contained in the chromosomes humans have 46, dogs78, mice40, some bacteriaonly one DNA gives the cells specific instructions to create protiens for the organism they belong to ...
... contained in the chromosomes humans have 46, dogs78, mice40, some bacteriaonly one DNA gives the cells specific instructions to create protiens for the organism they belong to ...
Structure and History of DNA 1-8
... “It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material”. • Besides copying, DNA must do ...
... “It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material”. • Besides copying, DNA must do ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.