here - St Vincent College
... Term that means the DNA has 2 strands that are twisted together (dh) There are 23 pairs of these in most human cells (c) ...
... Term that means the DNA has 2 strands that are twisted together (dh) There are 23 pairs of these in most human cells (c) ...
Name
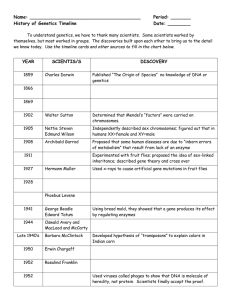
... To understand genetics, we have to thank many scientists. Some scientists worked by themselves, but most worked in groups. The discoveries built upon each other to bring us to the detail we know today. Use the timeline cards and other sources to fill in the chart below. ...
... To understand genetics, we have to thank many scientists. Some scientists worked by themselves, but most worked in groups. The discoveries built upon each other to bring us to the detail we know today. Use the timeline cards and other sources to fill in the chart below. ...
Restriction Enzymes, Vectors, and Genetic Libraries
... . Produce fragments of DNA using enzymes that cut DNA at specific base sequences. . Link these fragments to selfreplicating forms of DNA = vectors. ...
... . Produce fragments of DNA using enzymes that cut DNA at specific base sequences. . Link these fragments to selfreplicating forms of DNA = vectors. ...
Unit 4: Genetics
... • 1) Future understanding of many genetic diseases. • 2) Advanced, targeted pharmaceutical production. • 3) Bioethical implications, e.g. potential genetic discrimination. Courtesy of David Richfield ...
... • 1) Future understanding of many genetic diseases. • 2) Advanced, targeted pharmaceutical production. • 3) Bioethical implications, e.g. potential genetic discrimination. Courtesy of David Richfield ...
Reproduction
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and bonucIeic acid (ANA) are two of the cell’s most Important molecules. These nucleic acids have a complex three-dimensional structure that enab les them to direct protein synthesis in the cell. • Study the structure of the DNA and RNA molecules shown below. Fill in the ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and bonucIeic acid (ANA) are two of the cell’s most Important molecules. These nucleic acids have a complex three-dimensional structure that enab les them to direct protein synthesis in the cell. • Study the structure of the DNA and RNA molecules shown below. Fill in the ...
Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers In the nucleus of the
... Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers 1. In the nucleus of the cell 2. Wrapped around the chromosomes 3. A gene is a smaller portion of the chromosome, both of which are portions of the DNA molecule that is packed into the nucleus. 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and ...
... Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers 1. In the nucleus of the cell 2. Wrapped around the chromosomes 3. A gene is a smaller portion of the chromosome, both of which are portions of the DNA molecule that is packed into the nucleus. 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and ...
Biology 218 Microbial Metabolism and Genetics Chapter Six
... This experiment = part of the evidence that showed DNA was the genetic material. ...
... This experiment = part of the evidence that showed DNA was the genetic material. ...
Directed evolution
... revealed that they can be grouped onto families that are similar in size and amino acid sequence. Enzyme belonging to the same family have evolved from a common ancestor to acquire a new catabolic function through various genetic events, such as gene transfer, recombination, duplication, multiple po ...
... revealed that they can be grouped onto families that are similar in size and amino acid sequence. Enzyme belonging to the same family have evolved from a common ancestor to acquire a new catabolic function through various genetic events, such as gene transfer, recombination, duplication, multiple po ...
259071_DNAStructureStudyGuide
... 2. Scroll down the page until you find the section about Chargaff’s rule. What are the full names of the four nitrogenous bases? 3. Which bases have two carbon-nitrogen rings? Which have only one? 4. What are the two base pairing rules? 5. How would the DNA strand look if A paired with G and T w/ C? ...
... 2. Scroll down the page until you find the section about Chargaff’s rule. What are the full names of the four nitrogenous bases? 3. Which bases have two carbon-nitrogen rings? Which have only one? 4. What are the two base pairing rules? 5. How would the DNA strand look if A paired with G and T w/ C? ...
Genetics 1. What do the letters DNA stand for? 2. Two scientists are
... 7. These bases are of two different types of molecules: purines and pyrimides. Purines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure, and pyrimidines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure. ...
... 7. These bases are of two different types of molecules: purines and pyrimides. Purines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure, and pyrimidines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure. ...
UTACCEL 2010
... DNA is a long double-stranded molecule residing inside the nucleus of every cell. It is usually tightly coiled forming chromosomes in which it is protected by proteins. ...
... DNA is a long double-stranded molecule residing inside the nucleus of every cell. It is usually tightly coiled forming chromosomes in which it is protected by proteins. ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH13.QXD
... 2. Crossing dissimilar individuals to bring together the best of both Organisms is called ________________________ . 3. The continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics is called _______________________ . 4. Biologists change the DNA code of a living organism through ______________ ...
... 2. Crossing dissimilar individuals to bring together the best of both Organisms is called ________________________ . 3. The continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics is called _______________________ . 4. Biologists change the DNA code of a living organism through ______________ ...
Frontiers of Genetics
... • Bacteria have small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids separate from their larger single chromosome • Plasmids can replicate and pass between bacterial cells allowing gene sharing – associated with antibacterial resistance ...
... • Bacteria have small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids separate from their larger single chromosome • Plasmids can replicate and pass between bacterial cells allowing gene sharing – associated with antibacterial resistance ...
Name
... 6. How can single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP’s) lead to differences in DNA fragments after being cut with restriction enzymes? (1) SNP’s can alter the site at which the restriction enzyme is being cut, preventing the enzyme from cutting there. If the enzyme cannot cut the DNA there, the result wi ...
... 6. How can single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP’s) lead to differences in DNA fragments after being cut with restriction enzymes? (1) SNP’s can alter the site at which the restriction enzyme is being cut, preventing the enzyme from cutting there. If the enzyme cannot cut the DNA there, the result wi ...
What are the three steps in PCR?
... It is often used in DNA fingerprinting It requires gel electrophoresis which separates DNA by size ...
... It is often used in DNA fingerprinting It requires gel electrophoresis which separates DNA by size ...
Biotechnology Key Terms and Concepts
... modified plants and animals (GMOs) for a variety of reasons. including increased nutrition and pest resistance 2. Transgenic-an organism that has genes from more than one species due to genetic modification C. Gel Electrophoresis 1. Process used to separate different DNA segments 2. Restriction enzy ...
... modified plants and animals (GMOs) for a variety of reasons. including increased nutrition and pest resistance 2. Transgenic-an organism that has genes from more than one species due to genetic modification C. Gel Electrophoresis 1. Process used to separate different DNA segments 2. Restriction enzy ...
Journey Into dna
... How many cells does the human body contain? What is the only type of cell in the human body that contains no nucleus and therefore no nuclear DNA? ...
... How many cells does the human body contain? What is the only type of cell in the human body that contains no nucleus and therefore no nuclear DNA? ...
Introduction to biotechnology - Indiana University School of Informatics
... • Most vertebrate cells stop dividing after a finite number of cell divisions in culture – ...
... • Most vertebrate cells stop dividing after a finite number of cell divisions in culture – ...
DNA Structure and Function Vocabulary
... code that contains the instructions used to form all of an organism’s enzymes and structural proteins. ...
... code that contains the instructions used to form all of an organism’s enzymes and structural proteins. ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.