Working with Data Recombinant DNA
... Boyer pioneered the field of recombinant DNA technology when they demonstrated that biologically functional recombinant bacterial plasmids can be constructed in the laboratory. Specifically, the scientists used restriction enzymes to cut two E. coli plasmids containing a resistance gene for either k ...
... Boyer pioneered the field of recombinant DNA technology when they demonstrated that biologically functional recombinant bacterial plasmids can be constructed in the laboratory. Specifically, the scientists used restriction enzymes to cut two E. coli plasmids containing a resistance gene for either k ...
Fifth Lecture
... during mitosis and transcription of genetic information. • In addition, radiation can cause structural aberrations with pieces of the chromosomes break and form aberrant shapes. • Unequal division of nuclear chromatin material between daughter cells may result in production of nonviable, abnormal nu ...
... during mitosis and transcription of genetic information. • In addition, radiation can cause structural aberrations with pieces of the chromosomes break and form aberrant shapes. • Unequal division of nuclear chromatin material between daughter cells may result in production of nonviable, abnormal nu ...
Unit 1: Cells, Cell Reproduction, and Development
... What are the four phases of mitosis, and in what order do they occur in? What happens during each phase of mitosis? In what type of cells does meiosis occur in, and what it is purpose? What happens during each division of meiosis? What happens during each phase of meiosis? When is a developing baby ...
... What are the four phases of mitosis, and in what order do they occur in? What happens during each phase of mitosis? In what type of cells does meiosis occur in, and what it is purpose? What happens during each division of meiosis? What happens during each phase of meiosis? When is a developing baby ...
NTNU brevmal
... B) causing specific double-strand DNA breaks that result in blunt ends on both strands C) causing linear ends of the newly replicated DNA to circularize D) adding numerous short DNA sequences such as TTAGGG E) adding numerous GC pairs which resist hydrolysis and maintain chromosome integrity 19 The ...
... B) causing specific double-strand DNA breaks that result in blunt ends on both strands C) causing linear ends of the newly replicated DNA to circularize D) adding numerous short DNA sequences such as TTAGGG E) adding numerous GC pairs which resist hydrolysis and maintain chromosome integrity 19 The ...
Topic 4.4 genetic engineering
... 4.4.8 Outline a basic technique used for gene transfer involving plasmids, a host cell ( bacterium, yeast or other cell), restriction enzymes and DNA ligase. [ The use of E. coli in gene technology is well documented. Most of its DNA is in one circular chromosome, but it also has plasmids ( smaller ...
... 4.4.8 Outline a basic technique used for gene transfer involving plasmids, a host cell ( bacterium, yeast or other cell), restriction enzymes and DNA ligase. [ The use of E. coli in gene technology is well documented. Most of its DNA is in one circular chromosome, but it also has plasmids ( smaller ...
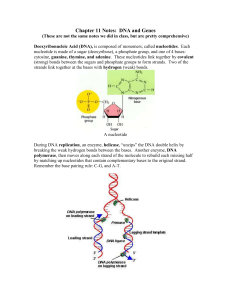
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
5-Premedical-Molec-bas-of-inh
... Adenine always pairs with thymine, Guanine always pairs with cytosine. Two strands of double helix ...
... Adenine always pairs with thymine, Guanine always pairs with cytosine. Two strands of double helix ...
Genetic Engineering
... Scientists at the American Association of Genetic Modification have identified the gene that makes blueberries blue and have put it into a strawberry. The genetically modified strawberries taste exactly the same, but are blue in color. It is hoped that this will make the fruit more appealing to chil ...
... Scientists at the American Association of Genetic Modification have identified the gene that makes blueberries blue and have put it into a strawberry. The genetically modified strawberries taste exactly the same, but are blue in color. It is hoped that this will make the fruit more appealing to chil ...
Nucleotide is composed of a ribose sugar, a base and a phosphate
... Genetic recombination – rearrangment/exchange of genetic material between two sources suitable media for isolation of strains. In bacteria, exchange of DNA from another cell. Consequences of recombination include new genotypes and phenotypes, eg. Ability to synthesis a new enzyme, antibiotic resista ...
... Genetic recombination – rearrangment/exchange of genetic material between two sources suitable media for isolation of strains. In bacteria, exchange of DNA from another cell. Consequences of recombination include new genotypes and phenotypes, eg. Ability to synthesis a new enzyme, antibiotic resista ...
Nucleic Acids and DNA Replication
... • Pyrimidines (1 ring) • Cytosine, C • Thymine, T (only in DNA) • Uracil, U (only in RNA) ...
... • Pyrimidines (1 ring) • Cytosine, C • Thymine, T (only in DNA) • Uracil, U (only in RNA) ...
Biotechnology II PPT
... the DNA at the restriction site, it creates fragments of DNA called restriction fragments. Restriction fragments have “sticky ends” that can match up with the ends of other fragments. ...
... the DNA at the restriction site, it creates fragments of DNA called restriction fragments. Restriction fragments have “sticky ends” that can match up with the ends of other fragments. ...
Modern Genetics Outline
... The four nitrogenous bases in DNA ______ (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact ...
... The four nitrogenous bases in DNA ______ (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact ...
NAME Period___________ Modern Genetics Outline
... The four nitrogenous bases in DNA ______ (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact ...
... The four nitrogenous bases in DNA ______ (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact ...
DNA Technology Notes
... Sorts according to size Samples of DNA being compared are loaded into wells on gel Electric current is run through gel DNA is negatively charged and moves towards positive end of gel Smaller DNA fragments move faster and will travel further along the gel ...
... Sorts according to size Samples of DNA being compared are loaded into wells on gel Electric current is run through gel DNA is negatively charged and moves towards positive end of gel Smaller DNA fragments move faster and will travel further along the gel ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... DNA — (deoxyribonucleic acid) A specialized molecule that contains the genetic information that allows characteristics to be passed from parents to offspring. The information contained in the DNA molecule provides a “blueprint,” or a set of codes, for building other molecules used by the cell. ...
... DNA — (deoxyribonucleic acid) A specialized molecule that contains the genetic information that allows characteristics to be passed from parents to offspring. The information contained in the DNA molecule provides a “blueprint,” or a set of codes, for building other molecules used by the cell. ...
DNA Replication
... Power Standard (s) Reference: Standard 6- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis State Standard: Goal 1.1: Understand Systems, Order, and Organization 9-10.B.1.1.1 Explain the scientific meaning of system, order, and organization. 9-10.B.1.1.2 Apply the concepts of order and organization to a given sys ...
... Power Standard (s) Reference: Standard 6- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis State Standard: Goal 1.1: Understand Systems, Order, and Organization 9-10.B.1.1.1 Explain the scientific meaning of system, order, and organization. 9-10.B.1.1.2 Apply the concepts of order and organization to a given sys ...
PowerPoint® slides
... students’ learning levels or to insert additional teaching aides. Modified slides may be used only by the modifying teacher in his or her classroom, or shared with other teachers of Science and Global Issues within the teacher’s school district, with these same restrictions. Modified slides may not ...
... students’ learning levels or to insert additional teaching aides. Modified slides may be used only by the modifying teacher in his or her classroom, or shared with other teachers of Science and Global Issues within the teacher’s school district, with these same restrictions. Modified slides may not ...
All life is based on the same genetic code
... Each form of a gene is an allele. The standard (wild type) and altered (mutant) forms of the gene associated with hemoglobin and sickle cell anemia provide an example. The DNA sequences of both alleles of the “hemoglobin gene” are 99.9% identical – a single nucleotide difference makes for a single a ...
... Each form of a gene is an allele. The standard (wild type) and altered (mutant) forms of the gene associated with hemoglobin and sickle cell anemia provide an example. The DNA sequences of both alleles of the “hemoglobin gene” are 99.9% identical – a single nucleotide difference makes for a single a ...
Whole Genome Scale DNA Methylation Differences in
... results to the other methods and only required 200 ng DNA. To date we have 10 paired samples of thymus thymocytes and stromal cells. Conclusion: These results suggest that changes in DNA methylation represented by T1D-MVPs must arise very early in the etiological process that leads to overt T1D. The ...
... results to the other methods and only required 200 ng DNA. To date we have 10 paired samples of thymus thymocytes and stromal cells. Conclusion: These results suggest that changes in DNA methylation represented by T1D-MVPs must arise very early in the etiological process that leads to overt T1D. The ...
transformation mean? transcription and translation
... What happens to mRNA after transcription? What is an intron? An exon? What is the benefit of mRNA processing/splicing? Know that the genetic code is universal – the same codon codes for the same amino acid in all species Know the 3 different types of RNA and their basic functions What is an anticodo ...
... What happens to mRNA after transcription? What is an intron? An exon? What is the benefit of mRNA processing/splicing? Know that the genetic code is universal – the same codon codes for the same amino acid in all species Know the 3 different types of RNA and their basic functions What is an anticodo ...
View Syllabus
... The course material will explore fundamental concepts in genetics through the sophisticated “eyes” of geneticists working with model organisms. The goals are to attain an appreciation for remarkable biologi ...
... The course material will explore fundamental concepts in genetics through the sophisticated “eyes” of geneticists working with model organisms. The goals are to attain an appreciation for remarkable biologi ...
rnalabreport_1
... Currency - Look for publication or copyright dates associated with the site; the more current the better. Links - What links does the site contain? A reliable website will offer links to other reliable websites, not to "junk" sites. ...
... Currency - Look for publication or copyright dates associated with the site; the more current the better. Links - What links does the site contain? A reliable website will offer links to other reliable websites, not to "junk" sites. ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.