3.12 Translation
... After a protein is done being made, it needs to have a signal to stop adding on more amino acids. All ...
... After a protein is done being made, it needs to have a signal to stop adding on more amino acids. All ...
没有幻灯片标题
... the duplicated state becomes visible only at the end. The molecular interactions of any individual crossing-over event involve two of the four duplex DNAs. ...
... the duplicated state becomes visible only at the end. The molecular interactions of any individual crossing-over event involve two of the four duplex DNAs. ...
Ch5hybridisationSNPRFLP
... • GMO = genetically modified organism, GMM = genetically modified microorganisme ...
... • GMO = genetically modified organism, GMM = genetically modified microorganisme ...
No Slide Title
... The gene for ribosomal RNAs occur as repetitive sequence and together with the genes for some transfer RNAs in several thousand of copies Structural genes are present in only a few copies, sometimes just single copy. Structural genes encoding for structurally and functionally related proteins of ...
... The gene for ribosomal RNAs occur as repetitive sequence and together with the genes for some transfer RNAs in several thousand of copies Structural genes are present in only a few copies, sometimes just single copy. Structural genes encoding for structurally and functionally related proteins of ...
downloadable file
... nucleotides and an enzyme called DNA polymerase which incorporates new nucleotide bases making a new piece of DNA which is a copy of the original piece. In Sanger’s original method, four different sequencing reactions are performed. Each reaction contains a different modified nucleotide that once in ...
... nucleotides and an enzyme called DNA polymerase which incorporates new nucleotide bases making a new piece of DNA which is a copy of the original piece. In Sanger’s original method, four different sequencing reactions are performed. Each reaction contains a different modified nucleotide that once in ...
DNA, RNA and Protein Power Point
... 1. RNA is single stranded 2. The sugar in RNA is Ribose, not deoxyribose as in DNA 3. The DNA nucleotide thymine is replaced by the RNA nucleotide Uracil ...
... 1. RNA is single stranded 2. The sugar in RNA is Ribose, not deoxyribose as in DNA 3. The DNA nucleotide thymine is replaced by the RNA nucleotide Uracil ...
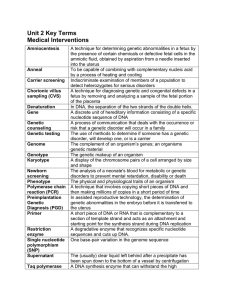
Unit 2 Terms
... by a process of heating and cooling Indiscriminate examination of members of a population to detect heterozygotes for serious disorders A technique for diagnosing genetic and congenital defects in a fetus by removing and analyzing a sample of the fetal portion of the placenta In DNA, the separation ...
... by a process of heating and cooling Indiscriminate examination of members of a population to detect heterozygotes for serious disorders A technique for diagnosing genetic and congenital defects in a fetus by removing and analyzing a sample of the fetal portion of the placenta In DNA, the separation ...
Information- Part 1 Study Guide
... (A) Viruses have highly efficient replicative capabilities that allow for rapid evolution and acquisition of new phenotypes. (B) Viruses replicate via a component assembly model allowing one virus to produce many progeny simultaneously via the lytic cycle. (C) Virus replication allows for mutations ...
... (A) Viruses have highly efficient replicative capabilities that allow for rapid evolution and acquisition of new phenotypes. (B) Viruses replicate via a component assembly model allowing one virus to produce many progeny simultaneously via the lytic cycle. (C) Virus replication allows for mutations ...
biology name
... 14. Codons are found on _________ while anticodons are found on _________. In each case, the code is really a sequence of ____ bases (use a number) that code for a particular _____________________. 15. What would the transfer RNA and corresponding amino acids be according to the mRNA below? mRNA ...
... 14. Codons are found on _________ while anticodons are found on _________. In each case, the code is really a sequence of ____ bases (use a number) that code for a particular _____________________. 15. What would the transfer RNA and corresponding amino acids be according to the mRNA below? mRNA ...
Lucerne Publishing F
... corresponding to 20 letters of our alphabet. You can then use this system to ‘spell’ the parts of a protein. The code is called the ‘DNA Alias’ and each letter represents a group of 3 letters (codon). When you see the DNA Alias of a protein, you can find the original DNA sequence by reversing the co ...
... corresponding to 20 letters of our alphabet. You can then use this system to ‘spell’ the parts of a protein. The code is called the ‘DNA Alias’ and each letter represents a group of 3 letters (codon). When you see the DNA Alias of a protein, you can find the original DNA sequence by reversing the co ...
Unit III: Introduction to Cells Unit IV: Cell Processes
... 2. Most of the time the DNA in our cells is loosely-arranged _______________. During interphase, the cell grows and chromatin ___________. Prior to dividing, the chromatin condenses forming structures known as__________________, which separate during Mitosis. 3. Discuss the role of centrioles during ...
... 2. Most of the time the DNA in our cells is loosely-arranged _______________. During interphase, the cell grows and chromatin ___________. Prior to dividing, the chromatin condenses forming structures known as__________________, which separate during Mitosis. 3. Discuss the role of centrioles during ...
Spring 2005 - Antelope Valley College
... Read ALL questions carefully during perusal time, you may write if you wish. Use the back of each sheet if you do not have enough writing space, but please label each answer. Question subheadings are NOT of equal points value. Points allocated for each subheading are shown at the end of the question ...
... Read ALL questions carefully during perusal time, you may write if you wish. Use the back of each sheet if you do not have enough writing space, but please label each answer. Question subheadings are NOT of equal points value. Points allocated for each subheading are shown at the end of the question ...
Document
... host organism for its survival and continued reproduction. host range •Viruses only infect in their ___________________. •Viruses that infect bacteria are called capsid DNA ____________________. bacteriophage or phage •All viruses act by forcing the host cell to manufacture 100’s or 1000’s of copies ...
... host organism for its survival and continued reproduction. host range •Viruses only infect in their ___________________. •Viruses that infect bacteria are called capsid DNA ____________________. bacteriophage or phage •All viruses act by forcing the host cell to manufacture 100’s or 1000’s of copies ...
pruitt_ppt_ch07
... • Scientists have focused efforts on three areas: – Developing crops capable of fending off insect pests without the use of insecticides – Engineering plants with a greater yield that grow in a wider ranges of climates – Make crops that are resistant to herbicides , so that fields can be treated for ...
... • Scientists have focused efforts on three areas: – Developing crops capable of fending off insect pests without the use of insecticides – Engineering plants with a greater yield that grow in a wider ranges of climates – Make crops that are resistant to herbicides , so that fields can be treated for ...
Using a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)
... • For a variation to be considered a SNP, it must occur in at least 1% of the population. • SNPs, which make up about 90% of all human genetic variation, occur every 100 to 300 bases along the 3-billion-base human genome. ...
... • For a variation to be considered a SNP, it must occur in at least 1% of the population. • SNPs, which make up about 90% of all human genetic variation, occur every 100 to 300 bases along the 3-billion-base human genome. ...
The Genetic Code
... into a polypeptide. It must first be converted into mRNA. The mRNA strand that is created from the DNA template is the COMPLEMENT. It differs from the DNA complement strand, as it contains Uracil (U) instead of Thymine (T) ...
... into a polypeptide. It must first be converted into mRNA. The mRNA strand that is created from the DNA template is the COMPLEMENT. It differs from the DNA complement strand, as it contains Uracil (U) instead of Thymine (T) ...
Supporting Methods Cells and SV40 infection BSC40 and U2OS
... ATRi treated SV40-infected or mock infected cells compared to SV40-infected cells in the presence of DMSO (Viability (% of DMSO), the OD of mock or SV40-infected cells in the presence/ absence of ATRi was divided by the OD generated from SV40 infected cells in the presence of DMSO. Plasmids and tran ...
... ATRi treated SV40-infected or mock infected cells compared to SV40-infected cells in the presence of DMSO (Viability (% of DMSO), the OD of mock or SV40-infected cells in the presence/ absence of ATRi was divided by the OD generated from SV40 infected cells in the presence of DMSO. Plasmids and tran ...
File
... functional components of living organisms (proteins) – Genetic information is passed on from one generation to the next through sexual reproduction – All traits passed down from parent to offspring are coded for by DNA ...
... functional components of living organisms (proteins) – Genetic information is passed on from one generation to the next through sexual reproduction – All traits passed down from parent to offspring are coded for by DNA ...
How is coordinated DNA damage repair and control of mitotic
... How is coordinated DNA damage repair and control of mitotic commitment ensuring longterm genomic stability during successive cell cycles? Candidates are welcome for a Postdoctoral position at Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus, Villejuif, France. Applications for funding will be submitted to European or F ...
... How is coordinated DNA damage repair and control of mitotic commitment ensuring longterm genomic stability during successive cell cycles? Candidates are welcome for a Postdoctoral position at Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus, Villejuif, France. Applications for funding will be submitted to European or F ...
Only One Strand of DNA Is Translated
... and “late” genes read from the same strand? Jayaraman and Goldberg separated the T4 DNA into heavy and light strands, and challenged each separately with “early” mRNA and “late” mRNA. They added a DNA endonculease that degraded single-stranded DNA, so that any DNA not bound by the mRNA was degraded. ...
... and “late” genes read from the same strand? Jayaraman and Goldberg separated the T4 DNA into heavy and light strands, and challenged each separately with “early” mRNA and “late” mRNA. They added a DNA endonculease that degraded single-stranded DNA, so that any DNA not bound by the mRNA was degraded. ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.