DNA Consulting Introduces Home DNA Fingerprint Test for Ancestry
... Comment: The mixture shows that the child is tri-racial and does have a high degree of Native American blood. Asian matches are probably to be interpreted as Native American, since these groups share deep ancestry. Because the Native American ancestry was “hidden” in the family tree, it would not ha ...
... Comment: The mixture shows that the child is tri-racial and does have a high degree of Native American blood. Asian matches are probably to be interpreted as Native American, since these groups share deep ancestry. Because the Native American ancestry was “hidden” in the family tree, it would not ha ...
Exercise week 10 File
... cytosines to 5-hydroxymethyl cytosine and thereby trigger CpG demethylation ...
... cytosines to 5-hydroxymethyl cytosine and thereby trigger CpG demethylation ...
DNA(Test 1)
... a. Bacterial proteins transferred from the donor bacterium by the phage to the recipient bacterium recombine with genes on the recipient’s chromosome. b. The recipient bacterium incorporates the transduced genetic material coding for phage proteins into its chromosome and synthesizes the correspondi ...
... a. Bacterial proteins transferred from the donor bacterium by the phage to the recipient bacterium recombine with genes on the recipient’s chromosome. b. The recipient bacterium incorporates the transduced genetic material coding for phage proteins into its chromosome and synthesizes the correspondi ...
Linkage and Chromosome Mapping in Eukaryotes
... If the same chromatids are involved, this leads to an exchange of an internal portion of the chromosome The order of genes can be determined by analyzing multiple crossovers Three-point tests Use a testcross for three genes to order the genes in one set of progeny When possible, this is much ...
... If the same chromatids are involved, this leads to an exchange of an internal portion of the chromosome The order of genes can be determined by analyzing multiple crossovers Three-point tests Use a testcross for three genes to order the genes in one set of progeny When possible, this is much ...
Lab Aseptic Techniques and Classification
... Enzyme's substrate ( ) is added, and reaction produces a product that causes a visible color change ( ). ...
... Enzyme's substrate ( ) is added, and reaction produces a product that causes a visible color change ( ). ...
Ch 20 Reading Guide - Dublin City Schools
... 1. Describe the natural function of restriction enzymes and explain how they are used in recombinant DNA technology. 2. Outline the procedures for cloning a eukaryotic gene in a bacterial plasmid. 3. Explain the rationale for including a gene for antibiotic resistance and a gene that codes for a hyd ...
... 1. Describe the natural function of restriction enzymes and explain how they are used in recombinant DNA technology. 2. Outline the procedures for cloning a eukaryotic gene in a bacterial plasmid. 3. Explain the rationale for including a gene for antibiotic resistance and a gene that codes for a hyd ...
Genetic Engineering
... clone of) taken from another adult. The fused cell is tricked into thinking its fertilized and begins to divide. The embryo is then placed in the reproductive system of a foster surrogate mother, where it develops normally. ...
... clone of) taken from another adult. The fused cell is tricked into thinking its fertilized and begins to divide. The embryo is then placed in the reproductive system of a foster surrogate mother, where it develops normally. ...
genetics review sheet
... 26. Restriction Enzyme BB reads GGCCTT and cuts between the G’s: ATCGGCCTTGCTTATCGGCCTTAAGCTTGGCCTT a. How many fragments are there? b. How many bases are there in each fragment? 27. What are the two steps in protein synthesis? 28. Where does the first step occur? 29. Where does the second step occu ...
... 26. Restriction Enzyme BB reads GGCCTT and cuts between the G’s: ATCGGCCTTGCTTATCGGCCTTAAGCTTGGCCTT a. How many fragments are there? b. How many bases are there in each fragment? 27. What are the two steps in protein synthesis? 28. Where does the first step occur? 29. Where does the second step occu ...
dna testing workshop 2005
... 2. Analysis of DNA sequencing traces. 3. Cancer databases. III. Fluorescence microscopy 1. Demonstration of fluorescence microscope/digital imaging system: Dr. Bachman's research with human cervical cancer cells. 2. Microscopic analysis of solid tumors and leukemias. 3. Cancer cytogenetics/chromoso ...
... 2. Analysis of DNA sequencing traces. 3. Cancer databases. III. Fluorescence microscopy 1. Demonstration of fluorescence microscope/digital imaging system: Dr. Bachman's research with human cervical cancer cells. 2. Microscopic analysis of solid tumors and leukemias. 3. Cancer cytogenetics/chromoso ...
DNA RNA
... • Three bases on the mRNA molecule that code for one amino acid is a(n) • A.) anti-codon. ...
... • Three bases on the mRNA molecule that code for one amino acid is a(n) • A.) anti-codon. ...
File
... _____ 11. Gene therapy is successful if the Figure 15–1 a. viruses carrying the replacement gene infect the person’s cells. b. replacement gene is replicated in the person’s cells. c. replacement gene is expressed in the person’s cells. d. replacement gene is successfully spliced to viral DNA. _____ ...
... _____ 11. Gene therapy is successful if the Figure 15–1 a. viruses carrying the replacement gene infect the person’s cells. b. replacement gene is replicated in the person’s cells. c. replacement gene is expressed in the person’s cells. d. replacement gene is successfully spliced to viral DNA. _____ ...
Sample submission form - National Institute of Plant Genome
... 5) Indents have to be submitted during the entry in the booking logbook. 6) Indents must be signed by any of the faculty members. (Photocopy of signature is not allowed). 7) DNA samples have to be loaded within 12 noon on the day of sequencing. 8) It will be understood that booking in the log book f ...
... 5) Indents have to be submitted during the entry in the booking logbook. 6) Indents must be signed by any of the faculty members. (Photocopy of signature is not allowed). 7) DNA samples have to be loaded within 12 noon on the day of sequencing. 8) It will be understood that booking in the log book f ...
Sugopa Sengupta - Presidency University
... endogenous inhibitors of an essential bacterial enzyme, DNA gyrase. My studies revealed that all these endogenous inhibitors essentially influence the enzyme activity by sequestering the enzyme away from DNA. None of them cause any cytotoxicity, which usually arises as a result of DNA damage caused ...
... endogenous inhibitors of an essential bacterial enzyme, DNA gyrase. My studies revealed that all these endogenous inhibitors essentially influence the enzyme activity by sequestering the enzyme away from DNA. None of them cause any cytotoxicity, which usually arises as a result of DNA damage caused ...
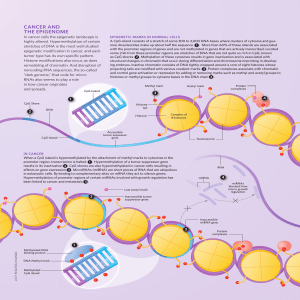
CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
ParScore Scantrons for Lecture Tests Introduction to Microbiology Use Your Textbook Wisely
... smaller) than eukaryotic cells ...
... smaller) than eukaryotic cells ...
DNA Workshop
... The single molecule of DNA in the bacteria, E. coli contains 4.7 x 106 nucleotide pairs. DNA replication begins at a single, fixed location in this molecule, called the replication origin, it proceeds at about _______ nucleotides per second, and thus is done in approximately _____ minutes. The avera ...
... The single molecule of DNA in the bacteria, E. coli contains 4.7 x 106 nucleotide pairs. DNA replication begins at a single, fixed location in this molecule, called the replication origin, it proceeds at about _______ nucleotides per second, and thus is done in approximately _____ minutes. The avera ...
Document
... 16.1 Recombinant DNA technology I. Gene Manipulation - moving genes from one organism to another A. Genetic Engineering - cleaving DNA into small fragments & inserting them into another organism of the same or different species B. Recombinant DNA - DNA made of connected fragments of different source ...
... 16.1 Recombinant DNA technology I. Gene Manipulation - moving genes from one organism to another A. Genetic Engineering - cleaving DNA into small fragments & inserting them into another organism of the same or different species B. Recombinant DNA - DNA made of connected fragments of different source ...
Genetics Study Guide
... What do the squares in the above pedigree represent? Males or Females How many people in the above example are carriers of albinism, but are not albino? ___ ...
... What do the squares in the above pedigree represent? Males or Females How many people in the above example are carriers of albinism, but are not albino? ___ ...
slides
... – Introns (intervening sequences) are regions of the iniFal RNA transcript that are not expressed in the amino acid sequence of the protein. – Introns are removed by splicing and the exons (expressed) ar ...
... – Introns (intervening sequences) are regions of the iniFal RNA transcript that are not expressed in the amino acid sequence of the protein. – Introns are removed by splicing and the exons (expressed) ar ...
Codon Practice
... 5. A certain mRNA molecule has the following sequence: 5’ G G U A U C C C G A U U 3’ A. How many codons are in this sequence? _________________ B. What amino acid sequences are in this sequence? _________________________ ...
... 5. A certain mRNA molecule has the following sequence: 5’ G G U A U C C C G A U U 3’ A. How many codons are in this sequence? _________________ B. What amino acid sequences are in this sequence? _________________________ ...
Ingenious Genes Curriculum Links for AQA GCSE Biology (8461
... slightly so that its appearance or function is not changed. (HT only) A few mutations code for an altered protein with a different shape. An enzyme may no longer fit the substrate binding site or a structural protein may lose its strength. (HT only) Not all parts of DNA code for proteins. Non-coding ...
... slightly so that its appearance or function is not changed. (HT only) A few mutations code for an altered protein with a different shape. An enzyme may no longer fit the substrate binding site or a structural protein may lose its strength. (HT only) Not all parts of DNA code for proteins. Non-coding ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.