Pharmacology II – Respiratory and Oxygenation
... What drug error has occurred, and how could this be avoided ?? ...
... What drug error has occurred, and how could this be avoided ?? ...
Mechanism of Drug Action and Drug Targets Receptors
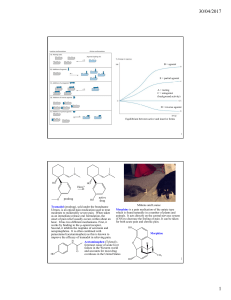
... Understand the concentration response curve and what information can be gained from it. Differentiate between inverse agonism, agonism and antagonism and explain them using the two state model of receptor activity. Differentiate between different types of antagonism and understand their impact on th ...
... Understand the concentration response curve and what information can be gained from it. Differentiate between inverse agonism, agonism and antagonism and explain them using the two state model of receptor activity. Differentiate between different types of antagonism and understand their impact on th ...
Materials and Methods
... range of concentrations starting from clinically relevant doses to supra-clinical doses. Thus are the first 2 concentrations of iloprost and treprostinil, the first 3 concentrations of epoprostenol and the first concentration of MRE-269 comparable to what is used in the clinic. This is based on prev ...
... range of concentrations starting from clinically relevant doses to supra-clinical doses. Thus are the first 2 concentrations of iloprost and treprostinil, the first 3 concentrations of epoprostenol and the first concentration of MRE-269 comparable to what is used in the clinic. This is based on prev ...
Antidepressant
... Venlafaxine and duloxetine selectively inhibit the re-uptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine. These agents may be effective in treating depression in patients in whom SSRIs are ineffective, in addition to treat the painful symptoms that associate depression such as backache and muscle aches. Th ...
... Venlafaxine and duloxetine selectively inhibit the re-uptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine. These agents may be effective in treating depression in patients in whom SSRIs are ineffective, in addition to treat the painful symptoms that associate depression such as backache and muscle aches. Th ...
投影片 1
... alpha2-adrenergic receptors. Blocking histamine (H1), 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptors. Causing less insomnia, sexual dysfunction, nausea/vomiting than SSRIs. Effective for pain, insomnia and anorexia/cachexia. Side effects: sedation, increased appetite, weight gain. ...
... alpha2-adrenergic receptors. Blocking histamine (H1), 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptors. Causing less insomnia, sexual dysfunction, nausea/vomiting than SSRIs. Effective for pain, insomnia and anorexia/cachexia. Side effects: sedation, increased appetite, weight gain. ...
Epinephrine
... inc. blood return to heart, inc. circulation, inc. BP 2. Alpha-2 = inhibits release of norepinephrine dec. in vasoconstriction, dec. BP 3. Beta-1 = inc. in heart rate & force on contraction 4. Beta-2 = relaxation of smooth muscle in bronchi, uterus, peripheral blood vessels Dopaminergic = dilate ves ...
... inc. blood return to heart, inc. circulation, inc. BP 2. Alpha-2 = inhibits release of norepinephrine dec. in vasoconstriction, dec. BP 3. Beta-1 = inc. in heart rate & force on contraction 4. Beta-2 = relaxation of smooth muscle in bronchi, uterus, peripheral blood vessels Dopaminergic = dilate ves ...
Blockade of D2 receptor increases prolactin release and causes
... Not curative, does not eliminate thinking disorder, but allow patient to function in supportive environment ...
... Not curative, does not eliminate thinking disorder, but allow patient to function in supportive environment ...
Release of norepinephrine: Removal of norepinephrine:
... increase in total peripheral resistance and blood pressure. Conversely, stimulation of β 1 receptors characteristically causes cardiac stimulation, whereas stimulation of β 2 receptors produces vasodilation (in skeletal vascular beds) and bronchiolar relaxation ...
... increase in total peripheral resistance and blood pressure. Conversely, stimulation of β 1 receptors characteristically causes cardiac stimulation, whereas stimulation of β 2 receptors produces vasodilation (in skeletal vascular beds) and bronchiolar relaxation ...
Problem Set
... prevent its proper folding and secretion are resistant to HIV infection. Based on this finding, you do a screen for new antagonist ligands at this receptor in hopes that they will be novel anti-‐-‐- ...
... prevent its proper folding and secretion are resistant to HIV infection. Based on this finding, you do a screen for new antagonist ligands at this receptor in hopes that they will be novel anti-‐-‐- ...
Cholinergic - stjpap 2011
... • They are structurally similar, but can be separated using selective drugs ...
... • They are structurally similar, but can be separated using selective drugs ...
A positive allosteric modulator (PAM)
... hormonal side effects such as hyperprolactinemia, and weight gain. Recent research has highlighted new targets for drug development based on mechanisms leading to glutamate system dysfunction. Normalizing excess glutamate levels by metabotropic glutamate group 2/3 receptor (mGluR2/3) agonists has l ...
... hormonal side effects such as hyperprolactinemia, and weight gain. Recent research has highlighted new targets for drug development based on mechanisms leading to glutamate system dysfunction. Normalizing excess glutamate levels by metabotropic glutamate group 2/3 receptor (mGluR2/3) agonists has l ...
FUN2: 11:00-12:00 Scribe: Taylor Nelson Wednesday, December
... i. The use of the term indirect is the same as the use for the term Cholinergic stimulus ii. These compounds produce their effects by releasing NE from the nerve terminals iii. They do not inhibit an enzyme iv. The best example, with a major indirect mechanism of action is amphetamine and its variou ...
... i. The use of the term indirect is the same as the use for the term Cholinergic stimulus ii. These compounds produce their effects by releasing NE from the nerve terminals iii. They do not inhibit an enzyme iv. The best example, with a major indirect mechanism of action is amphetamine and its variou ...
JV Poster Barcelona 2012
... o Mono-drugs replicate the properties of bifunctional drugs at ten-fold higher doses o Multi-target memory enhancers have a high potential for clinical implications ...
... o Mono-drugs replicate the properties of bifunctional drugs at ten-fold higher doses o Multi-target memory enhancers have a high potential for clinical implications ...
Non-Cardiac Chest Pain - Old
... Norepinephrine – released by practically all postganglionic neurons of the SNS (exception – sweat glands) Epinephrine – major neurotransmitter released by the adrenal medulla. The adrenal medulla also releases some norepinephrine. ...
... Norepinephrine – released by practically all postganglionic neurons of the SNS (exception – sweat glands) Epinephrine – major neurotransmitter released by the adrenal medulla. The adrenal medulla also releases some norepinephrine. ...
(2-aminoethyl) imidazole
... • Limitation of the entrance to central and increase the selectivity to H1 receptor, is the guiding ideology for design and searchin new antihistamine drugs. This resulted in the development of non-sedative H1 receptor antagonists. • Clemastine(aminoethers)、Acrivastine(propylamines)、 Loratadine(tric ...
... • Limitation of the entrance to central and increase the selectivity to H1 receptor, is the guiding ideology for design and searchin new antihistamine drugs. This resulted in the development of non-sedative H1 receptor antagonists. • Clemastine(aminoethers)、Acrivastine(propylamines)、 Loratadine(tric ...
Pharmacodynamics (08)
... 1) Reversible binding to the receptor. 2) The blockade can be overcome by increasing the agonist concentration. 3) The maximal response of the agonist is not decreased. 4) The agonist dose-response curve in the presence of a competitive antagonist is displaced to the right, parallel to the curve in ...
... 1) Reversible binding to the receptor. 2) The blockade can be overcome by increasing the agonist concentration. 3) The maximal response of the agonist is not decreased. 4) The agonist dose-response curve in the presence of a competitive antagonist is displaced to the right, parallel to the curve in ...
Bronchial Asthma: Pathophysiologic Concepts
... physiochemical reactions that STIMULATE/activate OR INHIBIT normal cellular function ...
... physiochemical reactions that STIMULATE/activate OR INHIBIT normal cellular function ...
Addiction: brain mechanisms and their treatment implications
... alcoholics with a history of violent crime have low brain 5-HT turnover, 30 perhaps due to a polymorphism in their gene for the synthetic enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase. This subgroup of alcoholics also shows altered 5-HT receptor sensitivity in that administration of the 5-HTz receptor agonist mCPP ...
... alcoholics with a history of violent crime have low brain 5-HT turnover, 30 perhaps due to a polymorphism in their gene for the synthetic enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase. This subgroup of alcoholics also shows altered 5-HT receptor sensitivity in that administration of the 5-HTz receptor agonist mCPP ...
CASE 7 - Caangay.com
... medication (called atypical antipsychotic medication) can be equally effective as older medication (called typical antipsychotic medication), but also affects serotonin function and may have slightly less of a dopamine blocking effect. In addition dopamine pathway dysfunction has not been reliably s ...
... medication (called atypical antipsychotic medication) can be equally effective as older medication (called typical antipsychotic medication), but also affects serotonin function and may have slightly less of a dopamine blocking effect. In addition dopamine pathway dysfunction has not been reliably s ...
1-alpha adrenergic blockers 2017-03-15 05:542.2 MB
... 1) Vasodilatation of blood vessels (α1 block). 2) Decrease peripheral vascular resistance 3) Postural hypotension. Increase cardiac output (α2 block). 4) Reflex tachycardia. 5) Increase in GIT motility and secretions Reflex tachycardia occurs by two mechanisms: Stimulation of *baroreceptor reflex t ...
... 1) Vasodilatation of blood vessels (α1 block). 2) Decrease peripheral vascular resistance 3) Postural hypotension. Increase cardiac output (α2 block). 4) Reflex tachycardia. 5) Increase in GIT motility and secretions Reflex tachycardia occurs by two mechanisms: Stimulation of *baroreceptor reflex t ...