Glossary Adaptability, evolvability or adaptive potential: the ability of
... can refer to a gene, a part of it or to non-genic DNA sequence. Genetic diversity: the total number of allelic and genotypic variants in a population or species. Genetic diversity can be measured for genes underlying traits under selection (with an effect on the phenotype, hence adaptive genetic div ...
... can refer to a gene, a part of it or to non-genic DNA sequence. Genetic diversity: the total number of allelic and genotypic variants in a population or species. Genetic diversity can be measured for genes underlying traits under selection (with an effect on the phenotype, hence adaptive genetic div ...
Natural selection
... : the development of new species over very long periods of geological time. ...
... : the development of new species over very long periods of geological time. ...
Slide ()
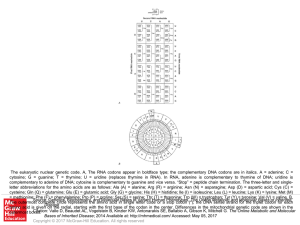
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
2-3 DNA to Proteins - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... chromosome so that a copy of the needed gene can be made. This is copy is called RNA (ribonucleic acid). RNA is similar to DNA except it is only one strand. o RNA to Ribosome – The RNA then leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome which “reads” the code on the ...
... chromosome so that a copy of the needed gene can be made. This is copy is called RNA (ribonucleic acid). RNA is similar to DNA except it is only one strand. o RNA to Ribosome – The RNA then leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome which “reads” the code on the ...
10 DNA Vocabulary - Petal School District
... 1. DNA—deoxyribonucleic acid 2. RNA—ribonucleic acid 3. nucleotide—the monomer for nucleic acids; made of a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen base 4. hydrogen bonds—hold nitrogen base pairs together 5. genetic code—the sequence of the nitrogen bases (nucleotides) on DNA 6. DNA replication—process that ...
... 1. DNA—deoxyribonucleic acid 2. RNA—ribonucleic acid 3. nucleotide—the monomer for nucleic acids; made of a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen base 4. hydrogen bonds—hold nitrogen base pairs together 5. genetic code—the sequence of the nitrogen bases (nucleotides) on DNA 6. DNA replication—process that ...
2014 113 vocabularies for any given word. My
... interest, the sharpest controversies, and the vast majority of scientific studies. There must be reasons for this, of which one is perhaps historical. To convince people that biological entities were not god-made creatures, Darwin and its followers had to simultaneously argue 1) that living forms cha ...
... interest, the sharpest controversies, and the vast majority of scientific studies. There must be reasons for this, of which one is perhaps historical. To convince people that biological entities were not god-made creatures, Darwin and its followers had to simultaneously argue 1) that living forms cha ...
Genetics
... us understand how genes work in humans Some model organisms include bacteria, yeast, roundworms, fruit flies, and mice. Model organisms may have simpler biological networks and can be manipulated experimentally. ...
... us understand how genes work in humans Some model organisms include bacteria, yeast, roundworms, fruit flies, and mice. Model organisms may have simpler biological networks and can be manipulated experimentally. ...
Specification
... maintains and transmits the genetic code with a high level of accuracy. The role of DNA in determining protein synthesis includes codons and anticodons, and the redundant ...
... maintains and transmits the genetic code with a high level of accuracy. The role of DNA in determining protein synthesis includes codons and anticodons, and the redundant ...
Product Information Sheet - Sigma
... information from one generation of cells or higher organism to the next via the gene and genome. A gene is a sequence of DNA nucleotides that specify the order of amino acids that are incorporated into a protein. A genome is the set of genes for an organism. Recent developments include the Human Gen ...
... information from one generation of cells or higher organism to the next via the gene and genome. A gene is a sequence of DNA nucleotides that specify the order of amino acids that are incorporated into a protein. A genome is the set of genes for an organism. Recent developments include the Human Gen ...
Population and Speciation
... • Selection of a mate based on similar characteristics is assortative mating ...
... • Selection of a mate based on similar characteristics is assortative mating ...
Detecting and Modeling Long Range Correlation in Genomic
... A genome encodes information that is needed to create complex machineries combining DNA, RNA and proteins. However, this structure has evolved by certain basic biological processes that modify the genome in a specific but stochastic manner, and has been shaped by selection pressure. With complete se ...
... A genome encodes information that is needed to create complex machineries combining DNA, RNA and proteins. However, this structure has evolved by certain basic biological processes that modify the genome in a specific but stochastic manner, and has been shaped by selection pressure. With complete se ...
Section 5.1
... DNA – (pg 74) = Code. The genetic material found in all living cells that contains the information needed for an organism to grow, maintain itself, and reproduce. Deoxyribonucleic acid A = T C = G ...
... DNA – (pg 74) = Code. The genetic material found in all living cells that contains the information needed for an organism to grow, maintain itself, and reproduce. Deoxyribonucleic acid A = T C = G ...
7th Grade Science-Chapter 11 Test Study Guide: Human Genetics
... Inbreeding- breeding technique that involves crossing two individuals that have similar desirable characteristics. This process produces organisms that are genetically very similar. This type of breeding leads to a greater chance for genetic disorders. Hybridization-breeding technique where breeders ...
... Inbreeding- breeding technique that involves crossing two individuals that have similar desirable characteristics. This process produces organisms that are genetically very similar. This type of breeding leads to a greater chance for genetic disorders. Hybridization-breeding technique where breeders ...
DNA, Proteins and the Proteome - Guiding
... DNA, Proteins and the Proteome Guiding Questions 1. What does the central dogma of molecular biology outline? 2. What is the ultimate expression of this information? 3. The three parts of the central dogma are? 4. DNA and RNA are both what? 5. What do protein molecules do? ...
... DNA, Proteins and the Proteome Guiding Questions 1. What does the central dogma of molecular biology outline? 2. What is the ultimate expression of this information? 3. The three parts of the central dogma are? 4. DNA and RNA are both what? 5. What do protein molecules do? ...
Lines of Evidence for Evolution
... however, non-synonymous mutations would be promoted by selection and would be more likely to remain within the population. Non-synonymous mutations more frequently observed. ...
... however, non-synonymous mutations would be promoted by selection and would be more likely to remain within the population. Non-synonymous mutations more frequently observed. ...
Evolution: Natural Selection and Phenotypes
... • A diverse gene pool is important for survival of a species in a changing environment. ...
... • A diverse gene pool is important for survival of a species in a changing environment. ...
Bio1100Ch20
... • A normal allele is inserted into somatic cells of a tissue affected by a genetic disorder. ...
... • A normal allele is inserted into somatic cells of a tissue affected by a genetic disorder. ...
Evolution Nat Selection and Phenotypes
... • A diverse gene pool is important for survival of a species in a changing environment. ...
... • A diverse gene pool is important for survival of a species in a changing environment. ...