Introduction to bioinformatics
... scientists predicted that it would take around 20 years to complete the project 3.000.000.000 base pairs were sequenced in 2003 Only 2% of the genome contains information about proteins. At this time, it is still unknown what the other 98% does => is this “junk” DNA? We have around 20,000 genes in o ...
... scientists predicted that it would take around 20 years to complete the project 3.000.000.000 base pairs were sequenced in 2003 Only 2% of the genome contains information about proteins. At this time, it is still unknown what the other 98% does => is this “junk” DNA? We have around 20,000 genes in o ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... is the use of transgenic farm animals to produce pharmaceuticals; genes that code for therapeutic and diagnostic proteins are incorporated into an animal’s DNA, and the proteins appear in the animal’s milk. 26.3 Gene Therapy Gene Therapy Gene therapy is the insertion of genetic material into human c ...
... is the use of transgenic farm animals to produce pharmaceuticals; genes that code for therapeutic and diagnostic proteins are incorporated into an animal’s DNA, and the proteins appear in the animal’s milk. 26.3 Gene Therapy Gene Therapy Gene therapy is the insertion of genetic material into human c ...
Document
... cell division. • DNA encodes proteins needed by the cell. • DNA is capable of mutation, providing raw material for evolutionary change. ...
... cell division. • DNA encodes proteins needed by the cell. • DNA is capable of mutation, providing raw material for evolutionary change. ...
SBI 4U Genetics 5
... together under the control of one promoter. The genes that help the bacterium E.coli digest lactose are found in the lac operon. ...
... together under the control of one promoter. The genes that help the bacterium E.coli digest lactose are found in the lac operon. ...
1.3 Ten themes unify the study of life
... Most multicellular organisms have cells that are specialized for different functions ...
... Most multicellular organisms have cells that are specialized for different functions ...
Lecture 5
... Abnormal methylation can lead to problems - Ex: FMR1 – hypermethylation leads to Fragile X syndrome; which is the leading Mendelian (single gene) disorder that causes mental retardation RNA Splicing One gene can result in a large number of different polypeptides Gene: Exon 1 ...
... Abnormal methylation can lead to problems - Ex: FMR1 – hypermethylation leads to Fragile X syndrome; which is the leading Mendelian (single gene) disorder that causes mental retardation RNA Splicing One gene can result in a large number of different polypeptides Gene: Exon 1 ...
Lecture Slides
... Each colored stripe in this fly embryo shows the expression of a different gene or set of genes. The spatial regulation of these genes allows the embryo to be divided up into different regions that will give rise to the head, the internal organs, the abdomen, etc. ...
... Each colored stripe in this fly embryo shows the expression of a different gene or set of genes. The spatial regulation of these genes allows the embryo to be divided up into different regions that will give rise to the head, the internal organs, the abdomen, etc. ...
here - VCU
... exon codes for a specific portion of the complete protein. In some species (including humans), a gene's exons are separated by long regions of DNA (called introns or sometimes "junk DNA") that have no apparent function. The DNA that makes up the human genome can be subdivided into information bytes ...
... exon codes for a specific portion of the complete protein. In some species (including humans), a gene's exons are separated by long regions of DNA (called introns or sometimes "junk DNA") that have no apparent function. The DNA that makes up the human genome can be subdivided into information bytes ...
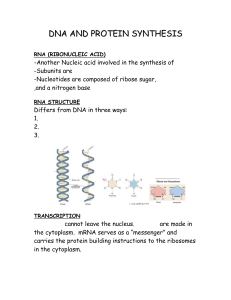
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
Chapter 21 - HCC Learning Web
... • The first evidence for mobile DNA segments came from geneticist Barbara McClintock’s breeding experiments with Indian corn • McClintock identified changes in the color of corn kernels that made sense only by postulating that some genetic elements move from other genome locations into the genes for ...
... • The first evidence for mobile DNA segments came from geneticist Barbara McClintock’s breeding experiments with Indian corn • McClintock identified changes in the color of corn kernels that made sense only by postulating that some genetic elements move from other genome locations into the genes for ...
Principles and Practices of Biosafety
... not require additional safety measures. In cases where these sequences are not characterized, a situation that is typically encountered when a library of genomic DNA of an organism is being established, a higher BSL will be required. Cloning of genes coding for proteins that have potential pharmacol ...
... not require additional safety measures. In cases where these sequences are not characterized, a situation that is typically encountered when a library of genomic DNA of an organism is being established, a higher BSL will be required. Cloning of genes coding for proteins that have potential pharmacol ...
DNA Repair - College of Arts and Sciences at Lamar University
... -Mutations are inherited changes in the DNA sequence. They can result (i) from replication errors,(ii) from damage to the DNA, or (iii) from errors during repair of damage. Point mutations are the changes of a single base pair. Transitions are mutations in which one purine is substituted for another ...
... -Mutations are inherited changes in the DNA sequence. They can result (i) from replication errors,(ii) from damage to the DNA, or (iii) from errors during repair of damage. Point mutations are the changes of a single base pair. Transitions are mutations in which one purine is substituted for another ...
UTACCEL 2010
... composed of one sugar molecule, one phosphate molecule and one nucleotide molecule. There are four types of nucleotides (or 'bases') in the DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The two strands of DNA are structured in such a way that an adenine on one strand is always attache ...
... composed of one sugar molecule, one phosphate molecule and one nucleotide molecule. There are four types of nucleotides (or 'bases') in the DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The two strands of DNA are structured in such a way that an adenine on one strand is always attache ...
CONFOUNDING PHYLOGENETIC TREES
... -according to rRNA based phylogenies, there are 3 kingdoms of life – bacteria, archaea and eukarya with eukarya derived from archaea -the sequencing of hundreds of genomes has called into question this tree because many proteins in any one organism can be archaeal or bacterial in origin -gene swappi ...
... -according to rRNA based phylogenies, there are 3 kingdoms of life – bacteria, archaea and eukarya with eukarya derived from archaea -the sequencing of hundreds of genomes has called into question this tree because many proteins in any one organism can be archaeal or bacterial in origin -gene swappi ...
What is disruptive selection?
... Factors that influence the survival of an individual within a population ...
... Factors that influence the survival of an individual within a population ...
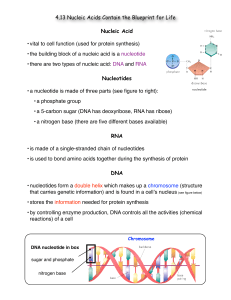
4.13 notes
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
Sem2 CA Bio Standards
... d. specialization of cells in multicellular organisms is usually due to different patterns of gene expression rather than to differences of the genes themselves. e. proteins can differ from one another in the number and sequence of amino acids. *f. why proteins having different amino acid sequences ...
... d. specialization of cells in multicellular organisms is usually due to different patterns of gene expression rather than to differences of the genes themselves. e. proteins can differ from one another in the number and sequence of amino acids. *f. why proteins having different amino acid sequences ...
Genomics and Forensics - MCCC Faculty & Staff Web Pages
... Bioinformatics – a discipline which combines biology, computer science and information technology ...
... Bioinformatics – a discipline which combines biology, computer science and information technology ...
1 Molecular Evolution I: Protein Evolution 1. Protein Evolution We
... Different proteins have different neutral mutation rates, and thus accumulate substitutions at different rates. This hypothesis is the basis of the neutral theory of molecular evolution. An important implication of the molecular clock is that once we know the rate of substitution for a given protein ...
... Different proteins have different neutral mutation rates, and thus accumulate substitutions at different rates. This hypothesis is the basis of the neutral theory of molecular evolution. An important implication of the molecular clock is that once we know the rate of substitution for a given protein ...