SBI 4U Cellular Respiration Review Game2
... 20. What is the overall equation of aerobic cellular respiration? 21. How many NADH, FADH2 and ATP are produced per glucose molecule in the Kreb’s Cycle? 22. What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain and describe what happens? 23. Where does the ETC occur in the cell? 24. H ...
... 20. What is the overall equation of aerobic cellular respiration? 21. How many NADH, FADH2 and ATP are produced per glucose molecule in the Kreb’s Cycle? 22. What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain and describe what happens? 23. Where does the ETC occur in the cell? 24. H ...
ch3b FA11 - Cal State LA
... • Redox reactions: the gain (reduction) or loss (oxidation) of electrons – Changes in organic molecules shift the degree of e- sharing • Carbon in C-H bond is reduced • Carbon in C=O bond is oxidized – EN diffs result in e- spending less time around C when bonded to O ...
... • Redox reactions: the gain (reduction) or loss (oxidation) of electrons – Changes in organic molecules shift the degree of e- sharing • Carbon in C-H bond is reduced • Carbon in C=O bond is oxidized – EN diffs result in e- spending less time around C when bonded to O ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... NADH and FADH2 are put through the chain so that their energy can be used to convert ADP into ATP These reactions require oxygen, which accepts the H+ ions to form water Occurs in the mitochondria The entire process of aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP molecules ...
... NADH and FADH2 are put through the chain so that their energy can be used to convert ADP into ATP These reactions require oxygen, which accepts the H+ ions to form water Occurs in the mitochondria The entire process of aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP molecules ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... NADH and FADH2 are put through the chain so that their energy can be used to convert ADP into ATP These reactions require oxygen, which accepts the H+ ions to form water Occurs in the mitochondria The entire process of aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP molecules ...
... NADH and FADH2 are put through the chain so that their energy can be used to convert ADP into ATP These reactions require oxygen, which accepts the H+ ions to form water Occurs in the mitochondria The entire process of aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP molecules ...
Chapter 9_ objectives
... In general terms, explain how the exergonic “slide” of electrons down the electron transport chain is coupled to the endergonic production of ATP by chemiosmosis. ...
... In general terms, explain how the exergonic “slide” of electrons down the electron transport chain is coupled to the endergonic production of ATP by chemiosmosis. ...
The Kreb`s Cycle - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • The products of aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide, water, and ATP (as was shown on the previous slide.) • Oxygen is needed for aerobic respiration because it is the final acceptor in the electron transport chain; without it the process ...
... • The products of aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide, water, and ATP (as was shown on the previous slide.) • Oxygen is needed for aerobic respiration because it is the final acceptor in the electron transport chain; without it the process ...
ATP - Mhanafi123`s Blog
... malate dehydrogenase Enzyme glyceraldehyde 3P dehydrogenase required NAD+ in function ...
... malate dehydrogenase Enzyme glyceraldehyde 3P dehydrogenase required NAD+ in function ...
Chapter 16.3: Anaerobic Respiration
... – C atoms removed in pairs as acetyl coenzyme A in lipids, fed into Krebs cycle – C-H skeletons of amino acids converted into pyruvate or acetyl CoA ...
... – C atoms removed in pairs as acetyl coenzyme A in lipids, fed into Krebs cycle – C-H skeletons of amino acids converted into pyruvate or acetyl CoA ...
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration
... The following information on cellular respiration is not all accurate I want you to read it and correct the mistakes. Anything in italics is correct and does not need to be corrected. There are approximately 60 mistakes that need to be fixed. We eat a potato which is full of the polysaccharide glyco ...
... The following information on cellular respiration is not all accurate I want you to read it and correct the mistakes. Anything in italics is correct and does not need to be corrected. There are approximately 60 mistakes that need to be fixed. We eat a potato which is full of the polysaccharide glyco ...
U4L21 fuel oxidation - The University of Sydney
... This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further reproduction or communication of this material by y ...
... This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further reproduction or communication of this material by y ...
Name: Date: 1. The is the source of most of the cellular energy. A
... metabolic pathways can be interconnected, and glucose could enter more than one ...
... metabolic pathways can be interconnected, and glucose could enter more than one ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... Some organisms, such as yeast and some bacteria, do not require oxygen and can survive on a less efficient way of getting energy Other organisms that generally require oxygen sometimes don’t have enough for all their cells to do aerobic respiration so they can use a less effiecent way of breaking do ...
... Some organisms, such as yeast and some bacteria, do not require oxygen and can survive on a less efficient way of getting energy Other organisms that generally require oxygen sometimes don’t have enough for all their cells to do aerobic respiration so they can use a less effiecent way of breaking do ...
Cellular Respiration PPT
... Glycolysis is the process in which one molecule of glucose(6C) is broken in half, producing two molecules of pyruvic acid(3C) Requires 2 ATP molecules to get it started, but produces 4 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules in return ...
... Glycolysis is the process in which one molecule of glucose(6C) is broken in half, producing two molecules of pyruvic acid(3C) Requires 2 ATP molecules to get it started, but produces 4 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules in return ...
AP Biology Chapter 5 Notes
... Chemiosmosis 14. As electrons are passed from on membrane protein to another, they are losing energy. Where is the energy going? Chemiosmosis 15. Fill in the information about the electron transport chain. ...
... Chemiosmosis 14. As electrons are passed from on membrane protein to another, they are losing energy. Where is the energy going? Chemiosmosis 15. Fill in the information about the electron transport chain. ...
Biology-1 Exam Two Sample Questions Substrates bind to an
... b. Enzymes are very specific for certain substrates. c. Enzymes are used up in chemical reactions. d. Enzymes emerge unchanged from the reactions they catalyze. e. An enzyme binds to its substrate at the enzyme's active site. 3. Which of the following statements about the ATP molecule is true? a. It ...
... b. Enzymes are very specific for certain substrates. c. Enzymes are used up in chemical reactions. d. Enzymes emerge unchanged from the reactions they catalyze. e. An enzyme binds to its substrate at the enzyme's active site. 3. Which of the following statements about the ATP molecule is true? a. It ...
NAME Chapter 9 VOCAB Cellular Respiration pp 220
... process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen FERMENTATION – process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN – series of proteins in which high energy electrons from the Krebs cycle are used to convert ...
... process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen FERMENTATION – process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN – series of proteins in which high energy electrons from the Krebs cycle are used to convert ...
The Citric Acid Cycle - Rubin Risto Gulaboski
... • The reactions of metabolism are MANY • In this class we will discuss some of the major reactions: – Glyco - Lysis (glycolysis) – The Citric Acid Cycle – The Electron Transport Chain ...
... • The reactions of metabolism are MANY • In this class we will discuss some of the major reactions: – Glyco - Lysis (glycolysis) – The Citric Acid Cycle – The Electron Transport Chain ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Review
... 1. Describe the ways in which ATP can be used to perform cell work. 2. Explain the difference between oxidation and reduction reactions. Be sure to mention the changes in energy that accompany these reactions. 3. Illustrate the reaction performed by dehydrogenase enzymes. 4. What is the role played ...
... 1. Describe the ways in which ATP can be used to perform cell work. 2. Explain the difference between oxidation and reduction reactions. Be sure to mention the changes in energy that accompany these reactions. 3. Illustrate the reaction performed by dehydrogenase enzymes. 4. What is the role played ...
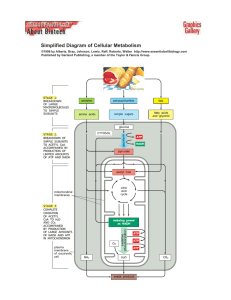
Simplified Diagram of Cellular Metabolism
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism Updated
... They can give rise to glucose by gluconeogenesis • Transamination :Oxaloacetate and α-ketoglutarate respectively, serve as precursors for the synthesis of aspartate and glutamate by transamination which in turn are used for the synthesis of other non essential amino acids, purines and pyrimidines. • ...
... They can give rise to glucose by gluconeogenesis • Transamination :Oxaloacetate and α-ketoglutarate respectively, serve as precursors for the synthesis of aspartate and glutamate by transamination which in turn are used for the synthesis of other non essential amino acids, purines and pyrimidines. • ...
Anaerobic metabolism is the production of ATP with oxygen
... 2. True or False: An enzyme is not changed by the reaction it causes. 3. True or False: An enzyme does not need to fit precisely with the reactant to catalyze the reaction. 4. True or False: The electron transport system is where most of the ATP is produced during aerobic metabolism. 5. True or Fals ...
... 2. True or False: An enzyme is not changed by the reaction it causes. 3. True or False: An enzyme does not need to fit precisely with the reactant to catalyze the reaction. 4. True or False: The electron transport system is where most of the ATP is produced during aerobic metabolism. 5. True or Fals ...
Cellular Energy hbio 09 tri 1
... • Electron transfer chain – Most energy – H+ and e- gradients • Drive ATP formation ...
... • Electron transfer chain – Most energy – H+ and e- gradients • Drive ATP formation ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑