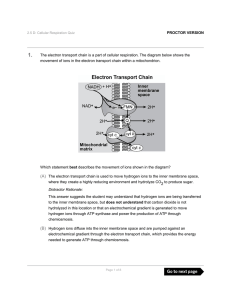
The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The
... This answer suggests the student may understand that photolysis occurs during the lightdependent reactions in photosynthesis, but does not understand that oxygen is not split and combined with carbon to form carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, and that the plant is undergoing cellular respiration, ...
... This answer suggests the student may understand that photolysis occurs during the lightdependent reactions in photosynthesis, but does not understand that oxygen is not split and combined with carbon to form carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, and that the plant is undergoing cellular respiration, ...
Homework # 9 Citric Acid Cycle, electron transport Chain, and
... The conversion of pyruvic acid to lactic acid requires NADH: Pyruvic Acid + NADH + H+ ---> Lactic Acid + NAD+ This pyruvic acid normally made by transamination of amino acids, is intended for conversion into glucose by gluconeogenesis. This pathway is inhibited by low concentrations of pyruvic acid, ...
... The conversion of pyruvic acid to lactic acid requires NADH: Pyruvic Acid + NADH + H+ ---> Lactic Acid + NAD+ This pyruvic acid normally made by transamination of amino acids, is intended for conversion into glucose by gluconeogenesis. This pathway is inhibited by low concentrations of pyruvic acid, ...
Life 9e - Garvness
... 48. The electron transport chain contains four large protein complexes (I, II, III, and IV), cytochrome c, and ubiquinone. The function of these molecules is to a. transport electrons. b. ensure the production of water and oxygen. c. regulate the passage of water through the chain. d. oxidize NADH. ...
... 48. The electron transport chain contains four large protein complexes (I, II, III, and IV), cytochrome c, and ubiquinone. The function of these molecules is to a. transport electrons. b. ensure the production of water and oxygen. c. regulate the passage of water through the chain. d. oxidize NADH. ...
CH 2 - Faperta UGM
... Fatty acid esters of trihydroxy alcohol The fast majorities in nature have all 3 of glycerol hydroxy groups esterified with fatty acids and are called triglycerides (triacylglycerols) They are the main constituents of natural fats and oil Food reserves in seeds and/or fleshy part of fruit ...
... Fatty acid esters of trihydroxy alcohol The fast majorities in nature have all 3 of glycerol hydroxy groups esterified with fatty acids and are called triglycerides (triacylglycerols) They are the main constituents of natural fats and oil Food reserves in seeds and/or fleshy part of fruit ...
Metabolism of lipids
... • fatty acyl-CoA is elongated by the addition with acetyl CoA • both NADH and NADPH serve as electron donors • essentially the reversal of the β-oxidation pathway • primarily to elongate FAs shorter than C16 ...
... • fatty acyl-CoA is elongated by the addition with acetyl CoA • both NADH and NADPH serve as electron donors • essentially the reversal of the β-oxidation pathway • primarily to elongate FAs shorter than C16 ...
Proteolytic activation
... The clotting process must be precisely regulated -Clots must form rapidly. -Activated clotting factors are short-lived because they diluted by blood flow, removed by the liver, and degraded by proteases. -Factor V and VIII are digested by protein C, switched on by the action of thrombin -Thrombin h ...
... The clotting process must be precisely regulated -Clots must form rapidly. -Activated clotting factors are short-lived because they diluted by blood flow, removed by the liver, and degraded by proteases. -Factor V and VIII are digested by protein C, switched on by the action of thrombin -Thrombin h ...
complex I
... - The hydride ion is removed from NADH (to regenerate NAD+) and is converted into a proton and two electrons (H- ⇒ H+ + 2e-). - Each of these ions being tightly bound to a protein molecule that alters the electron affinity of the metal ion. Most of the proteins involved are grouped into three large ...
... - The hydride ion is removed from NADH (to regenerate NAD+) and is converted into a proton and two electrons (H- ⇒ H+ + 2e-). - Each of these ions being tightly bound to a protein molecule that alters the electron affinity of the metal ion. Most of the proteins involved are grouped into three large ...
Introduction into Metabolism and Energy Exchange in Human
... energy inputs. Energy can be supplied in two ways: 1) by ATP transferred from the catabolic pathways; 2) in some cases, by highenergy hydrogen in a form of reduced NADPH. Catabolism is the sum total processes where complex molecules are broken down into simpler ones. There is the free energy formati ...
... energy inputs. Energy can be supplied in two ways: 1) by ATP transferred from the catabolic pathways; 2) in some cases, by highenergy hydrogen in a form of reduced NADPH. Catabolism is the sum total processes where complex molecules are broken down into simpler ones. There is the free energy formati ...
Microsoft Word
... effect of aspartic acid concentration is more than that of glycine and (c) During the interaction of glutamic acid and glycine, the effect of glutamic acid is more prominent than that of glycine. The three factor interaction analyses reveal that the effect of the three amino acids is in the order as ...
... effect of aspartic acid concentration is more than that of glycine and (c) During the interaction of glutamic acid and glycine, the effect of glutamic acid is more prominent than that of glycine. The three factor interaction analyses reveal that the effect of the three amino acids is in the order as ...
Events of The Krebs Cycle
... intermediate compound called Fructose-1,6Diphosphate (F-1,6-DP). This is accomplished by using two ATP molecules to phosphorylate the sugar at carbons 1 and 6. In phase two, the F-1,6-DP sugar then splits (lysis) into two, half sized sugar fragments which become Glyceraldehyde Phosphate and Dihydrox ...
... intermediate compound called Fructose-1,6Diphosphate (F-1,6-DP). This is accomplished by using two ATP molecules to phosphorylate the sugar at carbons 1 and 6. In phase two, the F-1,6-DP sugar then splits (lysis) into two, half sized sugar fragments which become Glyceraldehyde Phosphate and Dihydrox ...
liver physiology
... colonic) and partially in series. The liver is the reason for this, as it recieves 25% of its flow from the hepatic artery and the remainer from the portal system. The heaptic system has the capacity to increase flow arterial or portal flow if the reciprocal is decreased. The liver maintains a tight ...
... colonic) and partially in series. The liver is the reason for this, as it recieves 25% of its flow from the hepatic artery and the remainer from the portal system. The heaptic system has the capacity to increase flow arterial or portal flow if the reciprocal is decreased. The liver maintains a tight ...
2 H
... • An artifcial e- donor, phenylenediamine, is used to reduce the cytochrome oxidase • If the enzyme is present, the colorless reagent (reduced state) will turn blue (oxidized state) ...
... • An artifcial e- donor, phenylenediamine, is used to reduce the cytochrome oxidase • If the enzyme is present, the colorless reagent (reduced state) will turn blue (oxidized state) ...
Industrial Biotechnology
... • The final product of metabolic pathway inhibits the action of earlier enzymes (usually the first) of that sequence. • The inhibitor and the substrate need not resemble each other, hence the inhibition is often called allosteric. • In case of isosteic inhibition the inhibitor and substrate have the ...
... • The final product of metabolic pathway inhibits the action of earlier enzymes (usually the first) of that sequence. • The inhibitor and the substrate need not resemble each other, hence the inhibition is often called allosteric. • In case of isosteic inhibition the inhibitor and substrate have the ...
Jeopardy - Student Resources Home Page
... 1 pyruvic acid, 4 ATP, 2 NADH 2 pyruvic acid, 2 ATP, 2 NADH 1 pyruvic acid, 2 ATP, 4 NADH 2 pyruvic acid, 4 ATP, 2 NADH ANSWER BACK TO GAME ...
... 1 pyruvic acid, 4 ATP, 2 NADH 2 pyruvic acid, 2 ATP, 2 NADH 1 pyruvic acid, 2 ATP, 4 NADH 2 pyruvic acid, 4 ATP, 2 NADH ANSWER BACK TO GAME ...
Help is just a phone call away!
... solution and the child washed down with this. The child was then wrapped in a blanket and placed in bed to sleep. Three hours later the mother tried to awaken the child and could not. Mother stated child had a 5 second seizure. The child was taken to the ED VS: T 98 HR 132 RR 24 ...
... solution and the child washed down with this. The child was then wrapped in a blanket and placed in bed to sleep. Three hours later the mother tried to awaken the child and could not. Mother stated child had a 5 second seizure. The child was taken to the ED VS: T 98 HR 132 RR 24 ...
Metabolic fate of amino acid
... • L-amnio acid oxidase is present in liver and kideny tissue. • These autoxidizable flavoproteins oxidize amino acids to an a -imino acid that adds water and decomposes to the corresponding a -keto acid with release of ammonium ion (Fig.11.3). • The reduced flavin is reoxidized directly by molecular ...
... • L-amnio acid oxidase is present in liver and kideny tissue. • These autoxidizable flavoproteins oxidize amino acids to an a -imino acid that adds water and decomposes to the corresponding a -keto acid with release of ammonium ion (Fig.11.3). • The reduced flavin is reoxidized directly by molecular ...
Enzymes Problem Set 1 A) What concentration of the substrate
... 200 mM triethanolamine-HCl buffer 25 mM ,-dipyridyl 5 U glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase from rabbit muscle 2.0 M glycerol 2.0 mM NADH 20 mM MgCl2 20 mM dihydroxyacetone, DHA 20 mM ATP ...
... 200 mM triethanolamine-HCl buffer 25 mM ,-dipyridyl 5 U glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase from rabbit muscle 2.0 M glycerol 2.0 mM NADH 20 mM MgCl2 20 mM dihydroxyacetone, DHA 20 mM ATP ...
Ethanol
... breath, sweat and urine 2. ~ 90% ethanol removed by oxidation 3. Most of this ethanol oxidation occurs in the liver 4. Ethanol cannot be stored in the liver 5. No major feedback mechanisms to pace the rate of ethanol metabolism to the physiological conditions of the liver cell 6. Kinetics are zero-o ...
... breath, sweat and urine 2. ~ 90% ethanol removed by oxidation 3. Most of this ethanol oxidation occurs in the liver 4. Ethanol cannot be stored in the liver 5. No major feedback mechanisms to pace the rate of ethanol metabolism to the physiological conditions of the liver cell 6. Kinetics are zero-o ...
Case Study Powerpoints - Westford Academy Ap Bio
... (reduced free energy that must be absorbed for transition state) ...
... (reduced free energy that must be absorbed for transition state) ...
Human Body Systems
... the ATP energy needed for light exercise. • When there’s not enough Oxygen present, Anaerobic Respiration occurs. – Lactic acid builds up, causing fatigue – Lactic acid is washed out of muscles within 30 minutes after exercise. ...
... the ATP energy needed for light exercise. • When there’s not enough Oxygen present, Anaerobic Respiration occurs. – Lactic acid builds up, causing fatigue – Lactic acid is washed out of muscles within 30 minutes after exercise. ...
Chap 4 Study Guide
... Assume you have recently consumed a delicious cheeseburger as a source of body fuel. Also, assume that digestion and absorption into the body was successful such that simple sugars (like glucose) from carbohydrates, triglycerides from lipids, and amino acids from proteins are now present in your bod ...
... Assume you have recently consumed a delicious cheeseburger as a source of body fuel. Also, assume that digestion and absorption into the body was successful such that simple sugars (like glucose) from carbohydrates, triglycerides from lipids, and amino acids from proteins are now present in your bod ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑























