Mock Exam 2BY330 Summer 2014 Assume that 4 molecules of
... 12. True or False: All RNA transcripts in eukaryotes undergo post-transcriptional modifications. 13. _____________________ is the sequence of nucelotides present on the template strand of the gene for eukaryotic mRNA that signals UsnRNP to remove the over-transcript produced. This sequence is about ...
... 12. True or False: All RNA transcripts in eukaryotes undergo post-transcriptional modifications. 13. _____________________ is the sequence of nucelotides present on the template strand of the gene for eukaryotic mRNA that signals UsnRNP to remove the over-transcript produced. This sequence is about ...
Large Scale Gene Expression Analysis
... Transcription control in eucaryots is complex: • Eukaryotic RNA-polymerase needs „general transcription factors“ • Eukaryotic includes promotor plus regulative DNA sequences • Enhancer elements regulate genes in distance ...
... Transcription control in eucaryots is complex: • Eukaryotic RNA-polymerase needs „general transcription factors“ • Eukaryotic includes promotor plus regulative DNA sequences • Enhancer elements regulate genes in distance ...
Table S2. Functional classification of differentially expressed genes
... Nucleotide biosynthesis and metabolism ...
... Nucleotide biosynthesis and metabolism ...
RNA
... Fill in the correct Base pairs below A = ____, C = ____, G = ____, T =_____ Now write the “Complimentary Strand” underneath the following strand of DNA: DNA Strand 1 – A T T G C C T G C T A DNA Compliment REMEMBER!! ________________________ are the site of protein synthesis ________________________ ...
... Fill in the correct Base pairs below A = ____, C = ____, G = ____, T =_____ Now write the “Complimentary Strand” underneath the following strand of DNA: DNA Strand 1 – A T T G C C T G C T A DNA Compliment REMEMBER!! ________________________ are the site of protein synthesis ________________________ ...
Genomics
... How introns are removed? • This is because the amino acids that make up proteins are joined together based on codons, which consist of three nucleotides. • An imprecise intron removal thus may result in a framshift, which means that the genetic code would be read incorrectly. E.g BOB THE BIG TAN CA ...
... How introns are removed? • This is because the amino acids that make up proteins are joined together based on codons, which consist of three nucleotides. • An imprecise intron removal thus may result in a framshift, which means that the genetic code would be read incorrectly. E.g BOB THE BIG TAN CA ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Exercise - KEY
... 1. Histone deacetylation would be expected to increase association of histones and DNA, since the positively charged histones would interact tightly with the negatively charged DNA. 2. Transcription, DNA ...
... 1. Histone deacetylation would be expected to increase association of histones and DNA, since the positively charged histones would interact tightly with the negatively charged DNA. 2. Transcription, DNA ...
The indentification of protein-RNA interactions within the 5
... mRNA from the cytoplasmic ribosome fraction to the membrane-bound polysome fraction mediated by the signal recognition particle [4] in response to increasing glucose levels. The specificity of the glucose-induced increase in insulin biosynthesis is probably mediated via interactions with the preproi ...
... mRNA from the cytoplasmic ribosome fraction to the membrane-bound polysome fraction mediated by the signal recognition particle [4] in response to increasing glucose levels. The specificity of the glucose-induced increase in insulin biosynthesis is probably mediated via interactions with the preproi ...
Nucleic acids
... Gene Expression The process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product: Proteins • Transcription • RNA processing • RNA export • Translation • Folding • Protein transport ...
... Gene Expression The process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product: Proteins • Transcription • RNA processing • RNA export • Translation • Folding • Protein transport ...
Gene Expression
... • We need a means of getting the correct amino acid in the correct sequence. For this we use one more type of RNA : transfer RNA (tRNA). • tRNA is a single strand of RNA that is folded into the shape of a clover. It has an anticodon that matches the codon on the mRNA, and a spot for holding the amin ...
... • We need a means of getting the correct amino acid in the correct sequence. For this we use one more type of RNA : transfer RNA (tRNA). • tRNA is a single strand of RNA that is folded into the shape of a clover. It has an anticodon that matches the codon on the mRNA, and a spot for holding the amin ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... Sometimes the environment can change almost instantly Eukaryotes have to respond as well, although typically not as drastically With multicellular organisms, different types of cells express different sets of genes Structural genes encode proteins involved in metabolic or biosynthetic pathways ...
... Sometimes the environment can change almost instantly Eukaryotes have to respond as well, although typically not as drastically With multicellular organisms, different types of cells express different sets of genes Structural genes encode proteins involved in metabolic or biosynthetic pathways ...
Protein Synthesis
... • Ribosome moves along mRNA to the next codon, the anti-codon binds to the codon and the new amino acid attaches to the first amino acid forming a polypeptide chain until a stop codon occurs ...
... • Ribosome moves along mRNA to the next codon, the anti-codon binds to the codon and the new amino acid attaches to the first amino acid forming a polypeptide chain until a stop codon occurs ...
Targeted knock-up of endogenous genes using a
... The molecular repair toolbox has been augmented in the past year by the development of a technology that can specifically increase the amount of protein made by a targeted endogenous gene. This technology was first demonstrated in an elegant study by Carrieri et al (Nature 491:454). This paper descr ...
... The molecular repair toolbox has been augmented in the past year by the development of a technology that can specifically increase the amount of protein made by a targeted endogenous gene. This technology was first demonstrated in an elegant study by Carrieri et al (Nature 491:454). This paper descr ...
RNA Transcription
... once 'information' has passed into protein it cannot get out again. The transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein, may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid, is ...
... once 'information' has passed into protein it cannot get out again. The transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein, may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid, is ...
Protein Synthesis - Doral Academy High School
... the mRNA into a polypeptide chain • Ribosomes read mRNA 1 codon at a time and construct the proteins • tRNA carrying the amino acid specified by the codon binds and a peptide bond is formed between the two amino acids. • This process continues until a stop codon is reached. • The ribosome then falls ...
... the mRNA into a polypeptide chain • Ribosomes read mRNA 1 codon at a time and construct the proteins • tRNA carrying the amino acid specified by the codon binds and a peptide bond is formed between the two amino acids. • This process continues until a stop codon is reached. • The ribosome then falls ...
Central Dogma of Cell Biology
... http://wwwclass.unl.edu/biochem/gp2/m_biology/animation/gene/gene_a2.html ...
... http://wwwclass.unl.edu/biochem/gp2/m_biology/animation/gene/gene_a2.html ...
Ch 5
... mRNA has codons – a sequence of 3 nucleotides that codes for an amino acid. tRNA has anticodons that are complementary to mRNA’s codons. AUG is the universal ‘start’ codon that tells the ribosome to start translating. There are three ‘stop’codons – UAA, UAG and UGA – that tell the ribosome to stop t ...
... mRNA has codons – a sequence of 3 nucleotides that codes for an amino acid. tRNA has anticodons that are complementary to mRNA’s codons. AUG is the universal ‘start’ codon that tells the ribosome to start translating. There are three ‘stop’codons – UAA, UAG and UGA – that tell the ribosome to stop t ...
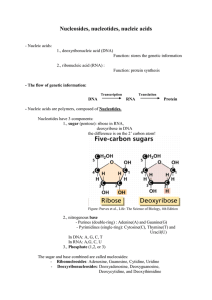
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... protein synthesis. Single stranded. - ribosomal RNA = rRNA : components of the ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis (translation). rRNA forms self-complementary double-stranded regions (in RNA there is Uracil instead of Thymine as a base, it forms double hydrogen bonds with Adenine). - t ...
... protein synthesis. Single stranded. - ribosomal RNA = rRNA : components of the ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis (translation). rRNA forms self-complementary double-stranded regions (in RNA there is Uracil instead of Thymine as a base, it forms double hydrogen bonds with Adenine). - t ...
Ch. 17 - Ltcconline.net
... 1. Once initiation is complete, amino acids are added one at a time till translation is complete 2. Each amino acid that is added onto the growing chain does so in 3 steps a. codon recognition b. peptide bond formation c. translocation 3. termination. 4. release factor J. Review 1. typically, severa ...
... 1. Once initiation is complete, amino acids are added one at a time till translation is complete 2. Each amino acid that is added onto the growing chain does so in 3 steps a. codon recognition b. peptide bond formation c. translocation 3. termination. 4. release factor J. Review 1. typically, severa ...
Study Guide for Understanding the Concept of Protein Synthesis
... Individual "escort" ribosomes from the cytoplasm appear to the amino acids. At the presence of these ribosomes, the amino acids release. Step #4: Transfer RNA (tRNA) acts as a "taxi" by which the "escort" ribosomes take the amino acids and position them into place as Ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Step #5: R ...
... Individual "escort" ribosomes from the cytoplasm appear to the amino acids. At the presence of these ribosomes, the amino acids release. Step #4: Transfer RNA (tRNA) acts as a "taxi" by which the "escort" ribosomes take the amino acids and position them into place as Ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Step #5: R ...
Transcription - Effingham County Schools
... because it’s too important that other people need to use it too. If you really need this information, you can make a copy of it for your own use, put the reference material back on the shelf so that others can use it too. Can you imagine if DNA was physically lost? That’s why chromosomes never leave ...
... because it’s too important that other people need to use it too. If you really need this information, you can make a copy of it for your own use, put the reference material back on the shelf so that others can use it too. Can you imagine if DNA was physically lost? That’s why chromosomes never leave ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.