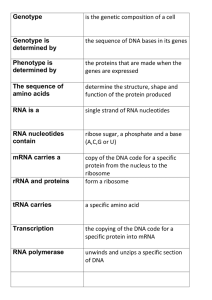
DNA Unit Test Corrections
... 22. Describe the process of translation.____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ...
... 22. Describe the process of translation.____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ...
Gene expression PPT
... – Transcription starts at RNA polymerase binding sites called promoters on DNA template strand. Transcription factor – Binds to promoter so that RNA polymerase can then bind Initiation – Other transcription factors bind, assembling a transcription initiation complex. – RNA polymerase begins to unwin ...
... – Transcription starts at RNA polymerase binding sites called promoters on DNA template strand. Transcription factor – Binds to promoter so that RNA polymerase can then bind Initiation – Other transcription factors bind, assembling a transcription initiation complex. – RNA polymerase begins to unwin ...
Gene Action
... Information from a specific section of DNA is first transcribed to produce a specific molecule of RNA RNA attaches to a ribosome where the information is translated into a corresponding sequence of amino acids ...
... Information from a specific section of DNA is first transcribed to produce a specific molecule of RNA RNA attaches to a ribosome where the information is translated into a corresponding sequence of amino acids ...
Molecular Genetics
... • RNA polymerase will initiate the making of mRNA in the same way that DNA polymerase replicates DNA. We call this the start codon. • A codon is a set of three bases and all RNA is divided up in sets of three. • The transcription continues until the stop codon is reached. Then, the polymerase releas ...
... • RNA polymerase will initiate the making of mRNA in the same way that DNA polymerase replicates DNA. We call this the start codon. • A codon is a set of three bases and all RNA is divided up in sets of three. • The transcription continues until the stop codon is reached. Then, the polymerase releas ...
Transcription and Translation
... Transcription I. Transcription is the process of copying one strand of DNA to ...
... Transcription I. Transcription is the process of copying one strand of DNA to ...
PowerPoint - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... (the details) Protein Synthesis involves two main steps: Transcription Translation ...
... (the details) Protein Synthesis involves two main steps: Transcription Translation ...
GENE EXPRESSION CH 17
... • Only one strand of the DNA is transcribed into RNA, the template strand • RNA strand is complementary to DNA strand copied • Enzyme is RNA polymerase ...
... • Only one strand of the DNA is transcribed into RNA, the template strand • RNA strand is complementary to DNA strand copied • Enzyme is RNA polymerase ...
BIO 101: Transcription and Translation
... In eukaryotes, pre-mRNA must be further processed to mRNA before it leaves the nucleus ...
... In eukaryotes, pre-mRNA must be further processed to mRNA before it leaves the nucleus ...
3.PROTEIN SYNTHESIS overview
... Ingram found that, in sickle cell anemia RBC’s, the amino acid ___________ substitutes for the normal amino acid in the protein This substitution leads to a change in the shape of the red blood cell (RBC) Ingram’s work showed that a gene specifies the _____________________of each amino acid in a pol ...
... Ingram found that, in sickle cell anemia RBC’s, the amino acid ___________ substitutes for the normal amino acid in the protein This substitution leads to a change in the shape of the red blood cell (RBC) Ingram’s work showed that a gene specifies the _____________________of each amino acid in a pol ...
The DNA Song
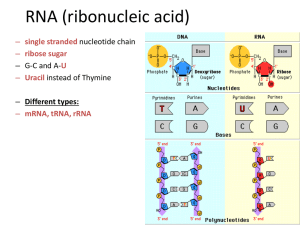
... so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA is single stranded. ...
... so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA is single stranded. ...
Proteome and Gene Expression Analysis
... genes are expressed. – To know when, where, what kind and how much of each protein is present. ...
... genes are expressed. – To know when, where, what kind and how much of each protein is present. ...
File
... chromosomes in the nucleus. Sections of the DNA strand code for specific information, called genes. These genes code for proteins. ...
... chromosomes in the nucleus. Sections of the DNA strand code for specific information, called genes. These genes code for proteins. ...
Proteins
... chromosomes in the nucleus. Sections of the DNA strand code for specific information, called genes. These genes code for proteins. ...
... chromosomes in the nucleus. Sections of the DNA strand code for specific information, called genes. These genes code for proteins. ...
HERE
... amino acids together into the protein strand is found on the mRNA base sequence. • Three bases make up the base sequence. • The three bases are called the CODON. • Scientists use tables to determine the correct match of codon to amino acids. • There are 21 amino acids in the body. ...
... amino acids together into the protein strand is found on the mRNA base sequence. • Three bases make up the base sequence. • The three bases are called the CODON. • Scientists use tables to determine the correct match of codon to amino acids. • There are 21 amino acids in the body. ...
Slide 1
... it first binds to one strand of the DNA at a site called the promoter and then moves down the DNA molecule and assembles a complementary copy of RNA transcription ends when the RNA polymerase reaches a certain nucleotide sequence that signals it stop ...
... it first binds to one strand of the DNA at a site called the promoter and then moves down the DNA molecule and assembles a complementary copy of RNA transcription ends when the RNA polymerase reaches a certain nucleotide sequence that signals it stop ...
protein synthesis
... What is the function of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases? ________________________________________________________________ List below are the steps involved in the attachment of the amino acid to its tRNA. Put them in the correct order. ______ ATP loses phosphates ______ AMP attaches to amino acid ______ ...
... What is the function of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases? ________________________________________________________________ List below are the steps involved in the attachment of the amino acid to its tRNA. Put them in the correct order. ______ ATP loses phosphates ______ AMP attaches to amino acid ______ ...
Protein Synthesis - NCEA Level 2 Biology
... • The function of tRNA is to pick up amino acids specific to the anticodon and carry them to the ribosomes. • They are clicked into place in the correct order to make a protein. ...
... • The function of tRNA is to pick up amino acids specific to the anticodon and carry them to the ribosomes. • They are clicked into place in the correct order to make a protein. ...
Chapter 4 Section 4 – The DNA Connection
... during translation; the mRNA provides the instructions for building a protein. ...
... during translation; the mRNA provides the instructions for building a protein. ...
What Processes Produce RNA from DNA and Protein from mRNA
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
File - EUREKA! Science
... One of the first examples of gene regulation in bacteria Consists three genes, all of which code for enzymes that breaks down lactose All under the control of a single promoter and operator ...
... One of the first examples of gene regulation in bacteria Consists three genes, all of which code for enzymes that breaks down lactose All under the control of a single promoter and operator ...
DNAandProteinSynthesis
... Genes • What is a GENE? – A gene is a segment of DNA that gives instructions to build ONE specific ...
... Genes • What is a GENE? – A gene is a segment of DNA that gives instructions to build ONE specific ...
Gene Expression Gene expression involves coded information on
... nucleotide bases. For transcription to begin RNA polymerase must also bind to a promotor region on the DNA. However, an active repressor molecule binds to an operator region preventing the RNA polymerase transcribing the gene. This active repressor is created by a regulatory gene which is upstream f ...
... nucleotide bases. For transcription to begin RNA polymerase must also bind to a promotor region on the DNA. However, an active repressor molecule binds to an operator region preventing the RNA polymerase transcribing the gene. This active repressor is created by a regulatory gene which is upstream f ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.