
biol-1406_ch3.ppt
... • Each carbon can form up to four bonds (single(2 electrons), double, or triple) and rings • Carbon makes bonds mostly with H, N, and O in living systems • Biomolecules are large and contain “functional groups” attached to the carbon backbone. • Functional groups in organic molecules confer chemical ...
... • Each carbon can form up to four bonds (single(2 electrons), double, or triple) and rings • Carbon makes bonds mostly with H, N, and O in living systems • Biomolecules are large and contain “functional groups” attached to the carbon backbone. • Functional groups in organic molecules confer chemical ...
Amino Acids - University of Houston
... Classification and Characteristics of Amino Acids R polarity: three main categories to describe amino acids: ...
... Classification and Characteristics of Amino Acids R polarity: three main categories to describe amino acids: ...
Amino acid
... • Peptide: A short polymer of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; they are classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. • Dipeptide: A molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. • Tripeptide: A molecule containing three amino acids joined by peptide bonds. • Polypeptide: ...
... • Peptide: A short polymer of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; they are classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. • Dipeptide: A molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. • Tripeptide: A molecule containing three amino acids joined by peptide bonds. • Polypeptide: ...
Biological Molecules wHelp Sheet
... 9. What three structural groups shown do all amino acids have in common? I 0 There are 20 naturally-occurring amino acids, and t’ach one only varies in the structure of the R side chain. Two amino acids are shown in Model I What are the R side chains in each? ...
... 9. What three structural groups shown do all amino acids have in common? I 0 There are 20 naturally-occurring amino acids, and t’ach one only varies in the structure of the R side chain. Two amino acids are shown in Model I What are the R side chains in each? ...
Some funcaon of proteins
... This structure is common to all but one of the α-‐amino acids. (Proline, a cyclic amino acid, is the excep9on.) The R group, or side chain (red), aOached to the α carbon (blue) is different i ...
... This structure is common to all but one of the α-‐amino acids. (Proline, a cyclic amino acid, is the excep9on.) The R group, or side chain (red), aOached to the α carbon (blue) is different i ...
Translation PPT
... • GENE- a sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait • GENETIC CODE - language of the mRNA instructions as determined by the N-bases • CODON- sequence of 3 nucleotides (or just the N-bases) on mRNA that code for one amino acid • POLYLPEPTIDES- proteins made by joining any c ...
... • GENE- a sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait • GENETIC CODE - language of the mRNA instructions as determined by the N-bases • CODON- sequence of 3 nucleotides (or just the N-bases) on mRNA that code for one amino acid • POLYLPEPTIDES- proteins made by joining any c ...
DNA WebQuest
... 5. To translate the mRNA sequence, drag the amino acid from the chart to the flashing box. List the order of amino acids for the entire mRNA molecule. List the order of your amino acids. ...
... 5. To translate the mRNA sequence, drag the amino acid from the chart to the flashing box. List the order of amino acids for the entire mRNA molecule. List the order of your amino acids. ...
Amino Acids as Protein Building Blocks [2]
... primary sequence of amino acids. The physical chemical properties of the amino acids contain the biological information required for folding and function. ...
... primary sequence of amino acids. The physical chemical properties of the amino acids contain the biological information required for folding and function. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 10.) If all of the H bonds in a protein structure were disrupted, which of the following folding levels would be least affected? a. Primary b. Secondary c. Tertiary d. Quaternary e. B and C f. All of the above 11.) An amino acid does NOT contain A. a carboxyl group B. an amino group C. a hydrogen at ...
... 10.) If all of the H bonds in a protein structure were disrupted, which of the following folding levels would be least affected? a. Primary b. Secondary c. Tertiary d. Quaternary e. B and C f. All of the above 11.) An amino acid does NOT contain A. a carboxyl group B. an amino group C. a hydrogen at ...
mRNA Codon/Amino Acid Chart
... • Find a codon’s first base in the first column of the chart; stay in this row. • Find the second base in the middle of the chart, stay in this box. • Locate the third base in the far right column, this is the amino acid that matches the mRNA codon. • Warn students against using the tRNA anticodon w ...
... • Find a codon’s first base in the first column of the chart; stay in this row. • Find the second base in the middle of the chart, stay in this box. • Locate the third base in the far right column, this is the amino acid that matches the mRNA codon. • Warn students against using the tRNA anticodon w ...
A Rapid iMethod™ Test for the Analysis of Amino Acids
... The purchase and use of certain chemicals listed above may require the end user to possess any necessary licenses, permits or approvals, if such are required in accordance with local laws and regulations. It is the responsibility of the end user to purchase these chemicals from a licensed supplier, ...
... The purchase and use of certain chemicals listed above may require the end user to possess any necessary licenses, permits or approvals, if such are required in accordance with local laws and regulations. It is the responsibility of the end user to purchase these chemicals from a licensed supplier, ...
Protein Synthesis and Mutations - Mrs. Gracie Gonzalez Biology Class
... (messenger) in the nucleus with the help of RNA polymerase. 2. When transcribing from DNA to RNA, Thymine is replaced by Uracil. 3. Only one side of the DNA is transcribed into mRNA. 4. mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels to the ribosome in the cytoplasm Translation: (translating for an amin ...
... (messenger) in the nucleus with the help of RNA polymerase. 2. When transcribing from DNA to RNA, Thymine is replaced by Uracil. 3. Only one side of the DNA is transcribed into mRNA. 4. mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels to the ribosome in the cytoplasm Translation: (translating for an amin ...
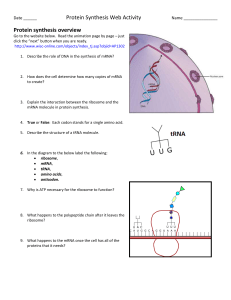
Name__________________________ Date______ Period
... 11. Where does translation occur in a cell? 12. The cell organelle known as the ___________ is where proteins are made. 13. Amino acids are carried to the ribosome by ___________. 14. Transfer RNA (tRNA) has a sequence of three nucleotides called the _____________ that binds to the ________ of mRNA. ...
... 11. Where does translation occur in a cell? 12. The cell organelle known as the ___________ is where proteins are made. 13. Amino acids are carried to the ribosome by ___________. 14. Transfer RNA (tRNA) has a sequence of three nucleotides called the _____________ that binds to the ________ of mRNA. ...
Proteins
... • Peptide: A short polymer of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; they are classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. • Dipeptide: A molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. • Tripeptide: A molecule containing three amino acids joined by peptide bonds. • Polypeptide: ...
... • Peptide: A short polymer of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; they are classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. • Dipeptide: A molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. • Tripeptide: A molecule containing three amino acids joined by peptide bonds. • Polypeptide: ...
Protein Structure Activity
... 5) Walk around the room and polymerize a polypeptide chain by carrying out dehydration synthesis with your amino acids. You’ll need scissors and tape to do this. NOTE: Save the water molecules you make in the process! ...
... 5) Walk around the room and polymerize a polypeptide chain by carrying out dehydration synthesis with your amino acids. You’ll need scissors and tape to do this. NOTE: Save the water molecules you make in the process! ...
Fermentation and Biosynthetic Pathways File
... joining glycerol and fatty acids. The glycerol portion of the fat is derived from dihydroxyacetone phosphate; fatty acids, are built up when two carbon fragments of acetyl CoA are successively added to each other. ...
... joining glycerol and fatty acids. The glycerol portion of the fat is derived from dihydroxyacetone phosphate; fatty acids, are built up when two carbon fragments of acetyl CoA are successively added to each other. ...
Amino Acids and Proteins
... protein. The structural formulas of di- and tripeptides are written. The secondary forms of protein structure include the alpha helix, pleated sheet and collagen. The interaction of side groups to form the cross-links of tertiary structure is discussed. The breakdown in the secondary and tertiary st ...
... protein. The structural formulas of di- and tripeptides are written. The secondary forms of protein structure include the alpha helix, pleated sheet and collagen. The interaction of side groups to form the cross-links of tertiary structure is discussed. The breakdown in the secondary and tertiary st ...
Protein mteabolism
... melatonin by the pineal gland in brain is inhibited by light and stimulated by darkness. For this reason melatonin has been called "the hormone of darkness. - Melatonin is sleep-inducing molecule -So ingestion of food rich in tryptophan leads to sleepiness. It is powerful antioxidant It has importan ...
... melatonin by the pineal gland in brain is inhibited by light and stimulated by darkness. For this reason melatonin has been called "the hormone of darkness. - Melatonin is sleep-inducing molecule -So ingestion of food rich in tryptophan leads to sleepiness. It is powerful antioxidant It has importan ...









![Amino Acids as Protein Building Blocks [2]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001231379_1-1c71e58dd2b4a4d156753bc870eff68b-300x300.png)












