Protein Structure
... state depends strongly on its local environment. This feature is often exploited and histidine is used as a molecular switch. ...
... state depends strongly on its local environment. This feature is often exploited and histidine is used as a molecular switch. ...
Translation (Protein Synthesis)
... * Remember to start translating at the first start codon and stop at the stop codon! ...
... * Remember to start translating at the first start codon and stop at the stop codon! ...
How Do Amino Acids React to Water and Oil?
... When amino acids are joined together in proteins, only their side chains (also called radicals or residues) are left free to interact with each other and molecules of their surrounding medium (water or lipids). These side chains, therefore, have a strong influence on how the protein behaves in water ...
... When amino acids are joined together in proteins, only their side chains (also called radicals or residues) are left free to interact with each other and molecules of their surrounding medium (water or lipids). These side chains, therefore, have a strong influence on how the protein behaves in water ...
essential amino acids
... Specific Cleavage of Peptides A number of enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds at specific points in an amino acid sequence. These enzymes are called proteases, peptidases or proteolytic enzymes. Trypsin is an example. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of polypeptides at the acyl group of arg ...
... Specific Cleavage of Peptides A number of enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds at specific points in an amino acid sequence. These enzymes are called proteases, peptidases or proteolytic enzymes. Trypsin is an example. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of polypeptides at the acyl group of arg ...
Nerve activates contraction
... between side chains (R-groups) of amino acids: • nonpolar side chains end up in clusters at the core of a protein – caused by the action of water molecules which exclude nonpolar substances • “hydrophobic interaction” ...
... between side chains (R-groups) of amino acids: • nonpolar side chains end up in clusters at the core of a protein – caused by the action of water molecules which exclude nonpolar substances • “hydrophobic interaction” ...
Translation
... mRNA is transported "om the nucleus cytoplasm where it attached with the ribosomes which are the site of protein synthesis. ...
... mRNA is transported "om the nucleus cytoplasm where it attached with the ribosomes which are the site of protein synthesis. ...
2016 Energetics Protein Enzyme WS
... (R) groups, it would most readily bind with a substrate region which is a. small, hydrophobic and positively charged b. small, hydrophilic and positively charged c. small, hydrophobic and negatively charged d. small, hydrophilic and negatively charged e. large, hydrophobic an positively charged The ...
... (R) groups, it would most readily bind with a substrate region which is a. small, hydrophobic and positively charged b. small, hydrophilic and positively charged c. small, hydrophobic and negatively charged d. small, hydrophilic and negatively charged e. large, hydrophobic an positively charged The ...
Libraries of Specific Assays Covering Whole
... different SRM transitions, true internal standardization can be achieved. The SRM method has been widely used on nonpeptide analytes such as drugs and metabolites for many years, and is used increasingly in clinical laboratories for the measurement of immunosuppressants, vitamin D, steroid hormones, ...
... different SRM transitions, true internal standardization can be achieved. The SRM method has been widely used on nonpeptide analytes such as drugs and metabolites for many years, and is used increasingly in clinical laboratories for the measurement of immunosuppressants, vitamin D, steroid hormones, ...
Basic organic chemistry of important macromolecules (Lecture 11-12)
... Energy from sunlight is converted into the C-C covalent bond energy. This energy is released in living organisms in such a way that not enough heat is generated at once to incinerate the organisms. One mole of glucose yields 673 Kcal of energy. (A calorie is the amount of heat needed to raise one gr ...
... Energy from sunlight is converted into the C-C covalent bond energy. This energy is released in living organisms in such a way that not enough heat is generated at once to incinerate the organisms. One mole of glucose yields 673 Kcal of energy. (A calorie is the amount of heat needed to raise one gr ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... with a number of chemicals, its structure can become disordered and the coiled peptide chains can unfold to give a more random conformation. Such changes in shape and the accompanying loss of biological activity are termed denaturation of the protein. Denaturation generally cannot be reversed (you c ...
... with a number of chemicals, its structure can become disordered and the coiled peptide chains can unfold to give a more random conformation. Such changes in shape and the accompanying loss of biological activity are termed denaturation of the protein. Denaturation generally cannot be reversed (you c ...
GLUCOGENIC & KETOGENIC AMINO ACIDS
... The non-essential amino acids, Amino acid remodeling, and Conversion of non-amino acid carbon skeletons into amino acids and other derivatives that contain ...
... The non-essential amino acids, Amino acid remodeling, and Conversion of non-amino acid carbon skeletons into amino acids and other derivatives that contain ...
B2.10a - Science @ St John`s
... You do not need to remember the details on this sheet for your exam but you could be asked to apply your knowledge to unfamiliar situations. The table shows how ribosomes decode the triplets of bases (codons) on an mRNA strand to make proteins. Each triplet is the code for one particular amino acid. ...
... You do not need to remember the details on this sheet for your exam but you could be asked to apply your knowledge to unfamiliar situations. The table shows how ribosomes decode the triplets of bases (codons) on an mRNA strand to make proteins. Each triplet is the code for one particular amino acid. ...
Chapter 19_CHEM 131
... • have molecular weights of ~6000 – several million u. • are too large to pass through cell membranes. • are contained inside the normal cells where they were formed. • can leak out if cell is damaged by disease or trauma. • Protein in urine can indicate damaged kidneys. • Heart enzymes in blood can ...
... • have molecular weights of ~6000 – several million u. • are too large to pass through cell membranes. • are contained inside the normal cells where they were formed. • can leak out if cell is damaged by disease or trauma. • Protein in urine can indicate damaged kidneys. • Heart enzymes in blood can ...
Titration curve of amino acids
... buffering capacity. Considering applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to the titration of glycine with acid and base, glycine has two Ionizable groups: a carboxyl group and an amino group, with pKa values of 2.34 and 9.6 respectively. In water at pH 6, glycine exists as a dipolar ion, or zwitt ...
... buffering capacity. Considering applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to the titration of glycine with acid and base, glycine has two Ionizable groups: a carboxyl group and an amino group, with pKa values of 2.34 and 9.6 respectively. In water at pH 6, glycine exists as a dipolar ion, or zwitt ...
Thermodynamics of Protein Folding
... Thermodynamic Principles of Protein Folding • Very difficult to determine how all factors blend together to give overall DGfolding – Use of averages contributions, but – Each protein is unique – Large stabilization factors, large destabilization factors, but small difference between them – Use RNas ...
... Thermodynamic Principles of Protein Folding • Very difficult to determine how all factors blend together to give overall DGfolding – Use of averages contributions, but – Each protein is unique – Large stabilization factors, large destabilization factors, but small difference between them – Use RNas ...
Protein
... Protein is made of chains of substances called amino acids: a type of organic acid. – Organic acids are molecules that contain a carboxyl group (COOH). – They also contain an amine group: two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of nitrogen (-NH2). ...
... Protein is made of chains of substances called amino acids: a type of organic acid. – Organic acids are molecules that contain a carboxyl group (COOH). – They also contain an amine group: two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of nitrogen (-NH2). ...
104371_Macromolecule_Basics
... bonds (9 calories per gram) Fats and oils differ because of the presence or lack of double bonds ...
... bonds (9 calories per gram) Fats and oils differ because of the presence or lack of double bonds ...
Lecture 10 - Protein Turnover and Amino Acid
... The arginine is hydrolyzed to produce the urea and to reform the ornithine. The ornithine reenters the mitochondrial matrix. ...
... The arginine is hydrolyzed to produce the urea and to reform the ornithine. The ornithine reenters the mitochondrial matrix. ...
biomolecules
... covalently bonded to a carbon backbone; they convey distinct properties, such as solubility and chemical reactivity, to the complete molecule. b. The common functional groups in biological molecules are: hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, and sulfhydryl c. see figure 3.5, page 3 ...
... covalently bonded to a carbon backbone; they convey distinct properties, such as solubility and chemical reactivity, to the complete molecule. b. The common functional groups in biological molecules are: hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, and sulfhydryl c. see figure 3.5, page 3 ...
Life`s First Scalding Steps
... The most detailed step-by-step blueprint for how Earth's oldest raw materials could have given rise to the stuff of life came out of the imagination of Günter Wächtershäuser, an organic chemist at the University of Regensberg in Germany. Ten years ago, Wächtershäuser conceived of an assembly-line pr ...
... The most detailed step-by-step blueprint for how Earth's oldest raw materials could have given rise to the stuff of life came out of the imagination of Günter Wächtershäuser, an organic chemist at the University of Regensberg in Germany. Ten years ago, Wächtershäuser conceived of an assembly-line pr ...
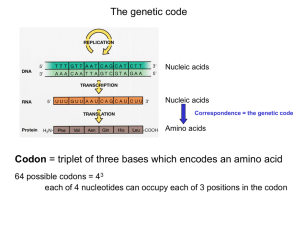
AUG
... - for STOP - UAA, UAG, UGA 61 codons encode 20 amino acids - most amino acids are specified by more than one codon - degeneracy of the genetic code ...
... - for STOP - UAA, UAG, UGA 61 codons encode 20 amino acids - most amino acids are specified by more than one codon - degeneracy of the genetic code ...