Module 12 Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Lecture 32 Amino
... 12.8.5 Synthesis of Peptides In peptide synthesis, one amino acid is protected at its amino end with group Y and the second is protected at its carboxyl end with a group Z. The condensation of these two protected amino acids using DCC generates a peptide bond. As per the requirement, one of the prot ...
... 12.8.5 Synthesis of Peptides In peptide synthesis, one amino acid is protected at its amino end with group Y and the second is protected at its carboxyl end with a group Z. The condensation of these two protected amino acids using DCC generates a peptide bond. As per the requirement, one of the prot ...
3 | Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins
... Ionization of Amino Acids • At acidic pH, the carboxyl group is protonated and the amino acid is in the cationic form. • At neutral pH, the carboxyl group is deprotonated but the amino group is protonated. The net charge is zero; such ions are called Zwitterions. • At alkaline pH, the amino gr ...
... Ionization of Amino Acids • At acidic pH, the carboxyl group is protonated and the amino acid is in the cationic form. • At neutral pH, the carboxyl group is deprotonated but the amino group is protonated. The net charge is zero; such ions are called Zwitterions. • At alkaline pH, the amino gr ...
3. What are macromolecules? LARGE ORGANIC
... 17. What subunits make up proteins? AMINO ACIDS 18. Proteins also act as ENZYMES in cells to control reactions. 19. Name the 2 functional groups in amino acids. carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group ...
... 17. What subunits make up proteins? AMINO ACIDS 18. Proteins also act as ENZYMES in cells to control reactions. 19. Name the 2 functional groups in amino acids. carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group ...
bottom-up-methodology
... # NOTE: GTP and ATP require each other. In order to overcome this impasse, just make sure that you have NDP kinases and can rephosphorylate ADP. Then, you can produce GTP from ATP and then use it to make ATP de novo. Start with GTP. # NOTE: Be sure to remove ATP as a prop nutrient/secretion! You are ...
... # NOTE: GTP and ATP require each other. In order to overcome this impasse, just make sure that you have NDP kinases and can rephosphorylate ADP. Then, you can produce GTP from ATP and then use it to make ATP de novo. Start with GTP. # NOTE: Be sure to remove ATP as a prop nutrient/secretion! You are ...
Activity 4.1/5.1 How can you identify organic macromolecules?
... 1. Twenty amino acids are commonly utilized in the synthesis of proteins. These amino acids differ in the chemical properties of their side chains (also called R groups). What properties does each of the following R groups have? (Note: A side chain may display more than one of these properties.) ...
... 1. Twenty amino acids are commonly utilized in the synthesis of proteins. These amino acids differ in the chemical properties of their side chains (also called R groups). What properties does each of the following R groups have? (Note: A side chain may display more than one of these properties.) ...
Chapter 21 Biosynthesis of amino acids, nucleotides and related
... turnover are often salvaged (reused). • Only certain bacteria are able to fix N2 into ammonia (NH3 or NH4+). ...
... turnover are often salvaged (reused). • Only certain bacteria are able to fix N2 into ammonia (NH3 or NH4+). ...
17 - Wiley
... 17.43 Hydrophilic side chains are characterized by the presence of N or O atoms that generate polar bonds and hydrogen-bonding capability, or an S–H bond that is polar. Among the structures shown in Problem 17.41, Tyr (O–H bond) and Glu (CO2H group) are hydrophilic, whereas Phe and Met are hydrophob ...
... 17.43 Hydrophilic side chains are characterized by the presence of N or O atoms that generate polar bonds and hydrogen-bonding capability, or an S–H bond that is polar. Among the structures shown in Problem 17.41, Tyr (O–H bond) and Glu (CO2H group) are hydrophilic, whereas Phe and Met are hydrophob ...
nucleic acid - 4J Blog Server
... You Must Know • The cellular functions of lipids. • How the sequence and subcomponents of lipids determine their properties. • The basic structure of a nucleic acid. • How changes in organic molecules would affect their function. ...
... You Must Know • The cellular functions of lipids. • How the sequence and subcomponents of lipids determine their properties. • The basic structure of a nucleic acid. • How changes in organic molecules would affect their function. ...
1 - Rosshall Academy
... State that proteins contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and NITROGEN. ...
... State that proteins contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and NITROGEN. ...
Horse pancreatic ribonuclease Scheffer, Albert Jan
... iiydrolysis after reduction and aminoethvlation). Sóme secondary cleavages were perforned with thermolysin, chyrnotryptil: and cyanogen bromide. Peptides were isolatecl and pu: rified by ge1 filtration, chrornatography on various ion exchangers, and column electrophoresis. The latter methocl proved ...
... iiydrolysis after reduction and aminoethvlation). Sóme secondary cleavages were perforned with thermolysin, chyrnotryptil: and cyanogen bromide. Peptides were isolatecl and pu: rified by ge1 filtration, chrornatography on various ion exchangers, and column electrophoresis. The latter methocl proved ...
DNA: Transcription & Translation
... • mRNA: transports information from DNA from the nucleus to the cell’s cytoplasm • rRNA: (makes up ribosomes): clamps on to mRNA and reads its information to assemble amino acids in the correct order • tRNA: transports amino acids to the ribosomes to be assembled into proteins ...
... • mRNA: transports information from DNA from the nucleus to the cell’s cytoplasm • rRNA: (makes up ribosomes): clamps on to mRNA and reads its information to assemble amino acids in the correct order • tRNA: transports amino acids to the ribosomes to be assembled into proteins ...
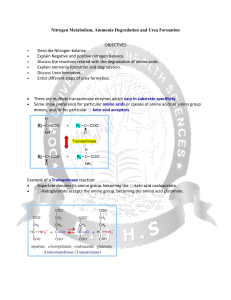
Nitrogen Metabolism, Ammonia Degradation and Urea Formation
... Hereditary deficiency of any of the Urea Cycle enzymes leads to hyperammonemia elevated [ammonia] in blood. Total lack of any Urea Cycle enzyme is lethal. Elevated ammonia is toxic, especially to the brain. ...
... Hereditary deficiency of any of the Urea Cycle enzymes leads to hyperammonemia elevated [ammonia] in blood. Total lack of any Urea Cycle enzyme is lethal. Elevated ammonia is toxic, especially to the brain. ...
Amino Acid composition of vegetables and fruits from
... analyzed for their amino acid composition. In all, thirty-three samples were pulverized, lyophilised and then were subjected to acid and alkaline hydrolyses. On the amino acid compositional basis, these foodstuffs would provide a balanced source of dietary protein in general, if supplemented by synt ...
... analyzed for their amino acid composition. In all, thirty-three samples were pulverized, lyophilised and then were subjected to acid and alkaline hydrolyses. On the amino acid compositional basis, these foodstuffs would provide a balanced source of dietary protein in general, if supplemented by synt ...
Amino acids
... Amino acids are classified as either hydrophobic or hydrophilic. Amino acid monomers are linked togetherin a dehydration reaction, joining carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of the next amino acid, ancreating a peptide bond. Additional amino acids can be added by the same process to ...
... Amino acids are classified as either hydrophobic or hydrophilic. Amino acid monomers are linked togetherin a dehydration reaction, joining carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of the next amino acid, ancreating a peptide bond. Additional amino acids can be added by the same process to ...
ANSWERS - Unit 1 Review File
... polypeptide is many aa’s (polymer of protein); a protein is a macromolecule also made of many aa’s (usually many polypeptides joined together). Draw the general formula for an amino acid. H2N-HCO-COOH; or amine-C-carboxylic acid A peptide bond is always formed between the amine group of one aa and t ...
... polypeptide is many aa’s (polymer of protein); a protein is a macromolecule also made of many aa’s (usually many polypeptides joined together). Draw the general formula for an amino acid. H2N-HCO-COOH; or amine-C-carboxylic acid A peptide bond is always formed between the amine group of one aa and t ...
3.2 Carbohydrates, lipids and proteins – summary of previous mark
... G. energy stored as starch in plants; H. complex carbohydrates / polysaccharides / starch / glycogen are also long term energy stores; I. complex carbohydrates / polysaccharides / starch / glycogen and lipids are insoluble / will not diffuse out of cells; J. complex carbohydrates / polysaccharides / ...
... G. energy stored as starch in plants; H. complex carbohydrates / polysaccharides / starch / glycogen are also long term energy stores; I. complex carbohydrates / polysaccharides / starch / glycogen and lipids are insoluble / will not diffuse out of cells; J. complex carbohydrates / polysaccharides / ...
Making probes/primers
... Isolated from many copies of plasmids following digestion and gel isolation ...
... Isolated from many copies of plasmids following digestion and gel isolation ...
Lecture: 28 TRANSAMINATION, DEAMINATION AND
... TRANSAMINATION, DEAMINATION AND DECARBOXYLATION Protein metabolism is a key physiological process in all forms of life. Proteins are converted to amino acids and then catabolised. The complete hydrolysis of a polypeptide requires mixture of peptidases because individual peptidases do not cleav ...
... TRANSAMINATION, DEAMINATION AND DECARBOXYLATION Protein metabolism is a key physiological process in all forms of life. Proteins are converted to amino acids and then catabolised. The complete hydrolysis of a polypeptide requires mixture of peptidases because individual peptidases do not cleav ...
Slide 1
... Nucleotides & Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are made up from nitrogen-containing chemical monomers, called nucleotides. The sequence of nucleotides in nucleic acids codes for the genetic information of proteins. The nucleic acid DNA is the blueprint molecule of all forms of life on planet Earth ...
... Nucleotides & Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are made up from nitrogen-containing chemical monomers, called nucleotides. The sequence of nucleotides in nucleic acids codes for the genetic information of proteins. The nucleic acid DNA is the blueprint molecule of all forms of life on planet Earth ...
dopamineSummary
... Dopamine Biosynthesis Model Guide Neurotransmitters Module: The Beery Twins’ Story© A Project-Based Learning Activity ...
... Dopamine Biosynthesis Model Guide Neurotransmitters Module: The Beery Twins’ Story© A Project-Based Learning Activity ...
Catalysis - University of California, Davis
... Proteins with a net charge generally tend to repel each other and allow their charged groups to interact with water. Proteins are least soluble at their pI, and proteinaceous structures (e.g., muscle fibers) tend to compact. ...
... Proteins with a net charge generally tend to repel each other and allow their charged groups to interact with water. Proteins are least soluble at their pI, and proteinaceous structures (e.g., muscle fibers) tend to compact. ...