Hydrolyzed Soy Protein
... Soy Advantage . When tested against other hydrolyzates, Vege Tech Hydrolyzed Soy Protein demonstrates superb Hair Repair by means of Cortex Penetration and FilmForming. With a Dalton range of approx. 1,000 to 10,000, it imparts increased Moisture Retention, Hair Tensile Strength & Thickness, Flexibi ...
... Soy Advantage . When tested against other hydrolyzates, Vege Tech Hydrolyzed Soy Protein demonstrates superb Hair Repair by means of Cortex Penetration and FilmForming. With a Dalton range of approx. 1,000 to 10,000, it imparts increased Moisture Retention, Hair Tensile Strength & Thickness, Flexibi ...
Biochemistry of the liver - Univerzita Karlova v Praze
... • liver controls blood FFA concentration • energy is produced mainly by -oxidation • synthesis of ketone bodies • synthesis of TAG (from FFA, glc, AA) • synthesis of cholesterol • synthesis of bile acids ...
... • liver controls blood FFA concentration • energy is produced mainly by -oxidation • synthesis of ketone bodies • synthesis of TAG (from FFA, glc, AA) • synthesis of cholesterol • synthesis of bile acids ...
Amino Acid Metabolism
... • Therefore need a small mobile pool of free AA in cells and blood – Pool size is regulated (no more than 50% changes) – Pool size is small relative to flux ...
... • Therefore need a small mobile pool of free AA in cells and blood – Pool size is regulated (no more than 50% changes) – Pool size is small relative to flux ...
Translation Definition - Mr. Barrow's Science Center
... (polypeptide) site tRNA in the E (exit site) leaves the ribsome mRNA shifts position New tRNA with anticodon enters the A site ...
... (polypeptide) site tRNA in the E (exit site) leaves the ribsome mRNA shifts position New tRNA with anticodon enters the A site ...
1 Amino Acid Metabolism
... • Therefore need a small mobile pool of free AA in cells and blood – Pool size is regulated (no more than 50% changes) – Pool size is small relative to flux ...
... • Therefore need a small mobile pool of free AA in cells and blood – Pool size is regulated (no more than 50% changes) – Pool size is small relative to flux ...
Biochemistry of neurotransmitters
... neurons into the haemolymph and which may therefore exert its effects on distant peripheral targets. Neurotransmitter: a messenger released from a neuron at an anatomically specialised junction, which diffuses across a narrow cleft to affect one or sometimes two postsynaptic neurons, a muscle cell, ...
... neurons into the haemolymph and which may therefore exert its effects on distant peripheral targets. Neurotransmitter: a messenger released from a neuron at an anatomically specialised junction, which diffuses across a narrow cleft to affect one or sometimes two postsynaptic neurons, a muscle cell, ...
1) Which residues prefer helix, strand, turn:
... Trp: Very hydrophobic; biggest amino acid and therefore hard to remove or insert by mutagenesis and by evolution, and thus the most conserved of all residues. Met: Start codon, and thus often positively charged on its backbone N because of which it is found at the protein surface than its hydrophobi ...
... Trp: Very hydrophobic; biggest amino acid and therefore hard to remove or insert by mutagenesis and by evolution, and thus the most conserved of all residues. Met: Start codon, and thus often positively charged on its backbone N because of which it is found at the protein surface than its hydrophobi ...
Amino Acids 40 Profile
... Amino acids, known as the "building blocks" of proteins, are found in every tissue of the body. They play a major role in nearly every chemical process that affects both physical and mental function including the formation of ligaments, tendons, bones, and antibodies, as well as regulation of enzyme ...
... Amino acids, known as the "building blocks" of proteins, are found in every tissue of the body. They play a major role in nearly every chemical process that affects both physical and mental function including the formation of ligaments, tendons, bones, and antibodies, as well as regulation of enzyme ...
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Basis of Medical
... blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level following an overnight fast. After an overnight fast, a patient went to the doctor’s office to have a fasting blood test. Most of the parameters (HDL, VLDL, heme iron, etc) came back normal, but you both noticed the BUN level was slightly elevated. Your partner says t ...
... blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level following an overnight fast. After an overnight fast, a patient went to the doctor’s office to have a fasting blood test. Most of the parameters (HDL, VLDL, heme iron, etc) came back normal, but you both noticed the BUN level was slightly elevated. Your partner says t ...
Chapter 18
... a. Vitamin A—necessary for synthesis of visual pigments, mucoproteins and mucopolysaccharides as well as for normal development of bones and teeth and the maintenance of epithelial cells. b. Vitamin D—promotes the absorption of calcium and phosphorus as well as promotes the development of teeth and ...
... a. Vitamin A—necessary for synthesis of visual pigments, mucoproteins and mucopolysaccharides as well as for normal development of bones and teeth and the maintenance of epithelial cells. b. Vitamin D—promotes the absorption of calcium and phosphorus as well as promotes the development of teeth and ...
Translation: Changing languages
... "The main idea was that it was very difficult to consider how DNA or RNA, in any conceivable form, could provide a direct template for the side-chains of the twenty standard amino acids. What any structure was likely to have was a specific pattern of atomic groups that could form hydrogen bonds. I t ...
... "The main idea was that it was very difficult to consider how DNA or RNA, in any conceivable form, could provide a direct template for the side-chains of the twenty standard amino acids. What any structure was likely to have was a specific pattern of atomic groups that could form hydrogen bonds. I t ...
Ribosomes and The Golgi Apparatus
... over the correct amino acid. It knows which amino acid is correct because it has an anti-codon on its base that is complimentary to the one on the mRNA Tyr A base U base G base C base ...
... over the correct amino acid. It knows which amino acid is correct because it has an anti-codon on its base that is complimentary to the one on the mRNA Tyr A base U base G base C base ...
3. What are macromolecules?
... 26. Lipids are nonpolar. What does this mean? ____________________________________________________________________ 27. What WILL lipids (oils and fats) dissolve in? (Question for thought) _________________________________________________ 28. _______________________ makes up cell membranes. 29. Name ...
... 26. Lipids are nonpolar. What does this mean? ____________________________________________________________________ 27. What WILL lipids (oils and fats) dissolve in? (Question for thought) _________________________________________________ 28. _______________________ makes up cell membranes. 29. Name ...
Lesson
... ELONGATION: THE STEPS 1. The start codon (methionine, AUG) is the first codon recognized by the ribosome. 2. Aminoacyl-tRNA carrying AUG enters the P site. 3. The next aminoacyl-tRNA enters the A site. 4. A peptide bond forms between the two amino acids. 5. The ribosome translocates over one codon ...
... ELONGATION: THE STEPS 1. The start codon (methionine, AUG) is the first codon recognized by the ribosome. 2. Aminoacyl-tRNA carrying AUG enters the P site. 3. The next aminoacyl-tRNA enters the A site. 4. A peptide bond forms between the two amino acids. 5. The ribosome translocates over one codon ...
Constructing a Model of Protein Synthesis
... determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins. In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequence into the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the mRNA carries this code out to the ribosomes ...
... determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins. In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequence into the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the mRNA carries this code out to the ribosomes ...
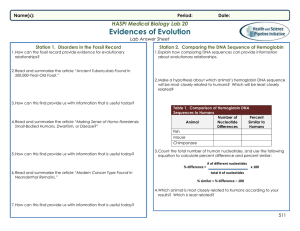
Evidence for Evolution Student Answer Sheet
... 6. Read and summarize the article “Modern Cancer Type Found In Neanderthal Remains.” ...
... 6. Read and summarize the article “Modern Cancer Type Found In Neanderthal Remains.” ...
Review - Columbus Labs
... 1. Ribosomes. Eukaryotic ribosomes are larger. (Slide 29, lecture 4) 2. Initiator tRNA. In eukaryotes, the initiating amino acid is methionine rather than N-formylmethionine. However, as in prokaryotes, a special tRNA participates in initiation. 3. Initiation. The initiating codon in eukaryotes is a ...
... 1. Ribosomes. Eukaryotic ribosomes are larger. (Slide 29, lecture 4) 2. Initiator tRNA. In eukaryotes, the initiating amino acid is methionine rather than N-formylmethionine. However, as in prokaryotes, a special tRNA participates in initiation. 3. Initiation. The initiating codon in eukaryotes is a ...
Proteins
... inherit from their parents • Each chromosome contains one long DNA molecule containing from several hundred to more than a thousand genes. • DNA programs all the cells activities by producing proteins as needed • DNA directs the synthesis of mRNA which then directs the production of amino acids ...
... inherit from their parents • Each chromosome contains one long DNA molecule containing from several hundred to more than a thousand genes. • DNA programs all the cells activities by producing proteins as needed • DNA directs the synthesis of mRNA which then directs the production of amino acids ...