Translocation of Structural P Proteins in the Phloem
... Figure 5. RT-PCR Gel Blot Analyses of Cucurbita PP1 and PP2 mRNAs from Intergeneric Grafts of Cucumis sativus Scions on Cucurbita maxima or Cucurbita ficifolia Stocks. RT-PCR products generated from total RNA with 59 and 39 primers that flank the protein coding sequences of genes encoding PP1 and PP ...
... Figure 5. RT-PCR Gel Blot Analyses of Cucurbita PP1 and PP2 mRNAs from Intergeneric Grafts of Cucumis sativus Scions on Cucurbita maxima or Cucurbita ficifolia Stocks. RT-PCR products generated from total RNA with 59 and 39 primers that flank the protein coding sequences of genes encoding PP1 and PP ...
167 renal and small intestinal sodium
... Magagnin et al. 1993; Markovich et al. 1993). At present, more detailed information about the N-glycosylation sites likely to be used is only available for the type II Na+/Pi symporter NaPi-2 from the rat. Site-directed mutagenesis has shown that amino acid residues Asn-298 and Asn-328 (located with ...
... Magagnin et al. 1993; Markovich et al. 1993). At present, more detailed information about the N-glycosylation sites likely to be used is only available for the type II Na+/Pi symporter NaPi-2 from the rat. Site-directed mutagenesis has shown that amino acid residues Asn-298 and Asn-328 (located with ...
The N Terminus of Bacterial Elongation Factor Tu
... reported to respond to structures characteristic for true fungi, such as the wall components chitin, chitosan, and glucan, the membrane component ergosterol, and the N-linked glycosylation characteristic of fungal glycoproteins. With regard to recognition of bacteria, plants have evolved perception ...
... reported to respond to structures characteristic for true fungi, such as the wall components chitin, chitosan, and glucan, the membrane component ergosterol, and the N-linked glycosylation characteristic of fungal glycoproteins. With regard to recognition of bacteria, plants have evolved perception ...
Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for protein
... 0.66 g protein/kg body weight per day based on a meta-analysis of nitrogen balance data as the average requirement (AR). In healthy adults, the protein requirement per kg body weight is considered to be the same for both sexes and for all body weights. Considering the 97.5th percentile of the popula ...
... 0.66 g protein/kg body weight per day based on a meta-analysis of nitrogen balance data as the average requirement (AR). In healthy adults, the protein requirement per kg body weight is considered to be the same for both sexes and for all body weights. Considering the 97.5th percentile of the popula ...
Preview Sample 2
... Diff: 4 Page Ref: 33 59) Which of the following organelles is specialized for lipid and steroid synthesis? A) rough endoplasmic reticulum B) smooth endoplasmic reticulum C) mitochondria D) lysosomes E) peroxisomes Answer: B Diff: 3 Page Ref: 33 60) Which of the following is an INCORRECT description ...
... Diff: 4 Page Ref: 33 59) Which of the following organelles is specialized for lipid and steroid synthesis? A) rough endoplasmic reticulum B) smooth endoplasmic reticulum C) mitochondria D) lysosomes E) peroxisomes Answer: B Diff: 3 Page Ref: 33 60) Which of the following is an INCORRECT description ...
Levy APS - Indiana University Bloomington
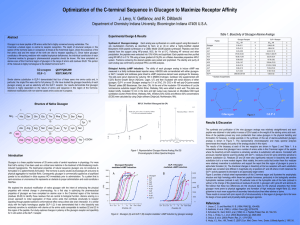
... immediately obvious that glucagon has a number of amino acids in this C-terminal region of the peptide where the bioactivity at both receptors is extremely sensitive to substitution with alanine. Consistent with previously reported alanine scanning studies with GLP-1, residues 22 and 23 were extreme ...
... immediately obvious that glucagon has a number of amino acids in this C-terminal region of the peptide where the bioactivity at both receptors is extremely sensitive to substitution with alanine. Consistent with previously reported alanine scanning studies with GLP-1, residues 22 and 23 were extreme ...
Lens Major Intrinsic Protein (MIP)
... turbidity assay. The absorbance time course at 350 nm was monitored when PC-Mbs vesicles (-) and PC vesicles (A)were mixed with 25 pM PS vesicles. Vesicles were incubated in the same solution described for Figure 1. After 3 min of preincubation, 25 r M PS vesicles was added to the cuvette (arrow). e ...
... turbidity assay. The absorbance time course at 350 nm was monitored when PC-Mbs vesicles (-) and PC vesicles (A)were mixed with 25 pM PS vesicles. Vesicles were incubated in the same solution described for Figure 1. After 3 min of preincubation, 25 r M PS vesicles was added to the cuvette (arrow). e ...
A Patch of Surface-Exposed Residues Mediates
... activation segment is composed of two recognizable regions: the T-loop, in which regulatory phosphorylation often occurs, and the Pþ1 loop, which forms the primary binding site for the substrate peptide. Regulatory phosphorylation causes the activation segment to flip out of the active site and assu ...
... activation segment is composed of two recognizable regions: the T-loop, in which regulatory phosphorylation often occurs, and the Pþ1 loop, which forms the primary binding site for the substrate peptide. Regulatory phosphorylation causes the activation segment to flip out of the active site and assu ...
p62/SQSTM1 Binds Directly to Atg8/LC3 to Facilitate Degradation of
... Waters) and subjected to data-dependent tandem mass specVOLUME 282 • NUMBER 33 • AUGUST 17, 2007 ...
... Waters) and subjected to data-dependent tandem mass specVOLUME 282 • NUMBER 33 • AUGUST 17, 2007 ...
Single Processing Center Models for Human Dicer and Bacterial
... processing of both strands in the central region of the substrate has taken place. The requirement for the primary processing event explains why no labeled products diagnostic of the cleavage at complementary sites on opposite RNA strands could be identified (Supplemental Figure S3 available on Cell ...
... processing of both strands in the central region of the substrate has taken place. The requirement for the primary processing event explains why no labeled products diagnostic of the cleavage at complementary sites on opposite RNA strands could be identified (Supplemental Figure S3 available on Cell ...
Answers - U of L Class Index
... a. A C10 fatty acid requires the formation of 4 malonyl ACP, which uses 4 HCO3 . b. 4 ATP are required to produce 4 malonyl CoA. c. 5 acetyl CoA are needed to make 1 acetyl ACP and 4 malonyl ACP. d. A C10 fatty acid requires 4 malonyl ACP and 1 acetyl ACP. e. A C10 fatty acid chain requires 4 cycles ...
... a. A C10 fatty acid requires the formation of 4 malonyl ACP, which uses 4 HCO3 . b. 4 ATP are required to produce 4 malonyl CoA. c. 5 acetyl CoA are needed to make 1 acetyl ACP and 4 malonyl ACP. d. A C10 fatty acid requires 4 malonyl ACP and 1 acetyl ACP. e. A C10 fatty acid chain requires 4 cycles ...
Intermediary Metabolism and Life-History Trade
... and SW morphs differ genetically in whole-organism flux (rate) through individual pathways of amino acid metabolism and in allocation of end products of metabolism to individual body compartments (amount of metabolic products accumulated in ovaries or soma [body minus ovaries] during the assay perio ...
... and SW morphs differ genetically in whole-organism flux (rate) through individual pathways of amino acid metabolism and in allocation of end products of metabolism to individual body compartments (amount of metabolic products accumulated in ovaries or soma [body minus ovaries] during the assay perio ...
by 3AB and 3ABC trans Complemented in Formation, and the
... nomenclature of the hepatitis A virus [HAV] polyprotein, see Fig. 1A). For optimal use of the low coding capacity of the RNA genome, it seems that not only mature but also intermediate products of proteolytic processing play important roles during the viral life cycle. In the past few years, it also ...
... nomenclature of the hepatitis A virus [HAV] polyprotein, see Fig. 1A). For optimal use of the low coding capacity of the RNA genome, it seems that not only mature but also intermediate products of proteolytic processing play important roles during the viral life cycle. In the past few years, it also ...
High-Molecular-Weight Forms of Tyrosinase and the
... TRP-2 migrated exclusively in a hig h - molecul ar-we ig ht form, as expected from its behavior on mol ecul ar sieve HPLC (Fig 1b, bottom). No TRP-2 was detected in association with th e peak of "free" tyrosinase from HPLC (Fig lb, lOp), Triton X-1 00 was used only in the initial phase of the purifi ...
... TRP-2 migrated exclusively in a hig h - molecul ar-we ig ht form, as expected from its behavior on mol ecul ar sieve HPLC (Fig 1b, bottom). No TRP-2 was detected in association with th e peak of "free" tyrosinase from HPLC (Fig lb, lOp), Triton X-1 00 was used only in the initial phase of the purifi ...
The Case of Protein Kinase CK2
... amino acid sequence of the catalytic domains of protein kinases has proven to be a good indicator of other features held in common by the different members of the family. The diversity of essential functions mediated by kinases is shown by the conservation of approximately 50 distinct kinase familie ...
... amino acid sequence of the catalytic domains of protein kinases has proven to be a good indicator of other features held in common by the different members of the family. The diversity of essential functions mediated by kinases is shown by the conservation of approximately 50 distinct kinase familie ...
... investigated whether differences could be observed in the inclusion bodies formed by the respective mutant AHSV-9 NS2 proteins. Transmission electron microscope analysis of recombinant baculovirus-infected Spodoptera frugiperda insect cells indicated that a mutant NS2 protein in which the serine re ...
Molecular cloning, characterization and gene expression of an
... organisms from eubacteria to eukaryotes [9,20e26], they are essential, strongly expressed, and tightly regulated [27]. Catalase comprises four ferriphotophorphyrin groups per molecule, and its enzymatic activity in tissues varies greatly [28,29]. Each monomer harbors a single heme and nicotinamide a ...
... organisms from eubacteria to eukaryotes [9,20e26], they are essential, strongly expressed, and tightly regulated [27]. Catalase comprises four ferriphotophorphyrin groups per molecule, and its enzymatic activity in tissues varies greatly [28,29]. Each monomer harbors a single heme and nicotinamide a ...
aminoacids
... Aminoacids enter into different body cells from blood circulation In cells, aminoacids are then bonded together to from specific proteins (tissue /species specific) These proteins then perform various but important functions of the cell/body Aminoacids ...
... Aminoacids enter into different body cells from blood circulation In cells, aminoacids are then bonded together to from specific proteins (tissue /species specific) These proteins then perform various but important functions of the cell/body Aminoacids ...
Aromatic amino acid requirements of the lactating sow
... and presented to the portal blood supply in the free form (Munro, 1976). Absorption across biological membranes is thought to involve a com petitive Na-dependent active transport system common to the large neutral amino acids, which include Phe, Tyr, tryptophan, leucine, isoleucine, valine, histidi ...
... and presented to the portal blood supply in the free form (Munro, 1976). Absorption across biological membranes is thought to involve a com petitive Na-dependent active transport system common to the large neutral amino acids, which include Phe, Tyr, tryptophan, leucine, isoleucine, valine, histidi ...
The Role of Cyclin B in Meiosis I
... of the mitotic cell cycles (Masui and Clarke, 1979). However, in contrast to somatic ceils, most embryonic cells have abbreviated cell cycles consisting of rapid, alternating periods of DNA synthesis (interphase) and mitosis (M phase). The G1 and G2 periods are absent or very short in these "cleavag ...
... of the mitotic cell cycles (Masui and Clarke, 1979). However, in contrast to somatic ceils, most embryonic cells have abbreviated cell cycles consisting of rapid, alternating periods of DNA synthesis (interphase) and mitosis (M phase). The G1 and G2 periods are absent or very short in these "cleavag ...
Protein Profile Characterization of Donkey Milk
... g/100 g of total fatty acids, when compared with ruminant species milks, in which the contents of the above mentioned Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids are always lower. To increase the total fat content in donkey milk, clinical studies [17, 35] suggested to enrich donkey milk with medium-chain triglyceri ...
... g/100 g of total fatty acids, when compared with ruminant species milks, in which the contents of the above mentioned Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids are always lower. To increase the total fat content in donkey milk, clinical studies [17, 35] suggested to enrich donkey milk with medium-chain triglyceri ...
HEMAGGLUTINATION BY PURIFIED TYPE I ESCHERICHIA
... Pilated and nonpilated bacterial variants were used in these earlier HA studies, but this approach does not permit detailed analysis. Purified pili must be used to prove conclusively that mannose-sensitive HA is caused by pili and to investigate further the characteristics of such binding. An outlin ...
... Pilated and nonpilated bacterial variants were used in these earlier HA studies, but this approach does not permit detailed analysis. Purified pili must be used to prove conclusively that mannose-sensitive HA is caused by pili and to investigate further the characteristics of such binding. An outlin ...
Bacteria under stress by complement and coagulation
... et al., 1981; Ricklin et al., 2010). This activation process is down regulated on host cells but quickly amplified on bacterial cells. Thanks to the large variety of recognition mechanisms, almost all bacteria will be recognized by the complement system. Many studies have shown that the relative imp ...
... et al., 1981; Ricklin et al., 2010). This activation process is down regulated on host cells but quickly amplified on bacterial cells. Thanks to the large variety of recognition mechanisms, almost all bacteria will be recognized by the complement system. Many studies have shown that the relative imp ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.