Post-transcriptional regulation of auxin transport proteins: cellular
... is also localized to the inner surface of hypocotyl bundle sheath cells where it appears to function in the redirection of auxin back into the vascular cylinder. PIN3 is also found in epidermal cells, and the pin3 mutant shows shorter epidermal cells in light-grown hypocotyls, thought to be caused b ...
... is also localized to the inner surface of hypocotyl bundle sheath cells where it appears to function in the redirection of auxin back into the vascular cylinder. PIN3 is also found in epidermal cells, and the pin3 mutant shows shorter epidermal cells in light-grown hypocotyls, thought to be caused b ...
Detergents and Surfactants
... membrane-bound proteins. Some detergents can also be used to solubilize recombinant protein, while others find their usage in the stabilization, crystallization, or denaturation of proteins. Additional applications include the extraction of DNA and RNA, the solubilization of specimens for diagnostic ...
... membrane-bound proteins. Some detergents can also be used to solubilize recombinant protein, while others find their usage in the stabilization, crystallization, or denaturation of proteins. Additional applications include the extraction of DNA and RNA, the solubilization of specimens for diagnostic ...
Essentiality of Histidine in Ruminant and Other Animals Including
... amino acids essential for immature rats might also be essential for ruminants. Among those, methionine, lysine and threonine have come to actually be taken as essential for sheep and cattle in the course of experiments for examining supplemental effects of amino acids to rumen microbial protein thro ...
... amino acids essential for immature rats might also be essential for ruminants. Among those, methionine, lysine and threonine have come to actually be taken as essential for sheep and cattle in the course of experiments for examining supplemental effects of amino acids to rumen microbial protein thro ...
Intraflagellar transport and the generation of dynamic, structurally
... cilia from most cell types, including liver, pancreas, kidney, olfactory epithelia, oviduct, respiratory tissue, and in rod or cone photoreceptors [24–29]. A bipartite axoneme consisting of microtubule doublets followed by singlets therefore represents an evolutionarily conserved feature of motile a ...
... cilia from most cell types, including liver, pancreas, kidney, olfactory epithelia, oviduct, respiratory tissue, and in rod or cone photoreceptors [24–29]. A bipartite axoneme consisting of microtubule doublets followed by singlets therefore represents an evolutionarily conserved feature of motile a ...
Amino acid homeostasis and signalling in mammalian cells and
... Entry and exit through amino acid transporters The study of amino acid transporters in mammalian cells was pioneered by Halvor Christensen [50], who recognised that certain groups of amino acids compete with each other for uptake into cells. More detailed studies revealed many transport activities, ...
... Entry and exit through amino acid transporters The study of amino acid transporters in mammalian cells was pioneered by Halvor Christensen [50], who recognised that certain groups of amino acids compete with each other for uptake into cells. More detailed studies revealed many transport activities, ...
Protein composition and function of red and white skeletal - AJP-Cell
... fast isoforms of contractile proteins, whereas red muscle has greater abundance of contractile protein slow isoforms and higher oxidative enzyme content (16, 38, 51). The larger oxidative capacity in red muscle is due, at least in part, to a two- to threefold greater mitochondrial content compared w ...
... fast isoforms of contractile proteins, whereas red muscle has greater abundance of contractile protein slow isoforms and higher oxidative enzyme content (16, 38, 51). The larger oxidative capacity in red muscle is due, at least in part, to a two- to threefold greater mitochondrial content compared w ...
biosynthesis of fatty acids - Academic Research Collections
... and lipids. Nucleic acids are the result of combination of C, H, O, N and P. Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids, grouped under a category called macromolecules, form the basic components that make life possible. In addition to these molecules there are micromolecules like hormones, vi ...
... and lipids. Nucleic acids are the result of combination of C, H, O, N and P. Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids, grouped under a category called macromolecules, form the basic components that make life possible. In addition to these molecules there are micromolecules like hormones, vi ...
Kinetic analysis of retroviral proteases by HELGA EIZERT
... antagonist for the host cells’ innate defense system, by neutralization of cellular APOBEC3 protein functions. Bel-3 does not have a defined role in the viral life cycle. ...
... antagonist for the host cells’ innate defense system, by neutralization of cellular APOBEC3 protein functions. Bel-3 does not have a defined role in the viral life cycle. ...
unexpected consequences for sense codon reassignment
... with the proteins that constitute the host’s translational system (e.g. endogenous aaRSs, elongation factors and tRNA modifying enzymes). To date, the majority of work expanding the genetic code has focused on re-engineering existing orthogonal tRNA/aaRS pairs to activate additional noncanonical ami ...
... with the proteins that constitute the host’s translational system (e.g. endogenous aaRSs, elongation factors and tRNA modifying enzymes). To date, the majority of work expanding the genetic code has focused on re-engineering existing orthogonal tRNA/aaRS pairs to activate additional noncanonical ami ...
Novel Allergen Structures with Tandem Amino Acid Repeats
... the full sequence is deposited in the GenBank. This long sequence (4058 base pairs) is untranslatable as a whole unit. However, Bla g 1.01 clearly aligns with the translatable part of Bla g Bd90K C terminus, including the sequence following the stop codon, and with other translated parts in differen ...
... the full sequence is deposited in the GenBank. This long sequence (4058 base pairs) is untranslatable as a whole unit. However, Bla g 1.01 clearly aligns with the translatable part of Bla g Bd90K C terminus, including the sequence following the stop codon, and with other translated parts in differen ...
Evolution of Brachyury proteins: identification of a novel regulatory
... The Brachyury proteins thus provide a powerful paradigm to study how evolutionarily conserved genes come to fulfill different functions across the animal kingdom. The surprising diversity of the roles of Brachyury in metazoans, and the availability of full-length cDNAs for orthologues from all major ...
... The Brachyury proteins thus provide a powerful paradigm to study how evolutionarily conserved genes come to fulfill different functions across the animal kingdom. The surprising diversity of the roles of Brachyury in metazoans, and the availability of full-length cDNAs for orthologues from all major ...
Eucalyptus Arabidopsis grandis thaliana
... The ever-growing demand for wood and wood derived cellulose products coupled with the public concern about the clearance of natural flora or agricultural land to make way for the forest tree plantations has sparked a renewed interest in the genetic improvement of forest tree species. Conventional br ...
... The ever-growing demand for wood and wood derived cellulose products coupled with the public concern about the clearance of natural flora or agricultural land to make way for the forest tree plantations has sparked a renewed interest in the genetic improvement of forest tree species. Conventional br ...
r Functional perspectives on the evolution of argasid tick
... Fig. 2.11: Determination of the disu lphide content of the savignygrins Fig. 2.12: The effect of disulphide bonds on activity Fig. 2.13: Inhibition of platelet aggregation by savignygrin Fig. 2.14: The disaggregation effect of savignygrin on aggregated platelets Fig. 2.15: Targeting of aIlb~3 by sav ...
... Fig. 2.11: Determination of the disu lphide content of the savignygrins Fig. 2.12: The effect of disulphide bonds on activity Fig. 2.13: Inhibition of platelet aggregation by savignygrin Fig. 2.14: The disaggregation effect of savignygrin on aggregated platelets Fig. 2.15: Targeting of aIlb~3 by sav ...
Identification of a Cytoplasm to Vacuole Targeting Determinant in
... 1990). Substantially more information is available regarding the vacuolar localization of API. Genetic studies in our laboratory have isolated a number of mutants that are defective in transporting API to the vacuole (Harding et al., 1995). These cytoplasm to vacuole targeting (cvt) mutants are una ...
... 1990). Substantially more information is available regarding the vacuolar localization of API. Genetic studies in our laboratory have isolated a number of mutants that are defective in transporting API to the vacuole (Harding et al., 1995). These cytoplasm to vacuole targeting (cvt) mutants are una ...
The Ovine Lens Cytoskeleton - Lincoln University Research Archive
... Intermediate filament proteins are referred to as such on the basis of their average diameter (10 nm) is intermediate to that of microfilaments (characteristically 5-8 nm in diameter) and the microtubules (typically 20-25 nm in diameter; Strelkov et al., 2003; Pitz & Moll, 2002). Intermediate filame ...
... Intermediate filament proteins are referred to as such on the basis of their average diameter (10 nm) is intermediate to that of microfilaments (characteristically 5-8 nm in diameter) and the microtubules (typically 20-25 nm in diameter; Strelkov et al., 2003; Pitz & Moll, 2002). Intermediate filame ...
how cells read the genome: from dna to protein
... molecule in a chromosome is first copied into RNA (a process called transcription). It is these RNA copies of segments of the DNA that are used directly as templates to direct the synthesis of the protein (a process called translation). The flow of genetic information in cells is therefore from DNA ...
... molecule in a chromosome is first copied into RNA (a process called transcription). It is these RNA copies of segments of the DNA that are used directly as templates to direct the synthesis of the protein (a process called translation). The flow of genetic information in cells is therefore from DNA ...
The Role of Different Sugars, Amino Acids and Few Other
... sealed capillary tube glued on a glass slide, was covered with a cover slip, and then was filled with 200 µl of washed bacterial cell suspension in chemotaxis buffer adjusted to a concentration of about 3 x 108 cells per ml (A560 of 0.4). The chemotaxis buffer was also used for washing cells twice b ...
... sealed capillary tube glued on a glass slide, was covered with a cover slip, and then was filled with 200 µl of washed bacterial cell suspension in chemotaxis buffer adjusted to a concentration of about 3 x 108 cells per ml (A560 of 0.4). The chemotaxis buffer was also used for washing cells twice b ...
Storage lipids of yeasts: a survey of nonpolar lipid metabolism in
... (Fei et al., 2011a, b; Grillitsch et al., 2011). Most of these LD proteins play an important role in lipid metabolism and homeostasis. However, LD were also discussed to contribute to other cellular functions such as storage and degradation of protein aggregates (Fujimoto et al., 2008). Under certai ...
... (Fei et al., 2011a, b; Grillitsch et al., 2011). Most of these LD proteins play an important role in lipid metabolism and homeostasis. However, LD were also discussed to contribute to other cellular functions such as storage and degradation of protein aggregates (Fujimoto et al., 2008). Under certai ...
Early events in protein folding
... polypeptide chain searches out its final native conformation from an inconceivably large number of available conformations. A polypeptide chain of 101 amino acid residues would have to sample 3100 = 5 × 1047 conformations, if each bond connecting two consecutive residues has only three possible conf ...
... polypeptide chain searches out its final native conformation from an inconceivably large number of available conformations. A polypeptide chain of 101 amino acid residues would have to sample 3100 = 5 × 1047 conformations, if each bond connecting two consecutive residues has only three possible conf ...
Protease Inhibitors - laboratornichemikalie.cz
... employed in order to prevent involuntary protein degradation. They may be synthesized in the laboratory or purified from natural sources. ...
... employed in order to prevent involuntary protein degradation. They may be synthesized in the laboratory or purified from natural sources. ...
The Plasma Membrane - Beck-Shop
... is well recognized that cells are highly organized with organelles having specific functions; examination of the plasma membrane demonstrates this structural precision also at the molecular level. The biologist readily focuses on the roles of lipid–protein interactions; however, it is equally importa ...
... is well recognized that cells are highly organized with organelles having specific functions; examination of the plasma membrane demonstrates this structural precision also at the molecular level. The biologist readily focuses on the roles of lipid–protein interactions; however, it is equally importa ...
- Iranian Journal of Analytical Chemistry
... and pharmaceutical compounds and also can be applied in synthesize of oligopeptides or other larger size biomolecules. They have also found applications in such areas as the biodegradable plastics industry [3], drug delivery systems [4] or in stereoselective laboratory synthesis [5]. Amino acids con ...
... and pharmaceutical compounds and also can be applied in synthesize of oligopeptides or other larger size biomolecules. They have also found applications in such areas as the biodegradable plastics industry [3], drug delivery systems [4] or in stereoselective laboratory synthesis [5]. Amino acids con ...
Polypeptides, Nucleic Acid Molecules, and Methods
... in this document. This Summary describes several embodiments of the pres ently-disclosed subject matter, and in many cases lists varia ...
... in this document. This Summary describes several embodiments of the pres ently-disclosed subject matter, and in many cases lists varia ...
Slide 1
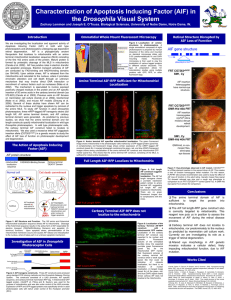
... (Cande et al. 2002). AIF has putative roles in electron transfer and apoptotic processes. Electron transport activities of AIF are conducted by FAD-binding and NADH-binding domains (aa 184-540). Upon cellular stress, AIF is released from the mitochondria and relocated to the nucleus, where it promot ...
... (Cande et al. 2002). AIF has putative roles in electron transfer and apoptotic processes. Electron transport activities of AIF are conducted by FAD-binding and NADH-binding domains (aa 184-540). Upon cellular stress, AIF is released from the mitochondria and relocated to the nucleus, where it promot ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.