Malate Dehydrogenase
... The loop is highly conserved among MDHs (residues 98-110), reflecting its crucial role in catalysis (Fig. 1). X-ray structures of MDHs crystallized in the presence and absence of substrate analogues, which bind to the active site, have identified 2 conformationally distinct forms of the enzyme with ...
... The loop is highly conserved among MDHs (residues 98-110), reflecting its crucial role in catalysis (Fig. 1). X-ray structures of MDHs crystallized in the presence and absence of substrate analogues, which bind to the active site, have identified 2 conformationally distinct forms of the enzyme with ...
Charakterisierung peroxisomaler und Lipid
... Mitotracker Orange to stain the mitochondria. The bar represents 1 mm, unless indicated otherwise. L, lipid body; M, mitochondrion; N, nucleus; P, peroxisome; V, vacuole. Taken with modifications from (107). The peroxisomal matrix harbours at least 50 different enzymes that are linked to diverse bio ...
... Mitotracker Orange to stain the mitochondria. The bar represents 1 mm, unless indicated otherwise. L, lipid body; M, mitochondrion; N, nucleus; P, peroxisome; V, vacuole. Taken with modifications from (107). The peroxisomal matrix harbours at least 50 different enzymes that are linked to diverse bio ...
Protein-Reactive Natural Products
... examples of protein-reactive natural products. These and related secondary metabolites are important because they have yielded insight into the cellular functions of key enzymes. Most natural products that covalently modify proteins possess structural features that render them chemically reactive, w ...
... examples of protein-reactive natural products. These and related secondary metabolites are important because they have yielded insight into the cellular functions of key enzymes. Most natural products that covalently modify proteins possess structural features that render them chemically reactive, w ...
insect transmitted plant pathogenic mollicutes, spiroplasma kunkelii
... importin α for nuclear transport. Transcripts corresponding to the phytoplasma proteins were detected in AY-WB phytoplasma-infected insects and plants by RT-PCR. Microarrays demonstrated that phytoplasma A11 protein affected the expression profiles of 53 tomato genes, including several transcription ...
... importin α for nuclear transport. Transcripts corresponding to the phytoplasma proteins were detected in AY-WB phytoplasma-infected insects and plants by RT-PCR. Microarrays demonstrated that phytoplasma A11 protein affected the expression profiles of 53 tomato genes, including several transcription ...
IDENTIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF SYNAPTONEMAL
... Ad (3). The order of events during meiotic prophase at the DNA-level and at the level of chromatin organization was studied by Padmore et al. (1991) in synchronized cultures of yeast. From this study it appears that the tripartite structure has no function in the initial event at the DNA-level prece ...
... Ad (3). The order of events during meiotic prophase at the DNA-level and at the level of chromatin organization was studied by Padmore et al. (1991) in synchronized cultures of yeast. From this study it appears that the tripartite structure has no function in the initial event at the DNA-level prece ...
148 - Blue Ridge Institute for Medical Research
... Afatinib (PubMed CID: 10184653) Ceritinib (PubMed CID: 57379345) Crizotinib (PubMed CID: 11626560) Erlotinib (PubMed CID: 176870) Gefitinib (PubMed CID: 123631) Imatinib (PubMed CID: 5291) Nilotinib (PubMed CID: 644241) PD173955 (PubMed CID: 447077) Sorafenib (PubMed CID: 216239) Vemurafenib (PubMed ...
... Afatinib (PubMed CID: 10184653) Ceritinib (PubMed CID: 57379345) Crizotinib (PubMed CID: 11626560) Erlotinib (PubMed CID: 176870) Gefitinib (PubMed CID: 123631) Imatinib (PubMed CID: 5291) Nilotinib (PubMed CID: 644241) PD173955 (PubMed CID: 447077) Sorafenib (PubMed CID: 216239) Vemurafenib (PubMed ...
Amino Acid Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships - Parkway C-2
... # OF DIFFERENCES FROM HUMAN CYTOCHROME c ...
... # OF DIFFERENCES FROM HUMAN CYTOCHROME c ...
Profilin regulates the activity of p42 , a novel Myb
... ATG codon in position +174 and encodes a hitherto-unknown protein of 393 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 41,890 kDa, which was termed p42POP (partner of profilin; GenBank AF364868; Fig. 1). Amino acid sequence comparisons in databases revealed p42POP as a novel protein. The N-terminu ...
... ATG codon in position +174 and encodes a hitherto-unknown protein of 393 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 41,890 kDa, which was termed p42POP (partner of profilin; GenBank AF364868; Fig. 1). Amino acid sequence comparisons in databases revealed p42POP as a novel protein. The N-terminu ...
Peroxisomes and peroxisomal disorders: The main facts
... The biogenesis of peroxisomes has long been matter of debate. A first model, called “growth and division” (Lazarow and Fujiki, 1985; Purdue and Lazarow, 2001) was elaborated. This model was based on the proposed idea of the possibility that peroxisomes are autonomous organelles that have evolved fro ...
... The biogenesis of peroxisomes has long been matter of debate. A first model, called “growth and division” (Lazarow and Fujiki, 1985; Purdue and Lazarow, 2001) was elaborated. This model was based on the proposed idea of the possibility that peroxisomes are autonomous organelles that have evolved fro ...
Identification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins that bind to
... solenoid model in that alternate nucleosomes interact with each other and sequential nucleosomes (nucleosomes connected by linker DNA) are positioned opposite each other. This way the linker DNA can remain more rigid and a secondary structure resembling a “two start” helix is formed (Dorigo et al. 2 ...
... solenoid model in that alternate nucleosomes interact with each other and sequential nucleosomes (nucleosomes connected by linker DNA) are positioned opposite each other. This way the linker DNA can remain more rigid and a secondary structure resembling a “two start” helix is formed (Dorigo et al. 2 ...
Natural abundance of 15N in amino acids and
... intermediate to form the final product homospd using the NADH produced by process (1). The exceedingly high enrichment of d15N in homospd molecules separated from nodules and the contrasting small enrichment of those from rhizobia ( Table 4) suggest the possibility that reactions to form homospd in ...
... intermediate to form the final product homospd using the NADH produced by process (1). The exceedingly high enrichment of d15N in homospd molecules separated from nodules and the contrasting small enrichment of those from rhizobia ( Table 4) suggest the possibility that reactions to form homospd in ...
Are You suprised ?
... is determined by the sequence of nucleotides in a gene. A change in the DNA nucleotide sequence (mutation) of a gene that codes for a protein may result in a change in the amino-acid sequence of the protein. Biochemical evidence of evolution compares favorably with structural evidence of evolution. ...
... is determined by the sequence of nucleotides in a gene. A change in the DNA nucleotide sequence (mutation) of a gene that codes for a protein may result in a change in the amino-acid sequence of the protein. Biochemical evidence of evolution compares favorably with structural evidence of evolution. ...
Mitochondrial trans-2-Enoyl-CoA Reductase of Wax Ester
... In the absence of oxygen, acetyl-CoA stemming from pyruvate serves as the terminal electron acceptor of glucose oxidation via an unusual mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis (4). The shift to anaerobic conditions leads to the malonyl-CoA-independent synthesis of wax esters, levels of which can reach u ...
... In the absence of oxygen, acetyl-CoA stemming from pyruvate serves as the terminal electron acceptor of glucose oxidation via an unusual mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis (4). The shift to anaerobic conditions leads to the malonyl-CoA-independent synthesis of wax esters, levels of which can reach u ...
Metabolite transport across the peroxisomal membrane
... transporters in other organisms are half-ABC transporters (which are thought to dimerize to produce a functional transporter) the A. thaliana PXA1 is a full ABC transporter (which is believed to operate as a monomer). The significance of this marked difference is unknown, but clearly the situation i ...
... transporters in other organisms are half-ABC transporters (which are thought to dimerize to produce a functional transporter) the A. thaliana PXA1 is a full ABC transporter (which is believed to operate as a monomer). The significance of this marked difference is unknown, but clearly the situation i ...
RNA helicase DDX19 stabilizes ribosomal elongation and
... in the cell has immediate negative effects on protein biosynthesis. It is important to note that the cellular concentration of eRF3 does not influence the rate of translation (a 60% decrease had no significant effect). These data confirm the important role of Dbp5 during translation in yeast. More r ...
... in the cell has immediate negative effects on protein biosynthesis. It is important to note that the cellular concentration of eRF3 does not influence the rate of translation (a 60% decrease had no significant effect). These data confirm the important role of Dbp5 during translation in yeast. More r ...
Role of hsp90 and the hsp90-binding immunophilins in signalling
... The ubiquitous protein chaperone hsp90 has been shown to regulate more than 100 proteins involved in cellular signalling. These proteins are called ‘client proteins’ for hsp90, and a multiprotein hsp90/hsp70-based chaperone machinery forms client protein hsp90 heterocomplexes in the cytoplasm and th ...
... The ubiquitous protein chaperone hsp90 has been shown to regulate more than 100 proteins involved in cellular signalling. These proteins are called ‘client proteins’ for hsp90, and a multiprotein hsp90/hsp70-based chaperone machinery forms client protein hsp90 heterocomplexes in the cytoplasm and th ...
Biochemical, biophysical and interaction studies of the stress
... Firstly I would like to thank all my supervisors, Dr Alexander Golovanov, Dr Costas Demonacos and Dr Stephen Prince for their continual guidance throughout this PhD. I would also like to thank my adviser Professor Andrew Doig for all his support and advice on PhD related issues and CD experiments. A ...
... Firstly I would like to thank all my supervisors, Dr Alexander Golovanov, Dr Costas Demonacos and Dr Stephen Prince for their continual guidance throughout this PhD. I would also like to thank my adviser Professor Andrew Doig for all his support and advice on PhD related issues and CD experiments. A ...
A novel exon within the mdm2 gene modulates translation
... 15 ± 125 for the human form) contains a deep hydrophobic cleft into which p53 residues TFSDLWKLL (amino acids 18 ± 26) bind as an amphipathic alpha helix. Binding eectively blocks the transactivation domain of p53 and targets p53 for rapid degradation by the ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic pathway ( ...
... 15 ± 125 for the human form) contains a deep hydrophobic cleft into which p53 residues TFSDLWKLL (amino acids 18 ± 26) bind as an amphipathic alpha helix. Binding eectively blocks the transactivation domain of p53 and targets p53 for rapid degradation by the ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic pathway ( ...
Characterization of a Bacillus anthracis spore coat
... B. anthracis coat proteins]. This peptide does not match any sequences other than Cotb and its orthologues in publicly available databases. To analyze the role of cotb in spore function and assembly, we inactivated it by replacing the gene with a kanamycin resistance cassette in the Sterne and Ames ...
... B. anthracis coat proteins]. This peptide does not match any sequences other than Cotb and its orthologues in publicly available databases. To analyze the role of cotb in spore function and assembly, we inactivated it by replacing the gene with a kanamycin resistance cassette in the Sterne and Ames ...
- Free Documents
... both cases it is the gain or loss oI phosphate groups that determines whether the protein is active or inactive. The largest class consists oI proteins that are activated or inactivated by . For these proteins, the switch is thrown in one Chapter phosphorylation discussed in direction by a protein k ...
... both cases it is the gain or loss oI phosphate groups that determines whether the protein is active or inactive. The largest class consists oI proteins that are activated or inactivated by . For these proteins, the switch is thrown in one Chapter phosphorylation discussed in direction by a protein k ...
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... A) bonding together of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds. B) order in which amino acids are joined in a polypeptide chain. C) unique three-dimensional shape of the fully folded polypeptide. D) organization of a polypeptide chain into an α helix or β pleated sheet. E) overall protein structure ...
... A) bonding together of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds. B) order in which amino acids are joined in a polypeptide chain. C) unique three-dimensional shape of the fully folded polypeptide. D) organization of a polypeptide chain into an α helix or β pleated sheet. E) overall protein structure ...
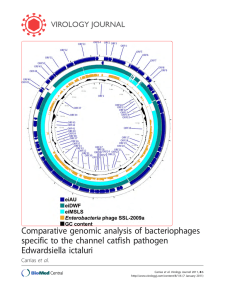
Virology Journal
... could not be linked to a putative function based on BLAST search or any other similarity searches. However, all of these ORFs with the exception of ORF28 have sequence similarity to proteins identified within other phage genomes (Table 1). The protein products of ORF34 and ORF35 may encode large and ...
... could not be linked to a putative function based on BLAST search or any other similarity searches. However, all of these ORFs with the exception of ORF28 have sequence similarity to proteins identified within other phage genomes (Table 1). The protein products of ORF34 and ORF35 may encode large and ...
Structure and Function Relationships between ATPase Family, AAA
... Faithful replication of a cell’s genetic material during replication is essential in order to pass genetic material from one generation to the next; however, DNA-damaging agents constantly injure the genome. High fidelity replication of the cell’s genetic material is normally carried out through the ...
... Faithful replication of a cell’s genetic material during replication is essential in order to pass genetic material from one generation to the next; however, DNA-damaging agents constantly injure the genome. High fidelity replication of the cell’s genetic material is normally carried out through the ...
Mutational Analysis of Synaptobrevin Transmembrane Domain
... recombinantly in E. coli. The two reports on dimerization of recombinant synaptobrevin used different detergents for the extraction from the E. coli cell pellet (16, 18). To see if this difference could explain the different estimates of the magnitude of dimerization, we directly compared the effect ...
... recombinantly in E. coli. The two reports on dimerization of recombinant synaptobrevin used different detergents for the extraction from the E. coli cell pellet (16, 18). To see if this difference could explain the different estimates of the magnitude of dimerization, we directly compared the effect ...
The glycocalyx of the sperm surface
... at these organisms to identify which sperm components and mechanisms may be involved in some of these very special functions (McConville and Ferguson, 1993). It has been estimated that the outer membrane of ejaculated human spermatozoa includes at least 300 different proteins, as detectable by vecto ...
... at these organisms to identify which sperm components and mechanisms may be involved in some of these very special functions (McConville and Ferguson, 1993). It has been estimated that the outer membrane of ejaculated human spermatozoa includes at least 300 different proteins, as detectable by vecto ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.