Unit 8 Objectives and Vocab L4
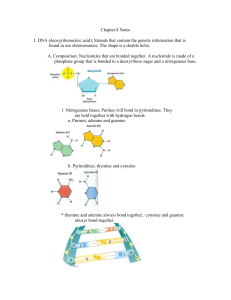
... Chase, Avery, MacLeod & McCarty, as well as Chargaff. 3. Describe the structure of DNA and explain what kind of chemical bond connects the nucleotides of each strand and what holds the two strands together. 4. Describe the process of DNA replication and explain the role of helicase, primase, DNA pol ...
... Chase, Avery, MacLeod & McCarty, as well as Chargaff. 3. Describe the structure of DNA and explain what kind of chemical bond connects the nucleotides of each strand and what holds the two strands together. 4. Describe the process of DNA replication and explain the role of helicase, primase, DNA pol ...
Genetics Keywords - No Brain Too Small
... A molecule that binds to the repressor protein (in prokaryotes) and transcription occurs because the repressor molecule cannot bind to the operator site and prevent transcription. ...
... A molecule that binds to the repressor protein (in prokaryotes) and transcription occurs because the repressor molecule cannot bind to the operator site and prevent transcription. ...
DNA Replication
... entire strand is copied Result is two strands of DNA Semi-Conservative Replication - Each strand is 50% new and 50% old DNA ...
... entire strand is copied Result is two strands of DNA Semi-Conservative Replication - Each strand is 50% new and 50% old DNA ...
ap: chapter 16: the molecular basis of inheritance
... 14. Why does the DNA have to add nucleotides in the 5’ to 3’ direction? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 15. Label the diagram of DNA replication. Include the directions and the terms ...
... 14. Why does the DNA have to add nucleotides in the 5’ to 3’ direction? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 15. Label the diagram of DNA replication. Include the directions and the terms ...
DNA Replication Graphic Organizer
... REVIEW: Explain the TWO things an enzyme does in chemical reactions in the body… ...
... REVIEW: Explain the TWO things an enzyme does in chemical reactions in the body… ...
No Slide Title
... Who had the transformation experiment that demonstrated the change of rough bacteria into smooth? ...
... Who had the transformation experiment that demonstrated the change of rough bacteria into smooth? ...
Exam II Study Guide
... Replication and function of telomeres Names and contributions of geneticists discussed in lectures, including their organisms Transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes (similarities and differences) Role of the carboxy tail domain of RNA polymerase II Three modifications resulting in the productio ...
... Replication and function of telomeres Names and contributions of geneticists discussed in lectures, including their organisms Transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes (similarities and differences) Role of the carboxy tail domain of RNA polymerase II Three modifications resulting in the productio ...
DNA Jeopardy Review
... 2. Prokaryotes: the polymerase binds to promoter directly in eukaryotes the polymerase requires transcription factors for binding a promoter (TATA) 3. In termination prokaryotic transcription hits a terminator sequence, but in eukaryotes the pre-mRNA is cleaved from the growing RNA chain ...
... 2. Prokaryotes: the polymerase binds to promoter directly in eukaryotes the polymerase requires transcription factors for binding a promoter (TATA) 3. In termination prokaryotic transcription hits a terminator sequence, but in eukaryotes the pre-mRNA is cleaved from the growing RNA chain ...
Chapter 11 Notes
... 2. m-RNA; Messenger RNA takes instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Instructions are in the form of three nitrogenous bases called a codon. * Codon determines which amino acid will be attached at the ribosome. 3. t-RNA; Transfer RNA carries amino acids to the riboso ...
... 2. m-RNA; Messenger RNA takes instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Instructions are in the form of three nitrogenous bases called a codon. * Codon determines which amino acid will be attached at the ribosome. 3. t-RNA; Transfer RNA carries amino acids to the riboso ...
Lesson 2 * Carbohydrates
... replicated as the molecule unzips but the other strand (the 3’ to 5’ side, called the lagging strand) needs to be replicated in sections then joined together later by an enzyme called DNA ligase. ...
... replicated as the molecule unzips but the other strand (the 3’ to 5’ side, called the lagging strand) needs to be replicated in sections then joined together later by an enzyme called DNA ligase. ...
Lecture #7 Date - Woodland Hills School District
... Helicase:catalyzes the untwisting of the DNA at the replication fork DNA polymerase:catalyzes the elongation of new DNA ...
... Helicase:catalyzes the untwisting of the DNA at the replication fork DNA polymerase:catalyzes the elongation of new DNA ...
Name Ch 12 Study Guide
... 10) Assume that the two parent strands of DNA have been separated and that the base sequence on one parent strand is A-T-T-C-G-C; the base sequence that will complement that parent strand is __________________________________________ 11) Who was Rosalind Franklin? 12) What was her contribution to th ...
... 10) Assume that the two parent strands of DNA have been separated and that the base sequence on one parent strand is A-T-T-C-G-C; the base sequence that will complement that parent strand is __________________________________________ 11) Who was Rosalind Franklin? 12) What was her contribution to th ...
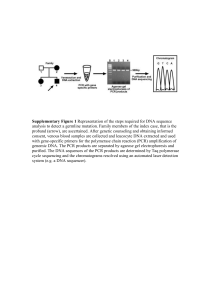
Figure 2 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
Answers
... 5. Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder. Patients with XP exhibit a cellular hypersensitivity to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, a high incidence of skin cancer and premature aging. Based on these clinical characteristics, what is the underlying cause for this disease? A. de ...
... 5. Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder. Patients with XP exhibit a cellular hypersensitivity to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, a high incidence of skin cancer and premature aging. Based on these clinical characteristics, what is the underlying cause for this disease? A. de ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.