Slide 1
... • How does a cell copy its genetic material? – Replication • Double helix separate • Copy instructions (DNA) with a DNA template that produces a new, complementary strand for each of the old template strands • (DNA copied before or after cell division?) ...
... • How does a cell copy its genetic material? – Replication • Double helix separate • Copy instructions (DNA) with a DNA template that produces a new, complementary strand for each of the old template strands • (DNA copied before or after cell division?) ...
File
... DNA is tightly coiled up around histone proteins so that it can all fit in the nucleus. The coiled DNA is called chromatin. ...
... DNA is tightly coiled up around histone proteins so that it can all fit in the nucleus. The coiled DNA is called chromatin. ...
DNA Replication Paper Clip Activity
... bonds with T. When this gene replicates in the nucleus of a cell, the double-strand begins to separate at one end. As it separates, new nucleotide bases are moved into place by enzymes, which form the beginning of two new identical molecules. These A, T, C, and G bases are present in the nucleus of ...
... bonds with T. When this gene replicates in the nucleus of a cell, the double-strand begins to separate at one end. As it separates, new nucleotide bases are moved into place by enzymes, which form the beginning of two new identical molecules. These A, T, C, and G bases are present in the nucleus of ...
MCB 142 second midterm: Molecular Genetics
... (b) in a given double helix, one strand is inherited directly from the parental helix and the other strand is newly synthesized as its complement (c) both strands are inherited from the parent, but DNA repair removes half of the sequence randomly, keeping (“conserving”) the other half. (d) If a (pre ...
... (b) in a given double helix, one strand is inherited directly from the parental helix and the other strand is newly synthesized as its complement (c) both strands are inherited from the parent, but DNA repair removes half of the sequence randomly, keeping (“conserving”) the other half. (d) If a (pre ...
Chapter 12-13 Notes
... The Role of DNA Store: Information: DNA stores information for genes that control patterns of development. Copy: Before a cell divides, it must make a complete copy of every one of its genes Transmit: the genetic information in a cell. ...
... The Role of DNA Store: Information: DNA stores information for genes that control patterns of development. Copy: Before a cell divides, it must make a complete copy of every one of its genes Transmit: the genetic information in a cell. ...
Exam 4
... Of the 64, _______________________ codon(s) is(are) start codons. Which amino acid is specified by a start codon? ___________________________. ...
... Of the 64, _______________________ codon(s) is(are) start codons. Which amino acid is specified by a start codon? ___________________________. ...
HGP - eduBuzz.org
... ‘If I were to study the carburettor of my car engine, even in exquisite detail, I would still have no idea about the overall function of the engine, much less the entire car. To understand what an engine is for, and how it works, I’d need to study the whole thing – I’d need to place the carburettor ...
... ‘If I were to study the carburettor of my car engine, even in exquisite detail, I would still have no idea about the overall function of the engine, much less the entire car. To understand what an engine is for, and how it works, I’d need to study the whole thing – I’d need to place the carburettor ...
Chapter 16: DNA: The Genetic Material
... 1. DNA replication requires the coordinated activity of many enzymes and other proteins 2. also requires the presence of nucleotide triphosphates B. origins of replication 1. DNA replication begins at specific sites synthesis generally proceeds in both directions from an origin, creating a “replic ...
... 1. DNA replication requires the coordinated activity of many enzymes and other proteins 2. also requires the presence of nucleotide triphosphates B. origins of replication 1. DNA replication begins at specific sites synthesis generally proceeds in both directions from an origin, creating a “replic ...
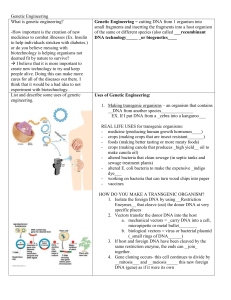
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
... medicines to combat illnesses (Ex. Insulin to help individuals stricken with diabetes.) or do you believe messing with biotechnology is helping organisms not deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can m ...
... medicines to combat illnesses (Ex. Insulin to help individuals stricken with diabetes.) or do you believe messing with biotechnology is helping organisms not deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can m ...
Markscheme for sample questions File
... occurs during (S phase of ) interphase/in preparation for mitosis/ cell division; DNA replication is semi-conservative; unwinding of double helix / separation of strands by helicase (at replication origin); hydrogen bonds between two strands are broken; each strand of parent DNA used as template for ...
... occurs during (S phase of ) interphase/in preparation for mitosis/ cell division; DNA replication is semi-conservative; unwinding of double helix / separation of strands by helicase (at replication origin); hydrogen bonds between two strands are broken; each strand of parent DNA used as template for ...
How the DNA Molecule Copies Itself
... using one template, DNA polymerase adds nucleotides in a continuous fashion; this new daughter strand is called the leading strand because the other template is a mirror image, directionality becomes a problem because DNA polymerase can build a new strand in one direction only • this second daug ...
... using one template, DNA polymerase adds nucleotides in a continuous fashion; this new daughter strand is called the leading strand because the other template is a mirror image, directionality becomes a problem because DNA polymerase can build a new strand in one direction only • this second daug ...
Transcription - Santa Susana High School
... • transcription - synthesis of RNA under the direction of DNA • messenger RNA (mRNA) - carries genetic message from DNA to the ribosome for the synthesis of protein • translation - synthesis of protein under the direction of mRNA • ribosome - site of protein synthesis (translation) • primary transcr ...
... • transcription - synthesis of RNA under the direction of DNA • messenger RNA (mRNA) - carries genetic message from DNA to the ribosome for the synthesis of protein • translation - synthesis of protein under the direction of mRNA • ribosome - site of protein synthesis (translation) • primary transcr ...
Sequence 1 - Human DNA
... 6. Another mutation changes the insulin gene to read T C T (instead of the normal T A G). Will this person be diabetic? Explain. ...
... 6. Another mutation changes the insulin gene to read T C T (instead of the normal T A G). Will this person be diabetic? Explain. ...
Final Review
... 21. Explain each of the following scientists’ contribution to biology: Watson & Crick, Avery, Griffiths, Hershey & Chase. 22. Name the three parts of a nucleotide. 23. Draw and label a diagram of DNA. What is the shape called? 24. How do the nitrogenous bases pair in DNA? In RNA? 25. Explain the pro ...
... 21. Explain each of the following scientists’ contribution to biology: Watson & Crick, Avery, Griffiths, Hershey & Chase. 22. Name the three parts of a nucleotide. 23. Draw and label a diagram of DNA. What is the shape called? 24. How do the nitrogenous bases pair in DNA? In RNA? 25. Explain the pro ...
Introduction to Molecular Biology, Part 1
... • Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes are descended from the same primitive cell • All extant cells are the result of 3.5 billion years of evolution ...
... • Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes are descended from the same primitive cell • All extant cells are the result of 3.5 billion years of evolution ...
Worksheet on DNA and RNA
... 35. Many RNA molecules from eukaryotic genes have sections called _____________ edited out of them before they become functional. The remaining pieces called __________ are then spliced together. 36. Proteins are made in the cytoplasm by cellular structures called _____________________. 37. Proteins ...
... 35. Many RNA molecules from eukaryotic genes have sections called _____________ edited out of them before they become functional. The remaining pieces called __________ are then spliced together. 36. Proteins are made in the cytoplasm by cellular structures called _____________________. 37. Proteins ...
Document
... 6. True or false. The 3’ end of the mRNA made from this region would be located in the 1 kb restriction fragment. 7. True or false. It would be impossible to produce a cDNA library of genes expressed in human red blood cells, since red blood cells do not contain a nucleus. Questions 8-9 pertain to t ...
... 6. True or false. The 3’ end of the mRNA made from this region would be located in the 1 kb restriction fragment. 7. True or false. It would be impossible to produce a cDNA library of genes expressed in human red blood cells, since red blood cells do not contain a nucleus. Questions 8-9 pertain to t ...
Molecular Genetics SBI4U MockTestMConly
... Part A: True or False (15 Marks) (K/I) 1. Adenine and guanine are pyrimidines. _____ 2. The DNA double helix makes a complete turn every 3.4 nm along its length. _____ 3. DNA’s backbone is held together by hydrogen bonds while the complementary bases are held together by phosphodiester bonds. _____ ...
... Part A: True or False (15 Marks) (K/I) 1. Adenine and guanine are pyrimidines. _____ 2. The DNA double helix makes a complete turn every 3.4 nm along its length. _____ 3. DNA’s backbone is held together by hydrogen bonds while the complementary bases are held together by phosphodiester bonds. _____ ...
CB-Nucleic Acids
... What would be the complementary base sequence for the strand of DNA below? ...
... What would be the complementary base sequence for the strand of DNA below? ...
Contemporary Biology Per
... maintain a breed of organisms once it is established. 13. The problem with inbreeding is that because the members of the breed are so genetically similar, crossing individuals of the same breed increases the chances of _______ alleles pairing, which can lead to an increase in genetic ________. 14. A ...
... maintain a breed of organisms once it is established. 13. The problem with inbreeding is that because the members of the breed are so genetically similar, crossing individuals of the same breed increases the chances of _______ alleles pairing, which can lead to an increase in genetic ________. 14. A ...
DNA Paper Model Activity Try to attach and mode the Gene Reading
... 1. Try to attach and mode the Gene Reading Machinery cut-out to any length of the inaccessible DNA ribbon that is not spooled around a histone or covered by a methyl. Can the machinery read any significant stretch of DNA? No, it cannot. 2. Refer to question 1, would this be an active or inactive gen ...
... 1. Try to attach and mode the Gene Reading Machinery cut-out to any length of the inaccessible DNA ribbon that is not spooled around a histone or covered by a methyl. Can the machinery read any significant stretch of DNA? No, it cannot. 2. Refer to question 1, would this be an active or inactive gen ...
Polymerase Chain Reaction and DNA Sequencing
... reactions can be radioactively labeled. • Bands detected by Xray film exposure. • Sequence can be read in the 5’ to 3’ direction from the bottom of the image towards the top. A A T C T A A C G ...
... reactions can be radioactively labeled. • Bands detected by Xray film exposure. • Sequence can be read in the 5’ to 3’ direction from the bottom of the image towards the top. A A T C T A A C G ...
Nucleic Acids
... • The strands of the DNA double helix create two continuous grooves (major and minor) • The sugar–phosphate backbone runs along the outside of the helix, and the amine bases hydrogen bond to one another on the inside • The major groove is slightly deeper than the minor groove, and both are lined by ...
... • The strands of the DNA double helix create two continuous grooves (major and minor) • The sugar–phosphate backbone runs along the outside of the helix, and the amine bases hydrogen bond to one another on the inside • The major groove is slightly deeper than the minor groove, and both are lined by ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.