DNA Technology Notes (13.1 & 13.2)
... DNA sequences and ____________ the DNA within the sequence. Scientists use restriction enzymes as powerful tools for ____________ specific genes or regions of the genome. ...
... DNA sequences and ____________ the DNA within the sequence. Scientists use restriction enzymes as powerful tools for ____________ specific genes or regions of the genome. ...
lecture CH22 chem131pikul UPDATED
... • The identity of the bases on the template strand determines the order of the bases on the new strand. • A must pair with T, and G must pair with C. • A new phosphodiester bond is formed between the 5 -phosphate of the nucleoside triphosphate and the 3 -OH group of the new DNA strand. • Replication ...
... • The identity of the bases on the template strand determines the order of the bases on the new strand. • A must pair with T, and G must pair with C. • A new phosphodiester bond is formed between the 5 -phosphate of the nucleoside triphosphate and the 3 -OH group of the new DNA strand. • Replication ...
Chapter 12
... 1. Genes of most eukaryotes have interrupted coding sequences a) Coding sequences are exons (expressed sequences); noncoding sequences are introns (intervening sequences) b) A typical eukaryotic gene has multiple exons and introns, with variable numbers of each 2. This terminology refers to sequence ...
... 1. Genes of most eukaryotes have interrupted coding sequences a) Coding sequences are exons (expressed sequences); noncoding sequences are introns (intervening sequences) b) A typical eukaryotic gene has multiple exons and introns, with variable numbers of each 2. This terminology refers to sequence ...
Pre-Lab: Molecular Biology
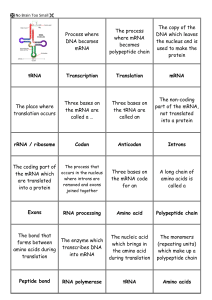
... The nucleotide bases in mRNA are complementary to the nucleotide bases in DNA. In mRNA, sequences of 3 nucleotide bases serve as codes for single amino acids and are called codons. The strands of mRNA are formed by the process called transcription, since they are transcripts of the DNA. The mRNA le ...
... The nucleotide bases in mRNA are complementary to the nucleotide bases in DNA. In mRNA, sequences of 3 nucleotide bases serve as codes for single amino acids and are called codons. The strands of mRNA are formed by the process called transcription, since they are transcripts of the DNA. The mRNA le ...
DNA and Genetics
... in a DNA strand into a complementary strand of RNA (messenger RNA or mRNA) with the aid of RNA polymerases. Although RNA polymerase traverses the DNA template strand from 3' → 5', the coding (nontemplate) strand is usually used as the reference point. Hence, the process proceeds in the 5' → 3' direc ...
... in a DNA strand into a complementary strand of RNA (messenger RNA or mRNA) with the aid of RNA polymerases. Although RNA polymerase traverses the DNA template strand from 3' → 5', the coding (nontemplate) strand is usually used as the reference point. Hence, the process proceeds in the 5' → 3' direc ...
Chapter 3 Proteins: - California State University San Marcos
... ►Inverted repeat recognized at ends and brought together forming loop ►Insertion catalyzed by transposase occurs at random sites through staggered breaks ►Break resealed but breakage and repair often alters DNA sequence resulting in mutations at site of excision ...
... ►Inverted repeat recognized at ends and brought together forming loop ►Insertion catalyzed by transposase occurs at random sites through staggered breaks ►Break resealed but breakage and repair often alters DNA sequence resulting in mutations at site of excision ...
A new drug inactivates the helicase enzyme by binding to its active
... (B) Diagram A, because a hybrid double helix of old and new DNA strands is never created, ensuring that genetic information is accurately transmitted by only pairing compatible DNA strands in a double helix, new with new and old with old Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may und ...
... (B) Diagram A, because a hybrid double helix of old and new DNA strands is never created, ensuring that genetic information is accurately transmitted by only pairing compatible DNA strands in a double helix, new with new and old with old Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may und ...
bacterial genetics
... 2. Restricted - When a specific bacteriophage transduces only a particular genetic trait. ...
... 2. Restricted - When a specific bacteriophage transduces only a particular genetic trait. ...
AP Biology The
... but is it the protein or the DNA of the chromosomes that are the genes? initially proteins were thought to ...
... but is it the protein or the DNA of the chromosomes that are the genes? initially proteins were thought to ...
Chapter 13 Gene Technology
... (-Polymerase chain reaction- copies DNA) 2. Cut the DNA into shorter fragments -Restriction enzymes (enzymes always cut at specific nucleotide sequences- so scientists know what ends of fragments look like.) 3. Separate fragments by size - Technique is gel electrophoresis 4. Compare patterns of DNA ...
... (-Polymerase chain reaction- copies DNA) 2. Cut the DNA into shorter fragments -Restriction enzymes (enzymes always cut at specific nucleotide sequences- so scientists know what ends of fragments look like.) 3. Separate fragments by size - Technique is gel electrophoresis 4. Compare patterns of DNA ...
DNA Technology
... • However, that new organism will be an individual • The two cats seen here are clones but have very different colors ...
... • However, that new organism will be an individual • The two cats seen here are clones but have very different colors ...
DNA - Shippensburg University
... replication fork, a Y-shaped region where new DNA strands are elongating • Helicases are enzymes that untwist the double helix at the replication forks • Single-strand binding protein binds to and stabilizes single-stranded DNA until it can be used as a template • Topoisomerase corrects “overwinding ...
... replication fork, a Y-shaped region where new DNA strands are elongating • Helicases are enzymes that untwist the double helix at the replication forks • Single-strand binding protein binds to and stabilizes single-stranded DNA until it can be used as a template • Topoisomerase corrects “overwinding ...
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of
... All four of the histones that make up the core of the nucleosome are relatively small proteins (102-135 amino acids), and they share a structural motif, known as the histone fold, formed from three alpha helices connected by two loops. ...
... All four of the histones that make up the core of the nucleosome are relatively small proteins (102-135 amino acids), and they share a structural motif, known as the histone fold, formed from three alpha helices connected by two loops. ...
Polymerase Chain Reaction
... Polygenic disorders: Genetic disorders resulting from the combined action of alleles of more than one gene (e.g., heart disease, diabetes, and some cancers). Although such disorders are inherited, they depend on the simultaneous presence of several alleles; thus the hereditary patterns are usually ...
... Polygenic disorders: Genetic disorders resulting from the combined action of alleles of more than one gene (e.g., heart disease, diabetes, and some cancers). Although such disorders are inherited, they depend on the simultaneous presence of several alleles; thus the hereditary patterns are usually ...
AP Biology
... Genes (DNA) and their products (proteins) document the hereditary background of an organism. Because DNA molecules are passed from parents to offspring, siblings have greater similarity than do unrelated individuals of the same species. This argument can be extended to develop a molecular gene ...
... Genes (DNA) and their products (proteins) document the hereditary background of an organism. Because DNA molecules are passed from parents to offspring, siblings have greater similarity than do unrelated individuals of the same species. This argument can be extended to develop a molecular gene ...
Supplemental Material
... CheB. The N-terminal response regulator receiver domain of WspF spans residues 1 to 122 and contains the major active site aspartate residues, which in CheB are Asp-10, Asp-11 and Asp-56 (Asp56 is thought to be the phosphorylation site) (STOCK and SURETTE 1996). The C-terminal methylesterase domain ...
... CheB. The N-terminal response regulator receiver domain of WspF spans residues 1 to 122 and contains the major active site aspartate residues, which in CheB are Asp-10, Asp-11 and Asp-56 (Asp56 is thought to be the phosphorylation site) (STOCK and SURETTE 1996). The C-terminal methylesterase domain ...
CSIRO DNA model
... Your body is made up of many different chemicals. An important group of chemicals is the proteins, which build your body and help it to function. Each protein is formed from over 100 amino acids. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be used to make proteins. The code in the DNA ladde ...
... Your body is made up of many different chemicals. An important group of chemicals is the proteins, which build your body and help it to function. Each protein is formed from over 100 amino acids. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be used to make proteins. The code in the DNA ladde ...
Obtain PCR-Ready Genomic DNA from Buccal Cells, HeLa Cells, Hair
... • Human buccal (cheek) cells collected using a Catch-All™ Sample Collection Swab and rotated 5 times in the QuickExtract Solution to disperse the cells. • 104 counted human cervical carcinoma tissue culture (HeLa) cells. ...
... • Human buccal (cheek) cells collected using a Catch-All™ Sample Collection Swab and rotated 5 times in the QuickExtract Solution to disperse the cells. • 104 counted human cervical carcinoma tissue culture (HeLa) cells. ...
topic B - Institute of Life Sciences
... from bacteriophage are used. T A collection of clones that includes all the DNA sequences of a given species is called a genomic library T A genomic library can be screened for clones containing a sequence of interest ...
... from bacteriophage are used. T A collection of clones that includes all the DNA sequences of a given species is called a genomic library T A genomic library can be screened for clones containing a sequence of interest ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.