Circulatory and Respiratory System Review
... How does your respiration rate change when you increase physical activity levels? During physical activity your respiration rate will increase because there is an increased need for oxygen in the blood. ...
... How does your respiration rate change when you increase physical activity levels? During physical activity your respiration rate will increase because there is an increased need for oxygen in the blood. ...
Unit 2 Metabolism and Survival Glossary
... Nutrient medium a mixture of nutrients (including carbon and nitrogen sources) required for growth Plasmid a circular, self-replicating DNA molecule that carries only a few genes Receptor cells which monitor changes in environment Respirometer a piece of equipment used to measure the rate of respira ...
... Nutrient medium a mixture of nutrients (including carbon and nitrogen sources) required for growth Plasmid a circular, self-replicating DNA molecule that carries only a few genes Receptor cells which monitor changes in environment Respirometer a piece of equipment used to measure the rate of respira ...
11 plant hormones
... involves an original stimulus and the body reacting to return that stimulus back to a normal level •Regulation of blood glucose involves two hormones produced by the pancreas ...
... involves an original stimulus and the body reacting to return that stimulus back to a normal level •Regulation of blood glucose involves two hormones produced by the pancreas ...
Chapter 1: Respiration
... 2. Haeomoglobin is red pigment found in red blood cells (erythrocytes). 3. Haemoglobin in the red blood cell combine with oxygen and it becomes oxyhaemoglobin. 4. blood acts as an efficient medium of transport of oxygen due to assistance from haemoglobin. 5. Haeomoglobin is an important carrier of o ...
... 2. Haeomoglobin is red pigment found in red blood cells (erythrocytes). 3. Haemoglobin in the red blood cell combine with oxygen and it becomes oxyhaemoglobin. 4. blood acts as an efficient medium of transport of oxygen due to assistance from haemoglobin. 5. Haeomoglobin is an important carrier of o ...
Which of the following statements about closed circulatory systems
... Blood remains in blood vessels. Blood pressure and blood flow are generally lower than in open circulatory systems. – YES Blood pressure is supplied by the heart. Blood flow can be directed to the specific tissues that need it the most. Vertebrates have this type of circulatory system. Some animals ...
... Blood remains in blood vessels. Blood pressure and blood flow are generally lower than in open circulatory systems. – YES Blood pressure is supplied by the heart. Blood flow can be directed to the specific tissues that need it the most. Vertebrates have this type of circulatory system. Some animals ...
E/F Physical Science
... 2. Circle the letter of each sentence that is correct for the chemical equation: C + O2 → CO2. a. Carbon and oxygen react and form carbon monoxide. b. Carbon and oxygen react and form carbon dioxide. c. Carbon dioxide yields carbon and oxygen. d. The reaction of carbon and oxygen yields carbon dioxi ...
... 2. Circle the letter of each sentence that is correct for the chemical equation: C + O2 → CO2. a. Carbon and oxygen react and form carbon monoxide. b. Carbon and oxygen react and form carbon dioxide. c. Carbon dioxide yields carbon and oxygen. d. The reaction of carbon and oxygen yields carbon dioxi ...
Chapter 21 - Cloudfront.net
... • All bronchioles end in alveoli. • Most of lung tissue is alveoli! (300 million of them!) • Capillaries surround each alveoli allowing the blood to exchange gas with the environment. ...
... • All bronchioles end in alveoli. • Most of lung tissue is alveoli! (300 million of them!) • Capillaries surround each alveoli allowing the blood to exchange gas with the environment. ...
Respiratory System
... Controlled by the autonomic nervous system Normally breath 12-15 times/minute Do have some conscious control over breathing but autonomic centers will ignore information if ph of blood is low (can’t hold your breath until you die) Mostly controlled by level of carbon dioxide in the blood (pH) – act ...
... Controlled by the autonomic nervous system Normally breath 12-15 times/minute Do have some conscious control over breathing but autonomic centers will ignore information if ph of blood is low (can’t hold your breath until you die) Mostly controlled by level of carbon dioxide in the blood (pH) – act ...
UNIT 2
... • Extracellular digestion: takes places outside the cells. Can be: • External digestion: takes place outside the body. Many insects • Internal digestion: takes place inside the digestive system. The transformation of food is both mechanical (food is broken down into smaller pieces) and chemical (foo ...
... • Extracellular digestion: takes places outside the cells. Can be: • External digestion: takes place outside the body. Many insects • Internal digestion: takes place inside the digestive system. The transformation of food is both mechanical (food is broken down into smaller pieces) and chemical (foo ...
Respiratory System Review
... The alveoli have a structure specialised for efficient gaseous exchange: ...
... The alveoli have a structure specialised for efficient gaseous exchange: ...
The_Respiratory_System_powerpoint3
... Allows gas exchange to all parts of the body. Functions of Respiratory System: (What does it do?) The major function of the respiratory system is gas exchange between the external environment and an organism's circulatory system. In humans and mammals, this exchange facilitates oxygenation of the bl ...
... Allows gas exchange to all parts of the body. Functions of Respiratory System: (What does it do?) The major function of the respiratory system is gas exchange between the external environment and an organism's circulatory system. In humans and mammals, this exchange facilitates oxygenation of the bl ...
Chapter 6
... Can you figure out what is missing in the following chemical reactions? 1. Aluminum resists corrosion (rust) because it reacts with a gas in the air to form a protective coating of aluminum oxide. Aluminum + ____________ → aluminum oxide ...
... Can you figure out what is missing in the following chemical reactions? 1. Aluminum resists corrosion (rust) because it reacts with a gas in the air to form a protective coating of aluminum oxide. Aluminum + ____________ → aluminum oxide ...
Respiratory System
... coughing and production of mucus in the bronchi and bronchioles. There are two versions of this condition: acute (short term) & chronic (long term). ...
... coughing and production of mucus in the bronchi and bronchioles. There are two versions of this condition: acute (short term) & chronic (long term). ...
Key - Wilson`s Web Page
... dioxide found in plasma? Give the name of the enzyme that aids the conversion of carbon dioxide both in the tissues and in the lungs. How does hemoglobin help with carbon dioxide transport? List two other ways carbon dioxide in smaller quantities is transported in the blood. (6 marks) The majority o ...
... dioxide found in plasma? Give the name of the enzyme that aids the conversion of carbon dioxide both in the tissues and in the lungs. How does hemoglobin help with carbon dioxide transport? List two other ways carbon dioxide in smaller quantities is transported in the blood. (6 marks) The majority o ...
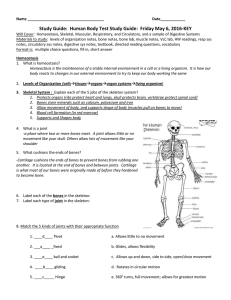
Homeostasis, Levels of Organization of Living Things, Skeletal
... of carbon dioxide that is the waste product from cells. Cellular respiration is when the our body cell uses oxygen to break down glucose and release energy (ATP) within the mitochondria of the cell. 14. List the pathway of oxygen as it travels through the respiratory system on its way to your blood. ...
... of carbon dioxide that is the waste product from cells. Cellular respiration is when the our body cell uses oxygen to break down glucose and release energy (ATP) within the mitochondria of the cell. 14. List the pathway of oxygen as it travels through the respiratory system on its way to your blood. ...
Human Systems Final
... 45. Where does blood enriched with oxygen from the lungs enter the heart? 46. What heart muscle divides the heart into a right side and a left side? 47. The aorta, the largest artery in the body, is connected to what section of the heart? 48. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs through bloo ...
... 45. Where does blood enriched with oxygen from the lungs enter the heart? 46. What heart muscle divides the heart into a right side and a left side? 47. The aorta, the largest artery in the body, is connected to what section of the heart? 48. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs through bloo ...
Section 16.3 - CPO Science
... the structure of many different molecules. Describe the importance of carbon to living organisms. Compare and contrast the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
... the structure of many different molecules. Describe the importance of carbon to living organisms. Compare and contrast the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
macromolecule packet
... Proteins are made of subunits (monomers) called amino acids and are used to build cells and do much of the work inside organisms. They also act as enzymes helping to control metabolic reactions in organisms. Amino acids contain two functional groups, the carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group (- ...
... Proteins are made of subunits (monomers) called amino acids and are used to build cells and do much of the work inside organisms. They also act as enzymes helping to control metabolic reactions in organisms. Amino acids contain two functional groups, the carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group (- ...
Respiratory System
... nutrient macromolecules to the chemical energy utilized by cells ATP • This process is an oxidation reaction a steady supply of oxygen is required to combust glucose to carbon dioxide and water ...
... nutrient macromolecules to the chemical energy utilized by cells ATP • This process is an oxidation reaction a steady supply of oxygen is required to combust glucose to carbon dioxide and water ...
Gas exchange: All (larger) organisms need to exchange oxygen and
... As it turns out, we actually monitor CO2 concentration. As CO2 increases, it reacts with water and creates carbonic acid. This causes changes in blood pH, which we sense. Oxygen concentration usually does not impact breathing: But very low blood pressure or volume (usually caused by massive bleeding ...
... As it turns out, we actually monitor CO2 concentration. As CO2 increases, it reacts with water and creates carbonic acid. This causes changes in blood pH, which we sense. Oxygen concentration usually does not impact breathing: But very low blood pressure or volume (usually caused by massive bleeding ...