Structural basics of human muscle fructose-1,6
... Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase) is an allosteric enzyme crucial for gluco- and glyconeogenesis pathways. It occurs almost in all living organisms. It catalyzes non-reversible hydrolysis of fructose1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate and inorganic phosphate. Moreover, the enzyme plays a key ...
... Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase) is an allosteric enzyme crucial for gluco- and glyconeogenesis pathways. It occurs almost in all living organisms. It catalyzes non-reversible hydrolysis of fructose1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate and inorganic phosphate. Moreover, the enzyme plays a key ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... and narrower, which restricts the flow of air and increases the work of the respiratory muscles ...
... and narrower, which restricts the flow of air and increases the work of the respiratory muscles ...
A-level
... It displays a greater affinity for oxygen and its oxygen dissociation curve is displaced to the left of haemoglobin. It acts as a storage of oxygen in resting muscle They release oxygen when supplies of oxyhaemoglobin have been exhausted such as severe muscular exercies. ...
... It displays a greater affinity for oxygen and its oxygen dissociation curve is displaced to the left of haemoglobin. It acts as a storage of oxygen in resting muscle They release oxygen when supplies of oxyhaemoglobin have been exhausted such as severe muscular exercies. ...
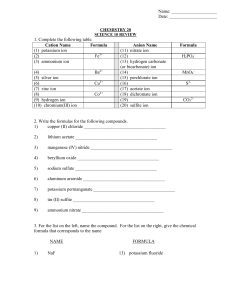
NAME
... j) a copper coil is placed into a solution of silver nitrate, silver crystals form on the surface of the copper. Additionally, highly soluble copper (I) nitrate is generated ...
... j) a copper coil is placed into a solution of silver nitrate, silver crystals form on the surface of the copper. Additionally, highly soluble copper (I) nitrate is generated ...
The Respiratory System
... Ventilation is the exchange of air between the external environment and the alveoli. Air moves by bulk flow from an area of high pressure to low pressure. All pressures in the respiratory system are relative to atmospheric pressure (760mmHg at sea level). Air will move in or out of the lungs dependi ...
... Ventilation is the exchange of air between the external environment and the alveoli. Air moves by bulk flow from an area of high pressure to low pressure. All pressures in the respiratory system are relative to atmospheric pressure (760mmHg at sea level). Air will move in or out of the lungs dependi ...
CH 13 DAY 5 - Wythe County Schools Moodle Site
... the RBCs to form oxyhemoglobin —HbO2 . A very small amount of oxygen is carried dissolved in the plasma. Most carbon dioxide is transported in plasma as the bicarbonate ion (HCO3−). A smaller amount (between 20 and 30 percent of the transported CO2) is carried inside the RBCs bound to hemoglobin. Ca ...
... the RBCs to form oxyhemoglobin —HbO2 . A very small amount of oxygen is carried dissolved in the plasma. Most carbon dioxide is transported in plasma as the bicarbonate ion (HCO3−). A smaller amount (between 20 and 30 percent of the transported CO2) is carried inside the RBCs bound to hemoglobin. Ca ...
Non-Metals
... Chemical Properties of Hydrogen • It has a neutral pH • It burns in air/oxygen • It combines with reactive metals to give hydrides : Mg + H2 MgH2 • It can act as a reducing agents e.g. in the extraction of metals CuO + H2 Cu + H2O ...
... Chemical Properties of Hydrogen • It has a neutral pH • It burns in air/oxygen • It combines with reactive metals to give hydrides : Mg + H2 MgH2 • It can act as a reducing agents e.g. in the extraction of metals CuO + H2 Cu + H2O ...
41. Testing for enzymes
... It may be useful to discuss how to decide which reaction is fastest. Teachers should be sensitive to the needs of vegetarian students. Manganese dioxide, copper oxide and calcium carbonate can also be tested as catalysts to illustrate biological and chemical catalysts. Cooked liver (well done) can a ...
... It may be useful to discuss how to decide which reaction is fastest. Teachers should be sensitive to the needs of vegetarian students. Manganese dioxide, copper oxide and calcium carbonate can also be tested as catalysts to illustrate biological and chemical catalysts. Cooked liver (well done) can a ...
Respiratory System Part B
... Have a total surface area (in males) of about 60 m2 (40 times that of one’s skin) Thicken if lungs become waterlogged and edematous, whereby gas exchange is inadequate and oxygen deprivation results Decrease in surface area with emphysema, when walls of adjacent alveoli break through ...
... Have a total surface area (in males) of about 60 m2 (40 times that of one’s skin) Thicken if lungs become waterlogged and edematous, whereby gas exchange is inadequate and oxygen deprivation results Decrease in surface area with emphysema, when walls of adjacent alveoli break through ...
21. Testing the pH of oxides
... that these are not solutions, the oxides do not dissolve – they have reactions with water. While it is important to maintain accuracy, it is suggested that an ‘…and water’ approach is taken. This is accurate and it allows the teacher to focus on the teaching point without the need to cover another s ...
... that these are not solutions, the oxides do not dissolve – they have reactions with water. While it is important to maintain accuracy, it is suggested that an ‘…and water’ approach is taken. This is accurate and it allows the teacher to focus on the teaching point without the need to cover another s ...
Examples
... ▫ 2. Active site - the small region on the enzyme that is involved in the chemical action ▫ 3. Enzyme-substrate complex substrates are the materials that are acted on by the enzyme - when the enzyme and substrate combine they form an enzyme-substrate ...
... ▫ 2. Active site - the small region on the enzyme that is involved in the chemical action ▫ 3. Enzyme-substrate complex substrates are the materials that are acted on by the enzyme - when the enzyme and substrate combine they form an enzyme-substrate ...
Removal of materials from the blood
... • During the conversion of ammonia into urea, two molecules of ammonia and one molecule of carbon dioxide combine to form one molecule of urea and one of water. Assisting this process there is a cyclical conversion of ornithine into citrulline, arginine, and then back to ornithine again. ...
... • During the conversion of ammonia into urea, two molecules of ammonia and one molecule of carbon dioxide combine to form one molecule of urea and one of water. Assisting this process there is a cyclical conversion of ornithine into citrulline, arginine, and then back to ornithine again. ...
U2.8P1 Respiration
... The heart is made of very special muscle, CARDIAC muscle. It must keep beating all the time for the rest of a persons life! If you tried to do the same action repeatedly (like the heart) your muscles would get tired and, after a while, they would stop working. For example if you clench and unclench ...
... The heart is made of very special muscle, CARDIAC muscle. It must keep beating all the time for the rest of a persons life! If you tried to do the same action repeatedly (like the heart) your muscles would get tired and, after a while, they would stop working. For example if you clench and unclench ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... Answer each of the following questions and give an example that helps with your explanation. 1. If a compound ends in –ide, what does it tell you about the compound? 2. If a compound ends in –ate what does it tell you about the compound? 3. If a compound ends in –ite what does it tell you about the ...
... Answer each of the following questions and give an example that helps with your explanation. 1. If a compound ends in –ide, what does it tell you about the compound? 2. If a compound ends in –ate what does it tell you about the compound? 3. If a compound ends in –ite what does it tell you about the ...
Long term effects of training/exercise
... coordinating them. On the other hand, your heart muscle gets energy directly from fat and sugar in your blood and even from a breakdown product of metabolism called lactic acid. It is virtually impossible for the heart muscle to run out of fuel unless you are starving to death. ...
... coordinating them. On the other hand, your heart muscle gets energy directly from fat and sugar in your blood and even from a breakdown product of metabolism called lactic acid. It is virtually impossible for the heart muscle to run out of fuel unless you are starving to death. ...
Ch. 2 Macromolecules
... ! Primary component of the cell membrane ! Secondary energy source; used when an organism doesn’t have carbohydrates in its body ...
... ! Primary component of the cell membrane ! Secondary energy source; used when an organism doesn’t have carbohydrates in its body ...
Air Pollution - San Jose State University
... • BURNING COAL RELEASES AIR POLLUTANTS LIKE NITROGEN DIOXIDE (FOUND IN SMOG), SULFUR DIOXIDE (FORMS ACID RAIN), AND CARBON DIOXIDE WHICH CONTRIBUTES TO GLOBAL WARMING AS WELL AS TOXIC MERCURY WHICH ENTERS OUR DIET THROUGH THE FISH WE EAT AND HAS BEEN LINKED TO BRAIN DAMAGE IN CHILDREN AND FETUSES • ...
... • BURNING COAL RELEASES AIR POLLUTANTS LIKE NITROGEN DIOXIDE (FOUND IN SMOG), SULFUR DIOXIDE (FORMS ACID RAIN), AND CARBON DIOXIDE WHICH CONTRIBUTES TO GLOBAL WARMING AS WELL AS TOXIC MERCURY WHICH ENTERS OUR DIET THROUGH THE FISH WE EAT AND HAS BEEN LINKED TO BRAIN DAMAGE IN CHILDREN AND FETUSES • ...
Human Body Systems
... To control the conditions in your body by making and sending chemicals from one part to another. ...
... To control the conditions in your body by making and sending chemicals from one part to another. ...
Chapter 1 Homework - due Tuesday, Sept
... and the citric acid cycle (both NAD+ and FAD), to form NADH and FADH2, which then carry these electrons to the electron transport chain. Oxygen acts at the end of this chain, receives the electrons, joining with hydrogen ions to produce water. 5. What is the final electron acceptor for ATP productio ...
... and the citric acid cycle (both NAD+ and FAD), to form NADH and FADH2, which then carry these electrons to the electron transport chain. Oxygen acts at the end of this chain, receives the electrons, joining with hydrogen ions to produce water. 5. What is the final electron acceptor for ATP productio ...
The Human Respiratory System
... • Diaphragm relaxes and lungs return to normal size, placing pressure on the lungs – Air rushes out of the lungs ...
... • Diaphragm relaxes and lungs return to normal size, placing pressure on the lungs – Air rushes out of the lungs ...
UE 415 Raw Lung
... The right lung is larger than the left and contains three parts called lobe whereas the left lung has only two lobes. The lungs are soft and spongy and contain countless tiny air sacs called alveoli. Lung tissue is pink in children and gray to black in adults. The structure of the lungs resembles th ...
... The right lung is larger than the left and contains three parts called lobe whereas the left lung has only two lobes. The lungs are soft and spongy and contain countless tiny air sacs called alveoli. Lung tissue is pink in children and gray to black in adults. The structure of the lungs resembles th ...