Respiratory System Overview
... • Internal respiration is the process by which the gases in the air that has already been drawn into the lungs by external respiration are exchanged with gases in the blood/tissues so that carbon dioxide (CO2) is removed from the blood and replaced with oxygen (O2). ...
... • Internal respiration is the process by which the gases in the air that has already been drawn into the lungs by external respiration are exchanged with gases in the blood/tissues so that carbon dioxide (CO2) is removed from the blood and replaced with oxygen (O2). ...
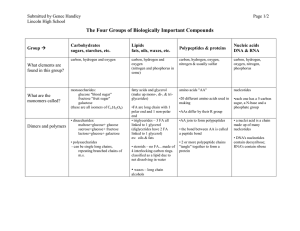
1 a Nutrients1 (2)
... 2. The enzyme grabs on to the substrate at a special area called the active site. Enzymes are very, very specific and don't just grab on to any molecule. The active site is a specially shaped area of the enzyme that fits around the substrate. ...
... 2. The enzyme grabs on to the substrate at a special area called the active site. Enzymes are very, very specific and don't just grab on to any molecule. The active site is a specially shaped area of the enzyme that fits around the substrate. ...
handout - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... C. Carbon dioxide -poor and oxygen –rich; D. Capillary blood to alveolar air; E. Capillary blood to tissue cells; F. Diffusion; G. Higher concentration; H. Lower concentration; I. Oxygen-poor and carbon dioxide – rich; J. Tissue cells to capillary blood. Gas exchange takes place bt the process of (1 ...
... C. Carbon dioxide -poor and oxygen –rich; D. Capillary blood to alveolar air; E. Capillary blood to tissue cells; F. Diffusion; G. Higher concentration; H. Lower concentration; I. Oxygen-poor and carbon dioxide – rich; J. Tissue cells to capillary blood. Gas exchange takes place bt the process of (1 ...
Unit 1 Practice Test
... 38. A nonprotein molecule necessary for the functioning of a certain enzyme is called a (a) catalyst (b) polypeptide (c) coenzyme (d) substrate 39. Which of the following variables has the least direct effect on the rate of an enzyme regulated reaction? (a) temperature (b) pH (c) carbon dioxide c ...
... 38. A nonprotein molecule necessary for the functioning of a certain enzyme is called a (a) catalyst (b) polypeptide (c) coenzyme (d) substrate 39. Which of the following variables has the least direct effect on the rate of an enzyme regulated reaction? (a) temperature (b) pH (c) carbon dioxide c ...
Respiratory System and Gas Exchange
... tissues by bulk flow of blood as it is pumped throughout body by heart 4. gases are exchanged between tissues and circulatory system by diffusion (oxygen diffuses out into tissue and carbon dioxide diffuses into capillaries based on concentration gradients) ...
... tissues by bulk flow of blood as it is pumped throughout body by heart 4. gases are exchanged between tissues and circulatory system by diffusion (oxygen diffuses out into tissue and carbon dioxide diffuses into capillaries based on concentration gradients) ...
HiQ VERISEQ Carbon dioxide
... Practice (cGMP) should be assured. With gases used in pharmaceutical production, producers need to fulfil the requirements of US FDA Title 21 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Parts 210 and 211 in order to assure batch uniformity and integrity of the drug product. API manufacturers should comply wit ...
... Practice (cGMP) should be assured. With gases used in pharmaceutical production, producers need to fulfil the requirements of US FDA Title 21 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Parts 210 and 211 in order to assure batch uniformity and integrity of the drug product. API manufacturers should comply wit ...
Respiratory System
... Why is the circulatory system important to the respiratory system? The circulatory system carries oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body. • Oxygen is needed by cells to make energy (cellular ...
... Why is the circulatory system important to the respiratory system? The circulatory system carries oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body. • Oxygen is needed by cells to make energy (cellular ...
VERISEQ® pharmaceutical grade gases. Carbon→dioxide.
... VERISEQ® Carbon dioxide helps the pharmaceutical industry to fulfil its requirements and to reach compliance with cGMP, as the gas is traceable back to product storage. VERISEQ® Carbon dioxide is produced according to documented manufacturing procedures, with any impurities and contaminants identifi ...
... VERISEQ® Carbon dioxide helps the pharmaceutical industry to fulfil its requirements and to reach compliance with cGMP, as the gas is traceable back to product storage. VERISEQ® Carbon dioxide is produced according to documented manufacturing procedures, with any impurities and contaminants identifi ...
File
... ▫ N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2NH3 (g) • Sodium metal reacts violently with water to produce sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. ▫ 2Na (s) + 2H2O (l) 2NaOH (aq) + H2 (g) ...
... ▫ N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2NH3 (g) • Sodium metal reacts violently with water to produce sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. ▫ 2Na (s) + 2H2O (l) 2NaOH (aq) + H2 (g) ...
AS Chemistry - Crawshaw Academy
... This AS (practical skills) unit is teacher assessed and externally moderated by OCR. Candidates are assessed on one task from each of the following categories: qualitative, quantitative and evaluative tasks. This controlled assessment component is integrated into the teaching of the modules ...
... This AS (practical skills) unit is teacher assessed and externally moderated by OCR. Candidates are assessed on one task from each of the following categories: qualitative, quantitative and evaluative tasks. This controlled assessment component is integrated into the teaching of the modules ...
Biology of the Cell - Practice Exam: Unit III
... When carbon dioxide is fixed to ribulose bisphosphate __________________________. A. B. C. D. E. ...
... When carbon dioxide is fixed to ribulose bisphosphate __________________________. A. B. C. D. E. ...
Biology of the Cell - Practice Exam: Unit III (Answer key)
... When carbon dioxide is fixed to ribulose bisphosphate __________________________. A. B. C. D. E. ...
... When carbon dioxide is fixed to ribulose bisphosphate __________________________. A. B. C. D. E. ...
Problem Set: Empirical and Molecular Formulas
... 1. Carbon monoxide can be combined with hydrogen to produce methanol, CH 3OH. If you had 152.5 g CO and 24.50 g H2, how many kilograms of CH3OH would be produced? (Hint: make sure equation is balanced first!) CO ...
... 1. Carbon monoxide can be combined with hydrogen to produce methanol, CH 3OH. If you had 152.5 g CO and 24.50 g H2, how many kilograms of CH3OH would be produced? (Hint: make sure equation is balanced first!) CO ...
PChem Data 7-9 Data Talk Version 2
... So did Fe-S enzymes form when a protein grabbed a Fe-S cluster? • This is the active part of an early hydrogenase ...
... So did Fe-S enzymes form when a protein grabbed a Fe-S cluster? • This is the active part of an early hydrogenase ...
Bio392 - Chapter 2-3 - notes
... body may need? • 3. How do you think your body used each of the foods that you ate? • 4. A common saying is “You are what you eat.” What do you think this statement means? ...
... body may need? • 3. How do you think your body used each of the foods that you ate? • 4. A common saying is “You are what you eat.” What do you think this statement means? ...
A and P lesson 4 - Calthorpe Park Moodle
... The process where oxygen from the air in the alveoli moves into the blood in the capillaries, while carbon dioxide moves from the blood in the capillaries into the air in the alveoli. ...
... The process where oxygen from the air in the alveoli moves into the blood in the capillaries, while carbon dioxide moves from the blood in the capillaries into the air in the alveoli. ...
name - cloudfront.net
... H is oxidized and N is reduced N is oxidized and Cl is reduced N is oxidized and O is reduced Cl is oxidized and O is reduced 24. What mass of C6H12O6 (glucose) is needed to prepare 450. mL of a 0.650 M solution of glucose in water? (52.7 g) 25. A 4.691 g sample of MgCl2 is dissolved in enough water ...
... H is oxidized and N is reduced N is oxidized and Cl is reduced N is oxidized and O is reduced Cl is oxidized and O is reduced 24. What mass of C6H12O6 (glucose) is needed to prepare 450. mL of a 0.650 M solution of glucose in water? (52.7 g) 25. A 4.691 g sample of MgCl2 is dissolved in enough water ...
The role of nitric oxide in skeletal muscle regeneration
... itric oxide (NO) is a labile lipid soluble gas synthesized in several cells and tissues, including the adipocytes, brain, endothelial cells, heart, hepatocytes, macrophages and skeletal muscles. The endogenous formation and biological significance of NO were revealed in a series of studies in the 198 ...
... itric oxide (NO) is a labile lipid soluble gas synthesized in several cells and tissues, including the adipocytes, brain, endothelial cells, heart, hepatocytes, macrophages and skeletal muscles. The endogenous formation and biological significance of NO were revealed in a series of studies in the 198 ...
STUDY GUIDE - West Ashley High School
... Carbohydrates: are composed primarily of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen and used primarily by living things as a source of energy and for structure. Monosaccharides: The simplest carbohydrates. Used directly by living cells to produce energy Ex. sugar : glucose C6H12O6. Polysaccharides : complex carbs ...
... Carbohydrates: are composed primarily of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen and used primarily by living things as a source of energy and for structure. Monosaccharides: The simplest carbohydrates. Used directly by living cells to produce energy Ex. sugar : glucose C6H12O6. Polysaccharides : complex carbs ...
Nutrition Test
... An organic compound consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and sulfur, used for liver transplants A thread-like structure running longitudinally through ;a muscle fiber consisting mainly of thick myofilaments and thin myofilaments An abundant steroid in animal tissue that is used for the synthesis of stero ...
... An organic compound consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and sulfur, used for liver transplants A thread-like structure running longitudinally through ;a muscle fiber consisting mainly of thick myofilaments and thin myofilaments An abundant steroid in animal tissue that is used for the synthesis of stero ...
Oxidative stress
... (AD). • The increased oxidative damage is an early event in AD that decreases with disease progression and lesion formation. ...
... (AD). • The increased oxidative damage is an early event in AD that decreases with disease progression and lesion formation. ...
File
... saturation of oxyhemoglobin (hemoglobin +oxygen complex) begins to plummet. However, the human body has both short-term and long-term adaptations to altitude that allow it to partially compensate for the lack of oxygen. SHORT TERM adaptations include breathing faster and deeper (hyperventilates) at ...
... saturation of oxyhemoglobin (hemoglobin +oxygen complex) begins to plummet. However, the human body has both short-term and long-term adaptations to altitude that allow it to partially compensate for the lack of oxygen. SHORT TERM adaptations include breathing faster and deeper (hyperventilates) at ...
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS 1 CHAPTER TWO
... d. Water (H2O) is always 1 g hydrogen for every 8 g of O present, while H2O2 is always 1 g hydrogen for every 16 g of O present. These are distinctly different compounds, each with its own unique relative number and types of atoms present. e. A chemical equation involves a reorganization of the atom ...
... d. Water (H2O) is always 1 g hydrogen for every 8 g of O present, while H2O2 is always 1 g hydrogen for every 16 g of O present. These are distinctly different compounds, each with its own unique relative number and types of atoms present. e. A chemical equation involves a reorganization of the atom ...