Animal System Review Key
... located in these walls also stretch and as a result, a signal is sent to the brain which in turn slows down the body’s heart rate. This slows the flow of blood through the arteries causing less pressure. As BP drops the baroreceptors become flaccid and a signal is sent to speed up the heart rate. ...
... located in these walls also stretch and as a result, a signal is sent to the brain which in turn slows down the body’s heart rate. This slows the flow of blood through the arteries causing less pressure. As BP drops the baroreceptors become flaccid and a signal is sent to speed up the heart rate. ...
B 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 – Breathing, lungs, inhaled and exhaled air
... lot of tiny blood vessels called capillaries. Diffusion is the process by where gases move from a high concentration to a low concentration: Oxygen diffuses from the air in the alveoli into the blood.Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the air in the alveoli. ...
... lot of tiny blood vessels called capillaries. Diffusion is the process by where gases move from a high concentration to a low concentration: Oxygen diffuses from the air in the alveoli into the blood.Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the air in the alveoli. ...
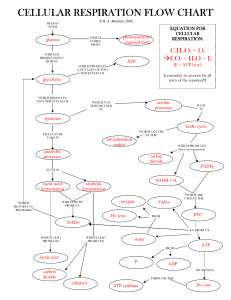
cellular respiration flow chart cellular respiration flow
... EQUATION FOR CELLULAR RESPIRATION: ...
... EQUATION FOR CELLULAR RESPIRATION: ...
A. The Respiratory Cycle
... 2. Inside the lungs, respiratory bronchioles bear outpouchings of their walls called alveoli (usually clustered as alveolar sacs), which provide a tremendous surface area for gaseous exchange with the blood located in the dense capillary network surrounding each alveolar sac. II. A Closer Look at Ga ...
... 2. Inside the lungs, respiratory bronchioles bear outpouchings of their walls called alveoli (usually clustered as alveolar sacs), which provide a tremendous surface area for gaseous exchange with the blood located in the dense capillary network surrounding each alveolar sac. II. A Closer Look at Ga ...
Respiratory System
... levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. • Carbon dioxide has a greater effect on breathing rate because it is toxic. • If you were exercising, the levels of carbon dioxide increase so breathing rate increases. ...
... levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. • Carbon dioxide has a greater effect on breathing rate because it is toxic. • If you were exercising, the levels of carbon dioxide increase so breathing rate increases. ...
Middle East Jeopardy
... The organ that produces 3 digestive enzymes, then delivers the enzymes to the small intestine. What is the pancreas? ...
... The organ that produces 3 digestive enzymes, then delivers the enzymes to the small intestine. What is the pancreas? ...
What is energy needed for?
... Respiration What is respiration? It is the release of energy from food substances in living cells. ...
... Respiration What is respiration? It is the release of energy from food substances in living cells. ...
BIOLOGY
... 1. Glycolysis is a series of chemical reactions in the cytoplasm of a cell that breaks down a molecule of GLUCOSE into two molecules of PYRUVIC ACID (pyruvate, a C3 compound). 4 ATPs per glucose molecule are produced; no oxygen is required for this process. This is known as anaerobic process. Pyruvi ...
... 1. Glycolysis is a series of chemical reactions in the cytoplasm of a cell that breaks down a molecule of GLUCOSE into two molecules of PYRUVIC ACID (pyruvate, a C3 compound). 4 ATPs per glucose molecule are produced; no oxygen is required for this process. This is known as anaerobic process. Pyruvi ...
Chapter 1 Homework - due Tuesday, Sept
... synthase channels down their concentration gradient c) c) ATP synthase complex – as hydrogen ions pass through the synthases, the production of ATP from ADP and Pi is catalyzed, and oxygen is reduced, forming water 4. What are the roles of NAD+ and FAD in aerobic respiration? NAD+ and FAD receive el ...
... synthase channels down their concentration gradient c) c) ATP synthase complex – as hydrogen ions pass through the synthases, the production of ATP from ADP and Pi is catalyzed, and oxygen is reduced, forming water 4. What are the roles of NAD+ and FAD in aerobic respiration? NAD+ and FAD receive el ...
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Technical Information
... Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) systems are one of the most promising technologies to meet the challenge of generating electricity from coal in an environmentally sustainable way. The IGCC technology uses a gasifier to convert coal to fuel gas, and then uses a combined cycle power bloc ...
... Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) systems are one of the most promising technologies to meet the challenge of generating electricity from coal in an environmentally sustainable way. The IGCC technology uses a gasifier to convert coal to fuel gas, and then uses a combined cycle power bloc ...
Macromolecule - cloudfront.net
... Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) and three fatty acid chains. This subunit is called a triglyceride. Color the glycerol molecule using the ...
... Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) and three fatty acid chains. This subunit is called a triglyceride. Color the glycerol molecule using the ...
Gas Exchange - Crestwood Local Schools
... Respiratory system needs: large respiratory surface (lungs, gills) a method for ventilating respiratory surface a pump and circulatory system to distribute gases ...
... Respiratory system needs: large respiratory surface (lungs, gills) a method for ventilating respiratory surface a pump and circulatory system to distribute gases ...
AP Chemistry
... C) Single Displacement (Redox) An element reacts with a compound totake the place of one of the elements of that compound. A new element is formed along with a new compound. a) Metal and Acid hydrogen + salt H2SO4(aq) + Fe(s) → FeSO4(aq) + H2(g) b) Metal and Water hydrogen + metal hydroxide OR me ...
... C) Single Displacement (Redox) An element reacts with a compound totake the place of one of the elements of that compound. A new element is formed along with a new compound. a) Metal and Acid hydrogen + salt H2SO4(aq) + Fe(s) → FeSO4(aq) + H2(g) b) Metal and Water hydrogen + metal hydroxide OR me ...
2.3 Biomolecules Hon
... Organic: contains carbon and hydrogen ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon and hydrogen ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
Chapter 1 Review Understanding Concepts
... have many branches and do not allow as many strong hydrogen bonds to occur along their lengths. Humans need cholesterol in their bodies to produce bile salts, to help produce vitamin D, to form sex hormones, and as structural components of cell membranes. However, many people have high cholesterol l ...
... have many branches and do not allow as many strong hydrogen bonds to occur along their lengths. Humans need cholesterol in their bodies to produce bile salts, to help produce vitamin D, to form sex hormones, and as structural components of cell membranes. However, many people have high cholesterol l ...
2011 CLASS-X BIOLOGY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS-LIFE PROCESSES
... 4.What is the similarity between chlorophyll and hemoglobin? 5.Name the products of photolysis of water. 6.What are the end products of light dependant reaction? 7.Which cell organelle is the site of photosynthesis? 8.What is the difference between digestion of heterotrophs and saprotrophs? 9.Give e ...
... 4.What is the similarity between chlorophyll and hemoglobin? 5.Name the products of photolysis of water. 6.What are the end products of light dependant reaction? 7.Which cell organelle is the site of photosynthesis? 8.What is the difference between digestion of heterotrophs and saprotrophs? 9.Give e ...
File
... – Lower resting heart rate and quicker recovery – Reduced risk of heart disease – Increased blood volume and red blood cells – Increased number of capillaries in muscle ...
... – Lower resting heart rate and quicker recovery – Reduced risk of heart disease – Increased blood volume and red blood cells – Increased number of capillaries in muscle ...
Word and Skeleton Equations Practice (ws Fall 2010)
... hydrogen, H2(g); nitrogen, N2(g); oxygen O2(g); fluorine, F2(g); chlorine Cl2(g); bromine, Br2(l); and iodine, I2(s). 1. Gaseous hydrogen and oxygen react to form gaseous water. 2. Solid sodium metal reacts with liquid water to form an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. 3. Solid ...
... hydrogen, H2(g); nitrogen, N2(g); oxygen O2(g); fluorine, F2(g); chlorine Cl2(g); bromine, Br2(l); and iodine, I2(s). 1. Gaseous hydrogen and oxygen react to form gaseous water. 2. Solid sodium metal reacts with liquid water to form an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. 3. Solid ...
Respiratory System
... even more carbon dioxide from the cells into the capillaries continues yet still manages to "package" the carbon dioxide for eventual passage out of the ...
... even more carbon dioxide from the cells into the capillaries continues yet still manages to "package" the carbon dioxide for eventual passage out of the ...
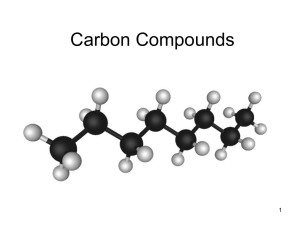
Carbon Compounds
... covalent bonds with many elements including hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur and nitrogen. ...
... covalent bonds with many elements including hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur and nitrogen. ...
Body Systems
... carries blood AWAY from heart, oxygen rich Veins- carries blood toward heart, oxygen poor Capillaries- tiny vessels that exchanges substances with the cells ...
... carries blood AWAY from heart, oxygen rich Veins- carries blood toward heart, oxygen poor Capillaries- tiny vessels that exchanges substances with the cells ...
Acid-Base Equilibria and pH Regulation of Blood Plasma
... Metabolic acidosis is the decrease in blood pH that results when excessive amounts of acidic substances are released into the blood. This can happen through prolonged physical exertion, by diabetes, or restricted food intake. The normal body response to this condition is increases breathing to reduc ...
... Metabolic acidosis is the decrease in blood pH that results when excessive amounts of acidic substances are released into the blood. This can happen through prolonged physical exertion, by diabetes, or restricted food intake. The normal body response to this condition is increases breathing to reduc ...