Degradation of Amino Acids
... were taken and analyzed for plasma amino acids for as long as 5 to 6 weeks following the fast. Blood ketone bodies increased at the end of the first week. Valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, and α aminobutyrate concentrations were transiently increased during the first week, but dropped below i ...
... were taken and analyzed for plasma amino acids for as long as 5 to 6 weeks following the fast. Blood ketone bodies increased at the end of the first week. Valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, and α aminobutyrate concentrations were transiently increased during the first week, but dropped below i ...
How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
... • For each glucose molecule that enters cellular respiration, chemiosmosis produces up to 38 ATP molecules Cytoplasmic fluid ...
... • For each glucose molecule that enters cellular respiration, chemiosmosis produces up to 38 ATP molecules Cytoplasmic fluid ...
lecture 6, cellular respiration, 031709
... We have focused on glucose as a fuel source for cellular respiration. • Cellular respiration also uses other carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. • The digestive process hydrolyzes large food molecules into monomers that can be used by glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. ...
... We have focused on glucose as a fuel source for cellular respiration. • Cellular respiration also uses other carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. • The digestive process hydrolyzes large food molecules into monomers that can be used by glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. ...
Word
... C) Galactokinase and galactose 1-phosphate uridyl transferase deficiencies cause mental retardation D) Galactose 1-phosphate uridyl transferase releases free glucose E) UDP-galactose requires a phosphoglucomutase to convert it to UDP-Glucose 21) Malonyl CoA, which was 14C labeled (a radioactive isot ...
... C) Galactokinase and galactose 1-phosphate uridyl transferase deficiencies cause mental retardation D) Galactose 1-phosphate uridyl transferase releases free glucose E) UDP-galactose requires a phosphoglucomutase to convert it to UDP-Glucose 21) Malonyl CoA, which was 14C labeled (a radioactive isot ...
Key Terms PDF - QuizOver.com
... transfer of an amine group from one molecule to another as a way to turn nitrogen waste into ammonia ...
... transfer of an amine group from one molecule to another as a way to turn nitrogen waste into ammonia ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS HOW PLANTS MAKE THEIR
... • OCCURS IN THE CYTOPLASM OF ALL CELLS • No O2 is required, anaerobic respiration • 1. THROUGH A SERIES OF REACTIONS, IT WILL PRODUCE: • 4 ATPS, AND 2 NADH+ & 2 PYRUVATES ...
... • OCCURS IN THE CYTOPLASM OF ALL CELLS • No O2 is required, anaerobic respiration • 1. THROUGH A SERIES OF REACTIONS, IT WILL PRODUCE: • 4 ATPS, AND 2 NADH+ & 2 PYRUVATES ...
Utilization of dietary glucose in the metabolic syndrome
... up glucose [55]; it does not affect brain glucose uptake, and neither does overload the liver, which lets glucose pass through undisturbed or uses it for lipogenesis (to add insult to injury, but to somehow limit the dangers of excess glucose) [118]. One of the few remaining sites large enough to us ...
... up glucose [55]; it does not affect brain glucose uptake, and neither does overload the liver, which lets glucose pass through undisturbed or uses it for lipogenesis (to add insult to injury, but to somehow limit the dangers of excess glucose) [118]. One of the few remaining sites large enough to us ...
Chapter 9: How do cells harvest energy?
... process at least some of the time; also called cellular respiration (How is this different from breathing, and how is it related to breathing?) B. anaerobic respiration – processes similar to aerobic respiration but that do not use O 2; used mainly by bacteria that live in ...
... process at least some of the time; also called cellular respiration (How is this different from breathing, and how is it related to breathing?) B. anaerobic respiration – processes similar to aerobic respiration but that do not use O 2; used mainly by bacteria that live in ...
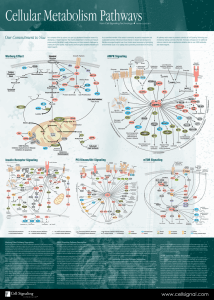
Cellular Metabolism Pathways
... Cancer cells frequently use glutamine as a secondary fuel source, which enters the mitochondria and can be used to replenish Krebs Cycle intermediates or can be used to produce more pyruvate through the action of malic enzyme. Highly proliferative cells need to produce excess lipid, nucleotide, and ...
... Cancer cells frequently use glutamine as a secondary fuel source, which enters the mitochondria and can be used to replenish Krebs Cycle intermediates or can be used to produce more pyruvate through the action of malic enzyme. Highly proliferative cells need to produce excess lipid, nucleotide, and ...
Ch8_CellularRespiration
... • 2 molecules of ATP are required for glycolysis, while 4 are produced, for a net gain of 2 ATPs. • Glycolysis supplies some energy, its product (pyruvate) can be broken down ...
... • 2 molecules of ATP are required for glycolysis, while 4 are produced, for a net gain of 2 ATPs. • Glycolysis supplies some energy, its product (pyruvate) can be broken down ...
Glycolysis
... In metabolic pathways, enzymes catalyzing essentially irreversible reactions are potential sites of control. In glycolysis, the reactions catalyzed by hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase are virtually irreversible; hence, these enzymes would be expected to have regulatory as well as ...
... In metabolic pathways, enzymes catalyzing essentially irreversible reactions are potential sites of control. In glycolysis, the reactions catalyzed by hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase are virtually irreversible; hence, these enzymes would be expected to have regulatory as well as ...
CHAPTER 1 1.1 Introduction In many developing countries, herbal
... Oncewithin the cellglucose gets phosphorylated by glucokinase (in the liver) and hexokinase (in other cells) into glucose-6-phosphate which can no longer leave the cell. The phosphorylation step is almost completely irreversible (except in certain cells e.g. hepatocytes) and serves to ensure that gl ...
... Oncewithin the cellglucose gets phosphorylated by glucokinase (in the liver) and hexokinase (in other cells) into glucose-6-phosphate which can no longer leave the cell. The phosphorylation step is almost completely irreversible (except in certain cells e.g. hepatocytes) and serves to ensure that gl ...
ALTACE® 10mg:
... Inhibitors of Intestinal Glucose Absorption: Acarbose (Precose) and Miglitol (Glyset) • Acts as an -glucosidase inhibitor: prevent cleavage of disaccharides to monosaccharides in the intestine •Delays carbohydrate absorption and reduced postprandial plasma glucose. •No effect on lipid profiles •Te ...
... Inhibitors of Intestinal Glucose Absorption: Acarbose (Precose) and Miglitol (Glyset) • Acts as an -glucosidase inhibitor: prevent cleavage of disaccharides to monosaccharides in the intestine •Delays carbohydrate absorption and reduced postprandial plasma glucose. •No effect on lipid profiles •Te ...
SLG MOCK MIDTERM – FOR PRACTICE ONLY
... C) Large polar but uncharged molecules. D) All of the above. E) None of the above. 23. Which of the following statements about enzymes is true? A) The increase the rate of chemical reactions. B) They function as biological catalysts by lowering the activation energy. C) They regulate chemical reacti ...
... C) Large polar but uncharged molecules. D) All of the above. E) None of the above. 23. Which of the following statements about enzymes is true? A) The increase the rate of chemical reactions. B) They function as biological catalysts by lowering the activation energy. C) They regulate chemical reacti ...
Chapter 5 : MAJOR METABOLIC PATHWAYS
... When ATP levels are high in the cell, the cell no longer needs metabolic energy production to occur. In this case, PFK's activity is inhibited by allosteric regulation by ATP itself, closing the valve on the flow of carbohydrates through glycolysis. Recall that allosteric regulators bind to a differ ...
... When ATP levels are high in the cell, the cell no longer needs metabolic energy production to occur. In this case, PFK's activity is inhibited by allosteric regulation by ATP itself, closing the valve on the flow of carbohydrates through glycolysis. Recall that allosteric regulators bind to a differ ...
Relationship between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... Occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of eukaryotic cells C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + (36 ATP) (what is oxidixed?reduced?) Exergonic reaction- high energy molecule, glucose, produces low energy ...
... Occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of eukaryotic cells C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + (36 ATP) (what is oxidixed?reduced?) Exergonic reaction- high energy molecule, glucose, produces low energy ...
6-APA - Teknologi Industri Pertanian
... used in the treatment of hypertension The complex of boric acid with mannitol is used in the production of dry electrolytic capacitors It is an extensively used polyol for the production of resins and surfactants It has low solubility in water of only 18% (w/w) at 25 oC In alkaline solutions, it is ...
... used in the treatment of hypertension The complex of boric acid with mannitol is used in the production of dry electrolytic capacitors It is an extensively used polyol for the production of resins and surfactants It has low solubility in water of only 18% (w/w) at 25 oC In alkaline solutions, it is ...
Energy In A Cell
... • Excited electrons that leave chlorophyll molecules are used to produce new molecules that temporarily store chemical energy, including ATP. AN excited electron jumps to a nearby molecule in the thylakoid membrane • Then the electron is passed through a series of molecules along the thylakoid membr ...
... • Excited electrons that leave chlorophyll molecules are used to produce new molecules that temporarily store chemical energy, including ATP. AN excited electron jumps to a nearby molecule in the thylakoid membrane • Then the electron is passed through a series of molecules along the thylakoid membr ...
Energy In A Cell
... • Excited electrons that leave chlorophyll molecules are used to produce new molecules that temporarily store chemical energy, including ATP. AN excited electron jumps to a nearby molecule in the thylakoid membrane • Then the electron is passed through a series of molecules along the thylakoid membr ...
... • Excited electrons that leave chlorophyll molecules are used to produce new molecules that temporarily store chemical energy, including ATP. AN excited electron jumps to a nearby molecule in the thylakoid membrane • Then the electron is passed through a series of molecules along the thylakoid membr ...
Focus on Metabolism
... The chemical reactions of metabolism are facilitated by enzymes. These protein molecules catalyze, or speed up, the reactions. To be active, most enzymes require the assistance of helper molecules called cofactors. Some enzymes or enzyme complexes require more than one cofactor. Some cofactors are i ...
... The chemical reactions of metabolism are facilitated by enzymes. These protein molecules catalyze, or speed up, the reactions. To be active, most enzymes require the assistance of helper molecules called cofactors. Some enzymes or enzyme complexes require more than one cofactor. Some cofactors are i ...
Cellular Respiration
... race? Initially, creatine phosphate powers the muscles during the race. However, near the end of the race, the swimmer uses rapid breathing to restore the oxygen supply to the muscles. The lactate diffuses out of the muscles and into blood where it be carried to the liver for conversion to glucose. ...
... race? Initially, creatine phosphate powers the muscles during the race. However, near the end of the race, the swimmer uses rapid breathing to restore the oxygen supply to the muscles. The lactate diffuses out of the muscles and into blood where it be carried to the liver for conversion to glucose. ...
1 ENZYME KINETICS [APPLICATION OF UV
... glucose oxidase with a precise volume of other solutions. For better results, solutions should be used the same day. If storage is required, store at 4 0 for no longer than three days and allow to warm to room temperature prior to use. Prepare a 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer and adjust to pH 7.0 Pre ...
... glucose oxidase with a precise volume of other solutions. For better results, solutions should be used the same day. If storage is required, store at 4 0 for no longer than three days and allow to warm to room temperature prior to use. Prepare a 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer and adjust to pH 7.0 Pre ...
carbohydrate metabolism
... Skeletal muscle contains about 3 to 4 times more Glycogen store than Liver o Mass of skeletal muscle is much greater than mass of Liver ...
... Skeletal muscle contains about 3 to 4 times more Glycogen store than Liver o Mass of skeletal muscle is much greater than mass of Liver ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.