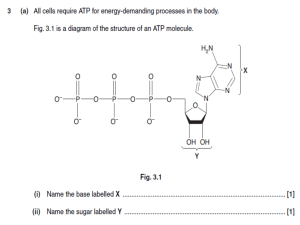
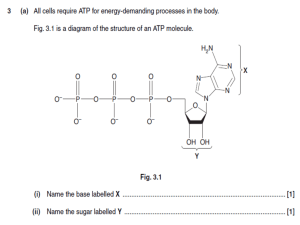
03-232 Biochemistry
... the energetically favorable reactions that were performed by different enzymes (and often regulated). 11. (12 pts) Please answer one of the following choices on pathway regulation: Choice A: Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis and the TCA cycle are each regulated by energy sensing. Choose one of these pathw ...
... the energetically favorable reactions that were performed by different enzymes (and often regulated). 11. (12 pts) Please answer one of the following choices on pathway regulation: Choice A: Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis and the TCA cycle are each regulated by energy sensing. Choose one of these pathw ...
1 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Introduction
... bacteria, live in environments that either lack or contain oxygen • either aerobic or anaerobic respiration ...
... bacteria, live in environments that either lack or contain oxygen • either aerobic or anaerobic respiration ...
1. Introduction and literature review
... 1.1. Glucose Glucose is primary energy source for the human .glucose is derived from the diet, through the digestion of dietary carbohydrate from body stores (glycogen) and from the endogenous synthesis of glucose from non carbohydrate sources (amino acid, glycerol, lactate ).Metabolism of carbohydr ...
... 1.1. Glucose Glucose is primary energy source for the human .glucose is derived from the diet, through the digestion of dietary carbohydrate from body stores (glycogen) and from the endogenous synthesis of glucose from non carbohydrate sources (amino acid, glycerol, lactate ).Metabolism of carbohydr ...
review on enhancement of glucose uptake and up
... adipocytes, and skeletal muscle cells. Medicinal plants or their active constituents that can up-regulate GLUT expression and translocation that helps in the treatment of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia. Evidence from insulin-resistant rodent models suggests that defective glucose transport in ...
... adipocytes, and skeletal muscle cells. Medicinal plants or their active constituents that can up-regulate GLUT expression and translocation that helps in the treatment of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia. Evidence from insulin-resistant rodent models suggests that defective glucose transport in ...
Respiration, Chapter 8
... • Oxidative Phosphorylation is the entire process of – ATP synthesis (by phosphorylation of ATP) coupled with the – Redox reactions in the Electron Transport Chain (which establishes the proton gradient needed to synthesize ATP) ...
... • Oxidative Phosphorylation is the entire process of – ATP synthesis (by phosphorylation of ATP) coupled with the – Redox reactions in the Electron Transport Chain (which establishes the proton gradient needed to synthesize ATP) ...
Metabolic flexibility and carnitine flux: The role of carnitine
... during fasting conditions to the suppression of lipid oxidation, and increased glucose uptake, oxidation and storage under insulin-stimulation. In contrast, metabolic inflexibility observed in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients is characterized by an inability of the organism to shift mitochondrial en ...
... during fasting conditions to the suppression of lipid oxidation, and increased glucose uptake, oxidation and storage under insulin-stimulation. In contrast, metabolic inflexibility observed in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients is characterized by an inability of the organism to shift mitochondrial en ...
Food Processing and Utilization
... preferred for catabolism because proteins and lipids are more important as structural components of cells and tissues. ...
... preferred for catabolism because proteins and lipids are more important as structural components of cells and tissues. ...
The Formation of Pyruvate from Citric Acid
... not be a major end product of glutamine metabolism in vivo. The substrate for rabbit tubules was a-oxoglutarate ( 5 mM) as neither glutamine nor glutamate gave satisfactory rates of gluconeogenesis, possibly due to inhibition of rabbit renal glutamate dehydrogenase by ammonia (see Klahr, 1971). The ...
... not be a major end product of glutamine metabolism in vivo. The substrate for rabbit tubules was a-oxoglutarate ( 5 mM) as neither glutamine nor glutamate gave satisfactory rates of gluconeogenesis, possibly due to inhibition of rabbit renal glutamate dehydrogenase by ammonia (see Klahr, 1971). The ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... (Nicotinamide andenine dinucleotide) : Delivers H and the high energy electrons released by redox reactions to electron carrier molecule of chain. ...
... (Nicotinamide andenine dinucleotide) : Delivers H and the high energy electrons released by redox reactions to electron carrier molecule of chain. ...
All the rest are carbohydrates.
... What are the two types of Nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids Press for answer.
Match each letter with
the correct group
...
... What are the two types of Nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids Press
How Cells Release Chemical Energy – Cellular Respiration
... Bacteria & yeast (unicellular fungus) use fermentation to produce: lactate or other organic acids alcohol (ethanol) and carbon dioxide yogurt, wine, beer, leavening of bread, ...
... Bacteria & yeast (unicellular fungus) use fermentation to produce: lactate or other organic acids alcohol (ethanol) and carbon dioxide yogurt, wine, beer, leavening of bread, ...
www.theallpapers.com
... Write in soft pencil. Do not use staples, paper clips, highlighters, glue or correction fluid. Write your name, Centre number and candidate number on the Answer Sheet in the spaces provided unless this has been done for you. There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. For each que ...
... Write in soft pencil. Do not use staples, paper clips, highlighters, glue or correction fluid. Write your name, Centre number and candidate number on the Answer Sheet in the spaces provided unless this has been done for you. There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. For each que ...
Chem 465 Biochemistry II
... Fructose 2,6-biphosphate is made from Fructose-6-P by the enzyme Phosphofructokinase-2 and is converted back to F-6-P by the enzyme fructose 2,6-biphosphatse-2. Both of these enzymatic activities are combined in one bifuctional protein that toggles between on activity and the other based on the phos ...
... Fructose 2,6-biphosphate is made from Fructose-6-P by the enzyme Phosphofructokinase-2 and is converted back to F-6-P by the enzyme fructose 2,6-biphosphatse-2. Both of these enzymatic activities are combined in one bifuctional protein that toggles between on activity and the other based on the phos ...
Canagliflozin, a New Sodium-Glucose Co
... Due to the progressive nature of type 2 diabetes, monotherapy with oral agents is associated with a high failure rate over approximately five years.7 Thus, the use of combination therapy consisting of agents with complementary mechanisms of action is important in maintaining glycemic control and min ...
... Due to the progressive nature of type 2 diabetes, monotherapy with oral agents is associated with a high failure rate over approximately five years.7 Thus, the use of combination therapy consisting of agents with complementary mechanisms of action is important in maintaining glycemic control and min ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... From here, pyruvate is eventually converted back to glucose and returned to muscle cells or stored as glycogen. ...
... From here, pyruvate is eventually converted back to glucose and returned to muscle cells or stored as glycogen. ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... From here, pyruvate is eventually converted back to glucose and returned to muscle cells or stored as glycogen. ...
... From here, pyruvate is eventually converted back to glucose and returned to muscle cells or stored as glycogen. ...
AP Biology PDQ`s
... 4. Is glucose the only molecule that can be catabolized during cellular respiration? Why do we use glucose as the model? 5. Why do hydrogen atoms accompany electrons as they are transferred in biological systems? 6. Why is it thought that glycolysis is the first catabolic pathway to have evolved in ...
... 4. Is glucose the only molecule that can be catabolized during cellular respiration? Why do we use glucose as the model? 5. Why do hydrogen atoms accompany electrons as they are transferred in biological systems? 6. Why is it thought that glycolysis is the first catabolic pathway to have evolved in ...
Metabolism and Nutrition
... Rise in blood glucose concentration stimulate insulin release from pancreatic beta cells. Insulin’s functions promotes entry of glucose into skeletal muscle & adipose tissue stimulates storage of glucose as glycogen in liver & muscle enhances synthesis of triglycerides in adipose tissue & liver Prom ...
... Rise in blood glucose concentration stimulate insulin release from pancreatic beta cells. Insulin’s functions promotes entry of glucose into skeletal muscle & adipose tissue stimulates storage of glucose as glycogen in liver & muscle enhances synthesis of triglycerides in adipose tissue & liver Prom ...
Lecture 33 - Carbohydrate Metabolism 1
... function enzyme called PFK-2/FBPase-2 When the PFK-2/FBPase-2 dual function enzyme is unphosphorylated, then the PFK-2 activity in the enzyme is stimulated resulting in the net phosphorylation of fructose-6P to produce more F-2,6-BP which stimulates glycolytic flux. In contrast, when PFK-2/FBPase-2 ...
... function enzyme called PFK-2/FBPase-2 When the PFK-2/FBPase-2 dual function enzyme is unphosphorylated, then the PFK-2 activity in the enzyme is stimulated resulting in the net phosphorylation of fructose-6P to produce more F-2,6-BP which stimulates glycolytic flux. In contrast, when PFK-2/FBPase-2 ...
1.18 Cellular Respiration
... Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are closely related. Plants carry out photosynthesis and cellular respiration because they contain chloroplasts and mitochondria. Animals can carry out cellular respiration but not photosynthesis because they possess mit ...
... Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are closely related. Plants carry out photosynthesis and cellular respiration because they contain chloroplasts and mitochondria. Animals can carry out cellular respiration but not photosynthesis because they possess mit ...
- WordPress.com
... Fructose is metabolized by A. fructose 1-phosphate pathway B. fructose 6-phosphate pathway C. glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate pathway D.both (a) and (b) Answer: Option D ...
... Fructose is metabolized by A. fructose 1-phosphate pathway B. fructose 6-phosphate pathway C. glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate pathway D.both (a) and (b) Answer: Option D ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.