Cellular Respiration
... 10. The second stage of cellular respiration, _______________, involves the creation of important electron-carriers needed to help synthesize ATP. a. the Krebs cycle b. glycolysis c. fermentation d. the electron transport chain 11. Which part of aerobic respiration produces the most ATP? a. the Kreb ...
... 10. The second stage of cellular respiration, _______________, involves the creation of important electron-carriers needed to help synthesize ATP. a. the Krebs cycle b. glycolysis c. fermentation d. the electron transport chain 11. Which part of aerobic respiration produces the most ATP? a. the Kreb ...
Document
... Principle: Barfoed test is Specific to Mono-saccharides – To differentiate between Monosaccharides (+ve) and Disaccharides (-ve). Barfoed reagent is formed from [Cu(CH3COO)2 + CH3COOH]. Reducing monosaccharides are oxidized by the copper ion in solution to form a carboxylic acid and a reddish precip ...
... Principle: Barfoed test is Specific to Mono-saccharides – To differentiate between Monosaccharides (+ve) and Disaccharides (-ve). Barfoed reagent is formed from [Cu(CH3COO)2 + CH3COOH]. Reducing monosaccharides are oxidized by the copper ion in solution to form a carboxylic acid and a reddish precip ...
Role of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4 in Regulation of Blood
... lower blood alanine levels and the importance of BCAAs as a source of amino groups for alanine formation. Liver glycogen levels are the same in wild-type and PDK4-/mice in the fed state but are lost more rapidly from the liver of PDK4-/- mice during fasting. Concentrations of glucose and intermedi ...
... lower blood alanine levels and the importance of BCAAs as a source of amino groups for alanine formation. Liver glycogen levels are the same in wild-type and PDK4-/mice in the fed state but are lost more rapidly from the liver of PDK4-/- mice during fasting. Concentrations of glucose and intermedi ...
Cellular Respiration
... broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of reactions. How much ATP is released during the Krebs cycle? ...
... broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of reactions. How much ATP is released during the Krebs cycle? ...
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
... resynthesizing ATP from ADP + P. The heart rate and respiratory rate must increase sufficiently to transport the required amount of O2 to the muscle cells, allowing glycogen to break down in the presence of oxygen. ...
... resynthesizing ATP from ADP + P. The heart rate and respiratory rate must increase sufficiently to transport the required amount of O2 to the muscle cells, allowing glycogen to break down in the presence of oxygen. ...
Electron transport chain
... Main Objective is discovering how cells use the energy stored in food molecules to make ATP. Catabolic pathways do not directly move anything, they are linked to work by a chemical drive shaft: ATP. ...
... Main Objective is discovering how cells use the energy stored in food molecules to make ATP. Catabolic pathways do not directly move anything, they are linked to work by a chemical drive shaft: ATP. ...
REPRODUCTION
... (COCs; within red square) within antral follicles are characterised as having compact cumulus vestments and are arrested at prophase I (germinal vesicle stage, GV) of meiosis (B). Maturation occurs in response to gonadotrophin surges in vivo or release of the COC in vitro and is characterised by (C) ...
... (COCs; within red square) within antral follicles are characterised as having compact cumulus vestments and are arrested at prophase I (germinal vesicle stage, GV) of meiosis (B). Maturation occurs in response to gonadotrophin surges in vivo or release of the COC in vitro and is characterised by (C) ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY - Illinois State University
... • Muscle lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvate to lactate • This reaction regenerates NAD+ for use by glyceraldehyde 3phosphate dehydrogenase in glycolysis • Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is transported to the liver • Liver lactate dehydrogenase can reconvert lactate to pyruva ...
... • Muscle lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvate to lactate • This reaction regenerates NAD+ for use by glyceraldehyde 3phosphate dehydrogenase in glycolysis • Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is transported to the liver • Liver lactate dehydrogenase can reconvert lactate to pyruva ...
accelerated glucose discoloration method
... D-glucose is a central substance for the human metabolism since it is a source of energy and a metabolic intermediate. Most of this energy is delivered through aerobic or anaerobic respiration. In human metabolism glucose is critical as a precursor for the production of proteins and in lipid metabol ...
... D-glucose is a central substance for the human metabolism since it is a source of energy and a metabolic intermediate. Most of this energy is delivered through aerobic or anaerobic respiration. In human metabolism glucose is critical as a precursor for the production of proteins and in lipid metabol ...
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle
... reduces NAD → NADH (stores energy) produces acetyl CoA ...
... reduces NAD → NADH (stores energy) produces acetyl CoA ...
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration Kreb`s Cycle
... reduces NAD NADH (stores energy) produces acetyl CoA ...
... reduces NAD NADH (stores energy) produces acetyl CoA ...
PDF
... the intracellular processes that occur during anaerobic homolactic fermentation. Perturbations in oxygen availability and especially the glucose concentrations are known to affect the intracellular concentrations of the adenosine phosphates in wild-type strains (Kresnowati et al., 2006). The drastic ...
... the intracellular processes that occur during anaerobic homolactic fermentation. Perturbations in oxygen availability and especially the glucose concentrations are known to affect the intracellular concentrations of the adenosine phosphates in wild-type strains (Kresnowati et al., 2006). The drastic ...
Cellular respiration
... – Muscles that are working hard enough to use up all the available oxygen ferment pyruvate to lactate – To regenerate NAD, muscle cells ferment pyruvate to lactate, using electrons from NADH and hydrogen ions – A variety of microorganisms use lactic acid fermentation, including the bacteria that co ...
... – Muscles that are working hard enough to use up all the available oxygen ferment pyruvate to lactate – To regenerate NAD, muscle cells ferment pyruvate to lactate, using electrons from NADH and hydrogen ions – A variety of microorganisms use lactic acid fermentation, including the bacteria that co ...
doc BIOC 311 Final Study Guide
... 4. UDP-galactose → UDP-glucose (via UDP-galactose-4-epimerase). a. This reaction can be reversed by coupling it to the hydrolysis of inorganic phosphate by inorganic phosphorylase (PPi → 2Pi). 5. Galactosemia (inability to metabolize galactose) can be caused by deficiency in one of three enzymes. a ...
... 4. UDP-galactose → UDP-glucose (via UDP-galactose-4-epimerase). a. This reaction can be reversed by coupling it to the hydrolysis of inorganic phosphate by inorganic phosphorylase (PPi → 2Pi). 5. Galactosemia (inability to metabolize galactose) can be caused by deficiency in one of three enzymes. a ...
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
... resynthesizing ATP from ADP + P. The heart rate and respiratory rate must increase sufficiently to transport the required amount of O2 to the muscle cells, allowing glycogen to break down in the presence of oxygen. ...
... resynthesizing ATP from ADP + P. The heart rate and respiratory rate must increase sufficiently to transport the required amount of O2 to the muscle cells, allowing glycogen to break down in the presence of oxygen. ...
Diabetes Mellitus
... Genetic predisposition • In an individual with a genetic predisposition, an event such as virus or toxin triggers autoimmune destruction of b-cells probably over a period of several years. ...
... Genetic predisposition • In an individual with a genetic predisposition, an event such as virus or toxin triggers autoimmune destruction of b-cells probably over a period of several years. ...
PHARMACODYNAMIC AND PHARMACOKINETIC DRUG INTERACTION OF GLICLAZIDE AND Research Article
... Drug interactions are usually seen in clinical practice and the mechanisms of interaction are evaluated usually in animal models. We studied the influence of risperidone on the pharmacodynamics of gliclazide in normal and diabetic rats and also in normal rabbits. Additonally pharmacokinetics of glic ...
... Drug interactions are usually seen in clinical practice and the mechanisms of interaction are evaluated usually in animal models. We studied the influence of risperidone on the pharmacodynamics of gliclazide in normal and diabetic rats and also in normal rabbits. Additonally pharmacokinetics of glic ...
2 ATP - Loyola Blakefield
... How does your body feel at the start of exercise, such as a long slow run? How do you feel 1 minute into the run; 10 minutes into the run? ...
... How does your body feel at the start of exercise, such as a long slow run? How do you feel 1 minute into the run; 10 minutes into the run? ...
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
... • while at the same time reducing NAD to NADH. • NADH can be used by the electron transport chain to create further ATP as part of oxidative phosphorylation. ...
... • while at the same time reducing NAD to NADH. • NADH can be used by the electron transport chain to create further ATP as part of oxidative phosphorylation. ...
Physiology 8 Endocrine and Gastroenterology
... Regarding the basal metabolic rate, which of the following is TRUE? a) it is measured in the absence of disease, at room temperature, within 12 hours of a meal with a Benedict apparatus and the subject asleep b) it increases 24% per degree Celsius of body temperature above 37° c) it is decreased dur ...
... Regarding the basal metabolic rate, which of the following is TRUE? a) it is measured in the absence of disease, at room temperature, within 12 hours of a meal with a Benedict apparatus and the subject asleep b) it increases 24% per degree Celsius of body temperature above 37° c) it is decreased dur ...
Biochemistry - Grade12BiologyCALC
... monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides? Give an example of each. ...
... monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides? Give an example of each. ...
Cellular Respiration
... •Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration The second stage of cellular respiration is either aerobic respiration (in the presence of oxygen) or anaerobic respiration (in the absence of oxygen). A large amount of ATP is made during aerobic respiration. NAD+ is recycled during the anaerobic process of fermen ...
... •Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration The second stage of cellular respiration is either aerobic respiration (in the presence of oxygen) or anaerobic respiration (in the absence of oxygen). A large amount of ATP is made during aerobic respiration. NAD+ is recycled during the anaerobic process of fermen ...
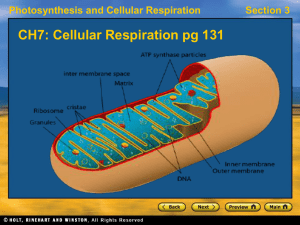
CH7Cellular-Respiration
... Efficiency of Cellular Respiration • In the first stage of cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to pyruvate during glycolysis, an anaerobic process. • Glycolysis results in 2 ATP molecules for each glucose molecule that is broken down. • In the 2nd stage, pyruvate EITHER passes through the ...
... Efficiency of Cellular Respiration • In the first stage of cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to pyruvate during glycolysis, an anaerobic process. • Glycolysis results in 2 ATP molecules for each glucose molecule that is broken down. • In the 2nd stage, pyruvate EITHER passes through the ...
7.014 Quiz I Handout
... i) What is the Keq for the coupled reaction (4) in terms of the Keq of reaction (2), at 25° C? Show your work. ...
... i) What is the Keq for the coupled reaction (4) in terms of the Keq of reaction (2), at 25° C? Show your work. ...
Review Questions
... d. energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase e. No external source of energy is required because the reaction is exergonic. ____ 17. Approximately what percentage of the energy of glucose ( ) is transferred to storage in ATP as a result of the complete oxidation of glucose to and ...
... d. energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase e. No external source of energy is required because the reaction is exergonic. ____ 17. Approximately what percentage of the energy of glucose ( ) is transferred to storage in ATP as a result of the complete oxidation of glucose to and ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.