Slide 1
... – Pay-off phase!! (Get 28 ATPs) – Electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 are deposited into ETC to generate ATP by chemiosmosis. – Each NADH = 2.5 ATPs (x10 = 25 ATP) – Each FADH2 = 1.5 ATPs (x2 = 3 ATP) ...
... – Pay-off phase!! (Get 28 ATPs) – Electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 are deposited into ETC to generate ATP by chemiosmosis. – Each NADH = 2.5 ATPs (x10 = 25 ATP) – Each FADH2 = 1.5 ATPs (x2 = 3 ATP) ...
RESPIRATION IN PLANTS
... Significance of fermentation Fermentation has a number of industrial applications. It is made use of on a large scale in certain industries. Micro-organisms like the different strains of bacteria and yeast are cultured in very large numbers and used for various purposes. 1. In bakeries for preparing ...
... Significance of fermentation Fermentation has a number of industrial applications. It is made use of on a large scale in certain industries. Micro-organisms like the different strains of bacteria and yeast are cultured in very large numbers and used for various purposes. 1. In bakeries for preparing ...
Biochemistry Spring 2015 Exam III Name: Points
... Choice B. What is the most likely secondary structure(s) of any proteins that are inserted into the membrane? Why? ...
... Choice B. What is the most likely secondary structure(s) of any proteins that are inserted into the membrane? Why? ...
Electron transport chain
... • Only 4 of 38 ATP ultimately produced by respiration of glucose are derived from substrate-level phosphorylation (2 from glycolysis and 2 from Krebs Cycle). • The vast majority of the ATP (90%) comes from the energy in the electrons carried by NADH and FADH2. • The energy in these electrons is used ...
... • Only 4 of 38 ATP ultimately produced by respiration of glucose are derived from substrate-level phosphorylation (2 from glycolysis and 2 from Krebs Cycle). • The vast majority of the ATP (90%) comes from the energy in the electrons carried by NADH and FADH2. • The energy in these electrons is used ...
The Many Faces of Carbohydrate Metabolism in Male Germ Cells
... have dual properties according its concentration. At 800 µM DHA, after 48 h of treatment, it has the capacity to indirectly stimulate NADPH, via the pentose phosphate pathway, and subsequent glutathione synthesis (Puskas et al., 2000). These activities of DHA molecules (or ascorbic acid oxidation) s ...
... have dual properties according its concentration. At 800 µM DHA, after 48 h of treatment, it has the capacity to indirectly stimulate NADPH, via the pentose phosphate pathway, and subsequent glutathione synthesis (Puskas et al., 2000). These activities of DHA molecules (or ascorbic acid oxidation) s ...
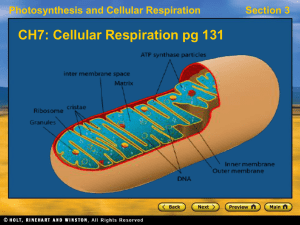
Cellular Respiration (Text Book)
... • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration • Each NADH (the reduce ...
... • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration • Each NADH (the reduce ...
Revision Questions What is the definition of energy and what are the
... 9. Give an overview of how ATP is produced in the ATP/PCr energy system. This system is only capable of producing energy for short duration in activities that demand large amounts of energy. As PC is stored in the muscle it is readily accessible as an energy source and can produce energy very rapid ...
... 9. Give an overview of how ATP is produced in the ATP/PCr energy system. This system is only capable of producing energy for short duration in activities that demand large amounts of energy. As PC is stored in the muscle it is readily accessible as an energy source and can produce energy very rapid ...
ATP
... 2. 12 Three-carbon molecules formed: ATP and NADPH use enzymes in the stroma to split the six carbon into 3 carbon sugars. 3. 2 Three-carbon sugars removed to make a glucose: The other 3 carbon molecules (10) stay in cycle. When 2 leave, they form glucose. 4. Three-carbon molecules recycled: Energy ...
... 2. 12 Three-carbon molecules formed: ATP and NADPH use enzymes in the stroma to split the six carbon into 3 carbon sugars. 3. 2 Three-carbon sugars removed to make a glucose: The other 3 carbon molecules (10) stay in cycle. When 2 leave, they form glucose. 4. Three-carbon molecules recycled: Energy ...
The Skinny on Low-Carbohydrate Diets
... Does a VLCarb Diet result in loss of muscle mass? • Protein needed for gluconeogenesis • BUT, liver makes ketones (which it can’t use), so ketones flow to extra-hepatic tissues (brain, muscle) for fuel • Ketones displace glucose utilization by the brain, thus sparing muscle mass. • The brain deri ...
... Does a VLCarb Diet result in loss of muscle mass? • Protein needed for gluconeogenesis • BUT, liver makes ketones (which it can’t use), so ketones flow to extra-hepatic tissues (brain, muscle) for fuel • Ketones displace glucose utilization by the brain, thus sparing muscle mass. • The brain deri ...
Blueberry Intake Alters Skeletal Muscle and Adipose
... phenotypes such as obesity, systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and hyperlipidemia. A recent epidemiological study indicated that blueberry intake reduced cardiovascular mortality in humans, but the possible genetic mechanisms of this effect are unknown. Blueberries are a rich source of antho ...
... phenotypes such as obesity, systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and hyperlipidemia. A recent epidemiological study indicated that blueberry intake reduced cardiovascular mortality in humans, but the possible genetic mechanisms of this effect are unknown. Blueberries are a rich source of antho ...
Ch 9 Cell Respiration HW Packet
... Chemical Energy and Food - Chemical energy is stored in food molecules. Energy is released when chemical bonds in food molecules are broken. Energy is measured in a unit called a calorie, the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1Celsius. Fats store more energy ...
... Chemical Energy and Food - Chemical energy is stored in food molecules. Energy is released when chemical bonds in food molecules are broken. Energy is measured in a unit called a calorie, the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1Celsius. Fats store more energy ...
Regulation of Glycolysis
... Because the principle function of glycolysis is to produce ATP, it must be regulated so that ATP is generated only when needed. The enzyme which controls the flux of metabolites through the glycolytic pathway is phosphofructokinase (PFK-1). PFK-1 is an allosteric enzyme that occupies the key regulat ...
... Because the principle function of glycolysis is to produce ATP, it must be regulated so that ATP is generated only when needed. The enzyme which controls the flux of metabolites through the glycolytic pathway is phosphofructokinase (PFK-1). PFK-1 is an allosteric enzyme that occupies the key regulat ...
Quiz Ch 6
... During intense exercise, this lactic is produced faster than is can be removed from the muscles, used to be thought this is what made you sore the next day ...
... During intense exercise, this lactic is produced faster than is can be removed from the muscles, used to be thought this is what made you sore the next day ...
Citric Acid Cycle Regulation
... Lactate is then shipped out of muscle, into blood stream to liver. When reaches liver, Lactate (muscle) Lactate (liver) ...
... Lactate is then shipped out of muscle, into blood stream to liver. When reaches liver, Lactate (muscle) Lactate (liver) ...
Lecture 2 – Week 7 Control of Microbial Growth
... – Carbohydrate: Each broth contains a single fermentable carbohydrate (glucose, lactose, sucrose). – Peptone: protein derivatives (other food for bacteria) – Phenol-Red: This is a pH indicator that is RED at pH 7 or higher (alkaline) but turns YELLOW at low pH (acidic). The broth is initially pH neu ...
... – Carbohydrate: Each broth contains a single fermentable carbohydrate (glucose, lactose, sucrose). – Peptone: protein derivatives (other food for bacteria) – Phenol-Red: This is a pH indicator that is RED at pH 7 or higher (alkaline) but turns YELLOW at low pH (acidic). The broth is initially pH neu ...
Glucose-Fatty Acid Interaction in Skeletal Muscle and Adipose
... reflection of the glucose disposal by the muscles (60-70 %) (DeFronzo et al. 1992) while adipose tissue only accounts for about 10 % of whole-body insulinstimulated glucose uptake (Smith 2002). This fact has led to the extrapolation that whole body insulin resistance not only occurs in muscles, but ...
... reflection of the glucose disposal by the muscles (60-70 %) (DeFronzo et al. 1992) while adipose tissue only accounts for about 10 % of whole-body insulinstimulated glucose uptake (Smith 2002). This fact has led to the extrapolation that whole body insulin resistance not only occurs in muscles, but ...
You Light Up My Life
... • Carried out by certain bacteria • Electron transfer chain is in bacterial plasma membrane • Final electron acceptor is compound from environment (such as nitrate), not oxygen • ATP yield is low ...
... • Carried out by certain bacteria • Electron transfer chain is in bacterial plasma membrane • Final electron acceptor is compound from environment (such as nitrate), not oxygen • ATP yield is low ...
Cellular Respiration
... Aerobic Respiration • 1st stage is the Krebs cycle – a series of reactions that produce electron carriers • (NADH and FADH2) ...
... Aerobic Respiration • 1st stage is the Krebs cycle – a series of reactions that produce electron carriers • (NADH and FADH2) ...
Chapter 9 Notes
... • Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space • H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through the proton, ATP synthase • ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP • Th ...
... • Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space • H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through the proton, ATP synthase • ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP • Th ...
nutrition, metabolism, and body temperature
... butter or stick margarine, this also counts as part of the discretionary calorie allowance. Click here for more details on discretionary calories. Select fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, trout, and herring, more often (See Why is it important to include fish, nuts, and seeds?). Live ...
... butter or stick margarine, this also counts as part of the discretionary calorie allowance. Click here for more details on discretionary calories. Select fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, trout, and herring, more often (See Why is it important to include fish, nuts, and seeds?). Live ...
L6 Cellular Respiration
... CO2 leaves cycle NAD+ The citric acid cycle yields One ATP from each acetyl CoA that enters the cycle, for a net gain of two ATP. ...
... CO2 leaves cycle NAD+ The citric acid cycle yields One ATP from each acetyl CoA that enters the cycle, for a net gain of two ATP. ...
Lipid Metabolism 1. What has a higher stored energy potential per
... 4. No, because animals cannot convert acetyl CoA to pyruvate. The only major source of stored energy for glucose production is amino acids or OAA. Note that the glycerol component of triglycerides does contribute in a minor way to carbohydrate production, but the fast majority of stored energy in fa ...
... 4. No, because animals cannot convert acetyl CoA to pyruvate. The only major source of stored energy for glucose production is amino acids or OAA. Note that the glycerol component of triglycerides does contribute in a minor way to carbohydrate production, but the fast majority of stored energy in fa ...
Human Physiology - Coastline Community College
... In absence of O2, NADH gives its Hs to pyruvate creating Lactic acid (Anaerobic Respiration) In ...
... In absence of O2, NADH gives its Hs to pyruvate creating Lactic acid (Anaerobic Respiration) In ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.