Research Interest
... age 6 to 17 years: prevalence, amounts, and sources, 1977/78 to 1994/1998. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. 2003;103:1326-1331. Funari, VA, et al. Fructose metabolism in the cerebellum. The Cerebellum. 2007;6:130140. Gao X, et al. Intake of added sugar and sugar-sweetened drink and seru ...
... age 6 to 17 years: prevalence, amounts, and sources, 1977/78 to 1994/1998. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. 2003;103:1326-1331. Funari, VA, et al. Fructose metabolism in the cerebellum. The Cerebellum. 2007;6:130140. Gao X, et al. Intake of added sugar and sugar-sweetened drink and seru ...
Cellular Energy
... intermembrane space creates a high H+ (pH = 7) concentration in the intermembrane space and a low H+ (pH = 8) concentration in the matrix – this proton gradient becomes the source of energy used by the mitochondria to synthesize ATP, which is released as H+ diffuse from the intermembrane space back ...
... intermembrane space creates a high H+ (pH = 7) concentration in the intermembrane space and a low H+ (pH = 8) concentration in the matrix – this proton gradient becomes the source of energy used by the mitochondria to synthesize ATP, which is released as H+ diffuse from the intermembrane space back ...
lopez 09_Lecture_Presentation
... CALLED THE REDUCING AGENT (THIS IS THE OIL PART) THE ELECTRON RECEPTOR IS CALLED THE OXIDIZING AGENT (THIS IS THE RIG PART) SOME REDOX REACTIONS DO NOT TRANSFER ELECTRONS BUT CHANGE THE ELECTRON SHARING IN COVALENT BONDS AN EXAMPLE IS THE REACTION BETWEEN Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., ...
... CALLED THE REDUCING AGENT (THIS IS THE OIL PART) THE ELECTRON RECEPTOR IS CALLED THE OXIDIZING AGENT (THIS IS THE RIG PART) SOME REDOX REACTIONS DO NOT TRANSFER ELECTRONS BUT CHANGE THE ELECTRON SHARING IN COVALENT BONDS AN EXAMPLE IS THE REACTION BETWEEN Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., ...
Lecture 5 - Fermentation and CHO feeder
... (stored as glycogen) The process of transporting lactate to the liver and its conversion to glucose takes from hours to days to complete. ...
... (stored as glycogen) The process of transporting lactate to the liver and its conversion to glucose takes from hours to days to complete. ...
Enzymes
... with, for example, a low constant activity provided by one enzyme but an inducible high activity from a second enzyme. Enzymes determine what steps occur in these pathways. Without enzymes, metabolism would neither progress through the same steps nor be fast enough to serve the needs of the cell. In ...
... with, for example, a low constant activity provided by one enzyme but an inducible high activity from a second enzyme. Enzymes determine what steps occur in these pathways. Without enzymes, metabolism would neither progress through the same steps nor be fast enough to serve the needs of the cell. In ...
Flux distributions in anaerobic, glucose-limited
... substrates from the medium, the secretion of products from the cells, and of the rate of biomass formation. Furthermore, measurements of the biomass composition and of the activity of key enzymes were used in the calculations. The stoichiometric network consists of 37 pathway reactions involving 43 ...
... substrates from the medium, the secretion of products from the cells, and of the rate of biomass formation. Furthermore, measurements of the biomass composition and of the activity of key enzymes were used in the calculations. The stoichiometric network consists of 37 pathway reactions involving 43 ...
2.8 Respiration - biology4friends
... 2.8.A1 Use of anaerobic cell respiration in yeasts to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide in baking. 16. Describe how and why yeast is used in bread making. ...
... 2.8.A1 Use of anaerobic cell respiration in yeasts to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide in baking. 16. Describe how and why yeast is used in bread making. ...
Biochemistry of the liver - Univerzita Karlova v Praze
... The figure was adopted from: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 ...
... The figure was adopted from: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 ...
APB Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... The electron transport chain consists of several molecules (primarily proteins) built into the inner cristae membrane of a mitochondrion of eukaryotic cells and the plasma membrane of aerobically respiring prokaryotes. ...
... The electron transport chain consists of several molecules (primarily proteins) built into the inner cristae membrane of a mitochondrion of eukaryotic cells and the plasma membrane of aerobically respiring prokaryotes. ...
Ch 8 Cellular Respiration
... -net yield of 32 or 34 ATP per glucose molecule - 6 H2O are formed when the electrons unite with O2* at the end of electron transport chain. * We breath because we need oxygen as the final electron acceptor! The resulting ATP is able to leave the mitochondria by the ATP transport protein in the mem ...
... -net yield of 32 or 34 ATP per glucose molecule - 6 H2O are formed when the electrons unite with O2* at the end of electron transport chain. * We breath because we need oxygen as the final electron acceptor! The resulting ATP is able to leave the mitochondria by the ATP transport protein in the mem ...
THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... The oxaloacetate then reacts with acetyl CoA forming the unstable compound, citryl CoA The formation of citryl CoA causes the enzyme to completely close and brings enzyme residues in close contact so that water can hydrolyze off the CoA After desorbing CoA and citrate, the enzyme returns to its open ...
... The oxaloacetate then reacts with acetyl CoA forming the unstable compound, citryl CoA The formation of citryl CoA causes the enzyme to completely close and brings enzyme residues in close contact so that water can hydrolyze off the CoA After desorbing CoA and citrate, the enzyme returns to its open ...
Cellular Respiration
... 9.2 Glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate • Glycolysis can occur whether or not O2 is present. o If O2 is present, the chemical energy stored in pyruvate and NADH can be extracted by the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation o More than 75% of the original e ...
... 9.2 Glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate • Glycolysis can occur whether or not O2 is present. o If O2 is present, the chemical energy stored in pyruvate and NADH can be extracted by the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation o More than 75% of the original e ...
Cellular Respiration - MF011 General Biology 2 (May 2011 Semester)
... Both processes use glycolysis to oxidize glucose and other organic fuels to pyruvate The processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in fermentation and O2 in cellular respiration Cellular respiration produces 38 ATP per glucose molecule; ...
... Both processes use glycolysis to oxidize glucose and other organic fuels to pyruvate The processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in fermentation and O2 in cellular respiration Cellular respiration produces 38 ATP per glucose molecule; ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_5_lecture
... 5. Pyruvic acid is then converted to glucose 6phosphate. a. This can be used to make glycogen or glucose b. Pyruvic acid Glucose = gluconeogenesis (making “new” glucose from noncarbohydrate molecules) c. Glucose is carried in the blood to the muscle cells, which completes the Cori Cycle. ...
... 5. Pyruvic acid is then converted to glucose 6phosphate. a. This can be used to make glycogen or glucose b. Pyruvic acid Glucose = gluconeogenesis (making “new” glucose from noncarbohydrate molecules) c. Glucose is carried in the blood to the muscle cells, which completes the Cori Cycle. ...
harvesting chemical energy
... The acetyl group of acetyl CoA joins the cycle by combining with the compound oxaloacetate, forming citrate. The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate. It is the regeneration of oxaloacetate that makes this process a cycle. Three CO2 molecules are released, including the ...
... The acetyl group of acetyl CoA joins the cycle by combining with the compound oxaloacetate, forming citrate. The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate. It is the regeneration of oxaloacetate that makes this process a cycle. Three CO2 molecules are released, including the ...
AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... A) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it does not require oxygen. B) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it is not located in a membrane-bound organelle. C) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it occu ...
... A) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it does not require oxygen. B) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it is not located in a membrane-bound organelle. C) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it occu ...
Obtaining Food
... teaching. However, please notice that some of the images in these slides have an associated URL photo credit to provide you with the location of their original source within internet cyberspace. Those images may have separate copyright protection. If you are seeking permission for use of those image ...
... teaching. However, please notice that some of the images in these slides have an associated URL photo credit to provide you with the location of their original source within internet cyberspace. Those images may have separate copyright protection. If you are seeking permission for use of those image ...
lecture 6 ppt
... Given an equation, particularly that for cellular respiration, determine which molecules are oxidized and reduced ...
... Given an equation, particularly that for cellular respiration, determine which molecules are oxidized and reduced ...
Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration
... This takes place in the mitochondria One carbon is lost (in the form of CO2) to form an acetyl molecule Acetyl joins to a carrier called coenzyme A to form ...
... This takes place in the mitochondria One carbon is lost (in the form of CO2) to form an acetyl molecule Acetyl joins to a carrier called coenzyme A to form ...
Document
... • Carbohydrate Catabolism – Many organisms oxidize carbohydrates as primary energy source for anabolic reactions – Glucose most common carbohydrate used – Glucose catabolized by two processes: cellular respiration and fermentation ...
... • Carbohydrate Catabolism – Many organisms oxidize carbohydrates as primary energy source for anabolic reactions – Glucose most common carbohydrate used – Glucose catabolized by two processes: cellular respiration and fermentation ...
7 | cellular respiration
... specificity that catalyzes the phosphorylation of six-carbon sugars. Hexokinase phosphorylates glucose using ATP as the source of the phosphate, producing glucose-6-phosphate, a more reactive form of glucose. This reaction prevents the phosphorylated glucose molecule from continuing to interact with ...
... specificity that catalyzes the phosphorylation of six-carbon sugars. Hexokinase phosphorylates glucose using ATP as the source of the phosphate, producing glucose-6-phosphate, a more reactive form of glucose. This reaction prevents the phosphorylated glucose molecule from continuing to interact with ...
4:6 Fermentation
... 4.6 Fermentation • Alcoholic fermentation is similar to lactic acid fermentation. – glycolysis splits glucose and the products enter fermentation – energy from NADH is used to split pyruvate into an alcohol and carbon dioxide – NADH is changed back into NAD+ – NAD+ is recycled to glycolysis ...
... 4.6 Fermentation • Alcoholic fermentation is similar to lactic acid fermentation. – glycolysis splits glucose and the products enter fermentation – energy from NADH is used to split pyruvate into an alcohol and carbon dioxide – NADH is changed back into NAD+ – NAD+ is recycled to glycolysis ...
Cell Respiration Power Point
... ATP for energy ATP powers cellular work- made in photosynthesis and cellular respiration A cell does three main kinds of work: Mechanical work, beating of cilia, contraction of muscle cells, and movement of ...
... ATP for energy ATP powers cellular work- made in photosynthesis and cellular respiration A cell does three main kinds of work: Mechanical work, beating of cilia, contraction of muscle cells, and movement of ...
Cellular Respiration Explained
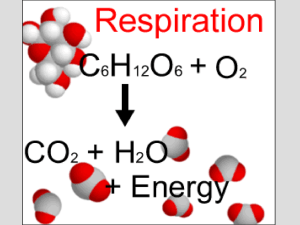
... made? The answer is in the mitochondria of cells. The overall reaction is C6H12O6 + 6O2→6CO2+ 6H2O+ Energy (ATP+ Heat). Notice that oxygen is required. When oxygen is used, it is called aerobic respiration. ANAEROBIC Respiration is called fermentation. No O2 used in fermentation. Without O2 there is ...
... made? The answer is in the mitochondria of cells. The overall reaction is C6H12O6 + 6O2→6CO2+ 6H2O+ Energy (ATP+ Heat). Notice that oxygen is required. When oxygen is used, it is called aerobic respiration. ANAEROBIC Respiration is called fermentation. No O2 used in fermentation. Without O2 there is ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.