Chapter 9 - H-W Science Website
... difficulty explaining the relationship of breathing and digestion to cellular respiration. Students may be confused by terms that have familiar, everyday meanings distinct from their biological definitions. The term respiration is particularly confusing, because it is an everyday term with two biolo ...
... difficulty explaining the relationship of breathing and digestion to cellular respiration. Students may be confused by terms that have familiar, everyday meanings distinct from their biological definitions. The term respiration is particularly confusing, because it is an everyday term with two biolo ...
metabolism - anatomymodelimages
... 1. Glucose – all carbohydrates are broken down to; taken up by body cells *All carbohydrates are broken down to this: a. glucagon b. glucose c. glycine d. glycogen 2. Glucose-6-phosphate – 1 ATP -ADP; trapped in all but liver, kidney, intestine cell 3. Glucose oxidation – cellular respiration; ATP p ...
... 1. Glucose – all carbohydrates are broken down to; taken up by body cells *All carbohydrates are broken down to this: a. glucagon b. glucose c. glycine d. glycogen 2. Glucose-6-phosphate – 1 ATP -ADP; trapped in all but liver, kidney, intestine cell 3. Glucose oxidation – cellular respiration; ATP p ...
LB Metabolic Diseases
... from fatty acid ßoxidation is either: 1) oxidized in TCA 2) repackaged 3) forms ketones ...
... from fatty acid ßoxidation is either: 1) oxidized in TCA 2) repackaged 3) forms ketones ...
What agents? What war?
... oxidized via the citric acid cycle to CO2 and H2O [NADH acts as a high energy compound] 2. Under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate must be converted to a reduced end product in order to reoxidize the NADH produced by the GAPDH reaction • alcoholic fermentation: in yeast, pyruvate is converted to ethano ...
... oxidized via the citric acid cycle to CO2 and H2O [NADH acts as a high energy compound] 2. Under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate must be converted to a reduced end product in order to reoxidize the NADH produced by the GAPDH reaction • alcoholic fermentation: in yeast, pyruvate is converted to ethano ...
breakdown of complex organic molecules into the simplest, stable
... infinite number of enzymes would be needed --- lignin degradation occurs in the same way it is formed, by random free radical attack via peroxidases produced by some bacteria and fungi --- woody plants use lignin as a means of defending and supporting cellulose fibers, lignin degradation is a slow p ...
... infinite number of enzymes would be needed --- lignin degradation occurs in the same way it is formed, by random free radical attack via peroxidases produced by some bacteria and fungi --- woody plants use lignin as a means of defending and supporting cellulose fibers, lignin degradation is a slow p ...
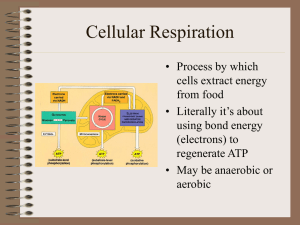
Cellular Respiration
... The Krebs cycle extracts the energy of sugar by breaking the acetic acid molecules all the way down to CO2 The cycle uses some of this energy to make ATP The cycle also forms NADH and FADH2 ( 2 energy carrier molecules) ...
... The Krebs cycle extracts the energy of sugar by breaking the acetic acid molecules all the way down to CO2 The cycle uses some of this energy to make ATP The cycle also forms NADH and FADH2 ( 2 energy carrier molecules) ...
Organic Molecules
... X is used to represent an unnamed molecule that the functional group is attached to. ...
... X is used to represent an unnamed molecule that the functional group is attached to. ...
Metabolic changes in Diabetes mellitus (DM)
... • The hemoglobin A1C percentage is a way of looking at average blood sugar control over a period of 3 months. • When plasma glucose is episodically elevated over time, small amounts of hemoglobin A are nonenzymatically glycosylated to form HbA1C. • Red blood cells live 90 to 120 days. This means tha ...
... • The hemoglobin A1C percentage is a way of looking at average blood sugar control over a period of 3 months. • When plasma glucose is episodically elevated over time, small amounts of hemoglobin A are nonenzymatically glycosylated to form HbA1C. • Red blood cells live 90 to 120 days. This means tha ...
pentose phosphate pathway
... buildup of lactate and NADH, due to oxygen shortage and the need for more glycolysis. NADH can be reoxidized during the reduction of pyruvate to lactate. Lactate is then returned to the liver, where it can be reoxidized to pyruvate by liver LDH. Liver provides glucose to muscle for exercise an ...
... buildup of lactate and NADH, due to oxygen shortage and the need for more glycolysis. NADH can be reoxidized during the reduction of pyruvate to lactate. Lactate is then returned to the liver, where it can be reoxidized to pyruvate by liver LDH. Liver provides glucose to muscle for exercise an ...
File
... Label the cuticle (used twice), epidermis (used twice) , guard cell, chloroplast, and stomata below. ...
... Label the cuticle (used twice), epidermis (used twice) , guard cell, chloroplast, and stomata below. ...
Sample Exam #1 ( file)
... Which of the following is NOT correct about amino acids? A. Amino acids contain asymmetric carbon atoms. B. Amino acids contain an amino group and a carboxyl group fastened to an asymmetric carbon. C. Amino acids can make peptide bonds. D. There are over 30 kinds of individual amino acids found in t ...
... Which of the following is NOT correct about amino acids? A. Amino acids contain asymmetric carbon atoms. B. Amino acids contain an amino group and a carboxyl group fastened to an asymmetric carbon. C. Amino acids can make peptide bonds. D. There are over 30 kinds of individual amino acids found in t ...
CHAPTER 7 _3_ - Doral Academy Preparatory
... reactions that give off CO2 and produce one ATP per cycle Turns twice per glucose molecule Produces two ATP Takes place in matrix of ...
... reactions that give off CO2 and produce one ATP per cycle Turns twice per glucose molecule Produces two ATP Takes place in matrix of ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Review
... 15. Is the phosphorylation reaction in the Krebs cycle substrate level or oxidative? 16. How is FADH2 similar to the NADH produced during glycolysis? 17. How is the structure of the mitochondrion suited to its function? 18. As electrons are passed along the ETC they lose energy. Where does this ener ...
... 15. Is the phosphorylation reaction in the Krebs cycle substrate level or oxidative? 16. How is FADH2 similar to the NADH produced during glycolysis? 17. How is the structure of the mitochondrion suited to its function? 18. As electrons are passed along the ETC they lose energy. Where does this ener ...
Introduction to Cellular Respiration •ATP is needed in order for cells
... •Free glucose is not the most common source of fuel in most animal diets, including the human diet. Each of the basic food types can be used as a source of energy. •Carbohydrates such as polysaccharides and glycogen are usually hydrolyzed by digestive enzymes to glucose, which enters glycolysis. ...
... •Free glucose is not the most common source of fuel in most animal diets, including the human diet. Each of the basic food types can be used as a source of energy. •Carbohydrates such as polysaccharides and glycogen are usually hydrolyzed by digestive enzymes to glucose, which enters glycolysis. ...
Introduction to Cellular Respiration •ATP is needed in order for cells
... •Free glucose is not the most common source of fuel in most animal diets, including the human diet. Each of the basic food types can be used as a source of energy. •Carbohydrates such as polysaccharides and glycogen are usually hydrolyzed by digestive enzymes to glucose, which enters glycolysis. ...
... •Free glucose is not the most common source of fuel in most animal diets, including the human diet. Each of the basic food types can be used as a source of energy. •Carbohydrates such as polysaccharides and glycogen are usually hydrolyzed by digestive enzymes to glucose, which enters glycolysis. ...
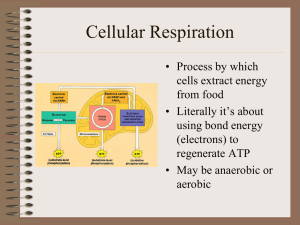
Cellular Respiration
... Glycolysis • 6C glucose split • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
... Glycolysis • 6C glucose split • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
SCI_7726_files/Cellular Respiration
... Glycolysis • 6C glucose split • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
... Glycolysis • 6C glucose split • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
Energy For Movement - Illinois Wesleyan University
... This process is rapid Does not require oxygen (O2) and is therefore anaerobic. Can only sustain maximum muscle work for 3-15 seconds. ...
... This process is rapid Does not require oxygen (O2) and is therefore anaerobic. Can only sustain maximum muscle work for 3-15 seconds. ...
METABOLISM - Doctor Jade Main
... electrons are transferred from sugar to O2 making H2O 6C6H12O2 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP do not see electron transfer in equation see changes in H ions glucose molecule loses hydrogen atoms as it is converted to CO2 O2 gains hydrogen atoms to form water O2 is an electron grabber – pulls harder th ...
... electrons are transferred from sugar to O2 making H2O 6C6H12O2 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP do not see electron transfer in equation see changes in H ions glucose molecule loses hydrogen atoms as it is converted to CO2 O2 gains hydrogen atoms to form water O2 is an electron grabber – pulls harder th ...
Biology 231
... joined almost entirely by covalent bonds may be very large and structurally complex carbon skeleton – chain of carbon atoms; each can form 4 covalent bonds functional groups – other atoms in specific arrangements attached to carbon skeleton; confer characteristic chemical properties CLASSES OF ORGAN ...
... joined almost entirely by covalent bonds may be very large and structurally complex carbon skeleton – chain of carbon atoms; each can form 4 covalent bonds functional groups – other atoms in specific arrangements attached to carbon skeleton; confer characteristic chemical properties CLASSES OF ORGAN ...
SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY - Georgia Institute of Technology
... Glycogen Phosphorylase cAMP activates PKA Glucagon stimulates this process ...
... Glycogen Phosphorylase cAMP activates PKA Glucagon stimulates this process ...
Glucose and ATP - cloudfront.net
... ATP molecules store smaller quantities of energy, but each releases just the right amount to actually do work within a cell. Muscle cell proteins, for example, pull each other with the energy released when bonds in ATP break open (discussed below). The process of photosynthesis also makes and uses A ...
... ATP molecules store smaller quantities of energy, but each releases just the right amount to actually do work within a cell. Muscle cell proteins, for example, pull each other with the energy released when bonds in ATP break open (discussed below). The process of photosynthesis also makes and uses A ...
Lecture Suggestions and Guidelines
... Answer: See textbook—Inorganic Substances Common in Cells. Critical Thinking Issue(s) 1. Although most carbon dioxide is transported in plasma, small amounts of carbon dioxide are carried bound to the hemoglobin inside of red blood cells. How is this possible, since red blood cells seek to transport ...
... Answer: See textbook—Inorganic Substances Common in Cells. Critical Thinking Issue(s) 1. Although most carbon dioxide is transported in plasma, small amounts of carbon dioxide are carried bound to the hemoglobin inside of red blood cells. How is this possible, since red blood cells seek to transport ...
Cellular Respiration
... Stage 3: Electron Transport • Electron transport releases the energy your cells need to make the most of their ATP • The molecules of electron transport chains are built into the inner membranes of mitochondria – The chain functions as a chemical machine that uses energy released by the “fall” of e ...
... Stage 3: Electron Transport • Electron transport releases the energy your cells need to make the most of their ATP • The molecules of electron transport chains are built into the inner membranes of mitochondria – The chain functions as a chemical machine that uses energy released by the “fall” of e ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.