Glucose homeostasis in the blood (2) – un-storing energy
... been exhausted new glucose still needs to enter the blood stream for Figure 9: In long-term the brain and the red blood cells. The liver will begin to rely more on fasting proteins and fats are used. amino acids for gluconeogenesis. Glycerol from triglycerides can be used to make new glucose, but th ...
... been exhausted new glucose still needs to enter the blood stream for Figure 9: In long-term the brain and the red blood cells. The liver will begin to rely more on fasting proteins and fats are used. amino acids for gluconeogenesis. Glycerol from triglycerides can be used to make new glucose, but th ...
No Slide Title
... 1. BREATHING OR EXTERNAL RESPIRATION 2. CELLULAR RESPIRATION - Process by which organic compounds are broken down to yield energy for work • This energy molecule is _________ ...
... 1. BREATHING OR EXTERNAL RESPIRATION 2. CELLULAR RESPIRATION - Process by which organic compounds are broken down to yield energy for work • This energy molecule is _________ ...
Bacterial Physiology Lec-7 Energy Release and Conservation
... such as pyruvate that act as the electron acceptor. Fermentation occurs under anaerobic conditions , but sometimes occur when oxygen is present. The amount of energy that resulted from respiration is high while limited energy released during fermentation, so fermentation can be defined: energy-yield ...
... such as pyruvate that act as the electron acceptor. Fermentation occurs under anaerobic conditions , but sometimes occur when oxygen is present. The amount of energy that resulted from respiration is high while limited energy released during fermentation, so fermentation can be defined: energy-yield ...
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration Other Metabolites
... balance the supply of raw materials with the products produced these molecules become feedback regulators they control enzymes at strategic points in ...
... balance the supply of raw materials with the products produced these molecules become feedback regulators they control enzymes at strategic points in ...
Lecture #22 - Suraj @ LUMS
... Liver and Alcohol • Though alcohol affects every organ of the body, it’s most dramatic impact is upon the liver. • The liver cells prefer fatty acids as fuel, and package excess fatty acids as triglycerides. • When alcohol is present, the liver cells are forced to first metabolize the alcohol, lett ...
... Liver and Alcohol • Though alcohol affects every organ of the body, it’s most dramatic impact is upon the liver. • The liver cells prefer fatty acids as fuel, and package excess fatty acids as triglycerides. • When alcohol is present, the liver cells are forced to first metabolize the alcohol, lett ...
1. The molecule that is most directly used to power different cell
... ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate. The tri in the name tells you that it has a 3 phosphate group tail. The triphosphate tail is an important part of the molecule because it store energy in this high energy bond. ...
... ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate. The tri in the name tells you that it has a 3 phosphate group tail. The triphosphate tail is an important part of the molecule because it store energy in this high energy bond. ...
Chapter 9 Study Guide
... ______13. When electrons move closer to a more electronegative atom: a. energy is released b. energy is consumed c. a proton gradient is established d. water is produced e. ATP is synthesized. ______14. In the reaction C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO6 + 6 H2O a. oxygen becomes reduced. b. glucose becomes red ...
... ______13. When electrons move closer to a more electronegative atom: a. energy is released b. energy is consumed c. a proton gradient is established d. water is produced e. ATP is synthesized. ______14. In the reaction C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO6 + 6 H2O a. oxygen becomes reduced. b. glucose becomes red ...
Unit: Carbohydrates (Glucose)
... dependent upon an adequate supply of glucose for its energy, the clinical symptoms of hypoglycemia resemble those of cerebral anoxia, which may include one or more of the following: faintness, weakness, dizziness, tremors, anxiety, hunger, palpitation of the heart, or “cold sweat”; there may even be ...
... dependent upon an adequate supply of glucose for its energy, the clinical symptoms of hypoglycemia resemble those of cerebral anoxia, which may include one or more of the following: faintness, weakness, dizziness, tremors, anxiety, hunger, palpitation of the heart, or “cold sweat”; there may even be ...
Citric Acid (or Krebs) Cycle - BYU
... 2 electrons will be removed from NADH and put onto pyruvate. This causes pyruvate to become lactate. You have probably heard of lactic acid before. Lactic acid is acid form of the conjugate base lactate. It has often mistakenly been referred to as a negative thing – a waste product or a product that ...
... 2 electrons will be removed from NADH and put onto pyruvate. This causes pyruvate to become lactate. You have probably heard of lactic acid before. Lactic acid is acid form of the conjugate base lactate. It has often mistakenly been referred to as a negative thing – a waste product or a product that ...
Free Fatty acids - Sheffield Metabolic Laboratory
... metabolites (IMs), include lactate, pyruvate, acetoacetate as well as 3-hydroxybutyrate and free fatty acids (or non-esterified, NEFA). All are normally present in blood and have a vital role in energy metabolism. These compounds are linked through a number of different pathways, which interact depe ...
... metabolites (IMs), include lactate, pyruvate, acetoacetate as well as 3-hydroxybutyrate and free fatty acids (or non-esterified, NEFA). All are normally present in blood and have a vital role in energy metabolism. These compounds are linked through a number of different pathways, which interact depe ...
Multiple Choice Questions - Elmwood Park Public Schools
... A) the citric acid cycle. B) glycolysis. C) the electron transport system. D) fermentation. E) the preparatory reaction. 10. Which process produces both NADH and FADH2? A) the citric acid cycle B) glycolysis C) the electron transport system D) fermentation E) the preparatory reaction 11. Which proce ...
... A) the citric acid cycle. B) glycolysis. C) the electron transport system. D) fermentation. E) the preparatory reaction. 10. Which process produces both NADH and FADH2? A) the citric acid cycle B) glycolysis C) the electron transport system D) fermentation E) the preparatory reaction 11. Which proce ...
Note Set 11 1 GLYCOLYSIS (also known as: EMBDEN
... CH 3COCOOH---->CH 3CHO (acetaldehyde) + CO 2 •the reducing equivalents of NADH generated in glycolysis are then used to reduce acetaldehyde to ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase CH 3CHO + NADH + H+---->CH 3CH 2OH (EtOH, ethanol) + NAD+ 3. under aerobic conditions all eukaryotic cells and many bacteria ...
... CH 3COCOOH---->CH 3CHO (acetaldehyde) + CO 2 •the reducing equivalents of NADH generated in glycolysis are then used to reduce acetaldehyde to ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase CH 3CHO + NADH + H+---->CH 3CH 2OH (EtOH, ethanol) + NAD+ 3. under aerobic conditions all eukaryotic cells and many bacteria ...
GLUCONEOGENESIS
... The source of pyruvate and oxaloacetate for gluconeogenesis during fasting or carbohydrate starvation is mainly amino acid catabolism. Some amino acids are catabolized to pyruvate, oxaloacetate, or precursors of these. Muscle proteins may break down to supply amino acids. These are transported to l ...
... The source of pyruvate and oxaloacetate for gluconeogenesis during fasting or carbohydrate starvation is mainly amino acid catabolism. Some amino acids are catabolized to pyruvate, oxaloacetate, or precursors of these. Muscle proteins may break down to supply amino acids. These are transported to l ...
Gluconeogenesis - Assignment Point
... Overview of gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the generation of glucose from other substrates. Like many metabolic pathways it happens mostly in the liver, and is triggered by the action of insulin. Gluconeogenesis begins with various substrates converted into pyruvate.and this proceed though ...
... Overview of gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the generation of glucose from other substrates. Like many metabolic pathways it happens mostly in the liver, and is triggered by the action of insulin. Gluconeogenesis begins with various substrates converted into pyruvate.and this proceed though ...
untitled file - Blue Earth Area Schools
... • Takes place in anaerobic conditions • NADH produced in glycolysis must release its high energy electron, but there is no O2 to be the final electron acceptor • NADH donates the high energy electron back to pyruvate to form either lactic acid or ethanol and CO2 • Then NAD+ is recycled and glycolysi ...
... • Takes place in anaerobic conditions • NADH produced in glycolysis must release its high energy electron, but there is no O2 to be the final electron acceptor • NADH donates the high energy electron back to pyruvate to form either lactic acid or ethanol and CO2 • Then NAD+ is recycled and glycolysi ...
Energy Systems
... •Untrained individuals will have a low lactate threshold Therefore, the lower your LT, the less efficient your energy systems are working, or the poorer your energy systems are ...
... •Untrained individuals will have a low lactate threshold Therefore, the lower your LT, the less efficient your energy systems are working, or the poorer your energy systems are ...
Bio260 Exam1.1 MW review
... – Understand the factors that influence enzyme activity: temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and inhibitors. – Understand competitive and noncompetitive inhibition. ...
... – Understand the factors that influence enzyme activity: temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and inhibitors. – Understand competitive and noncompetitive inhibition. ...
Toxicology
... • Tox patients usually younger low likelihood of COPD so do not worry about decreased CO2 drive • Opioids-stimulate respiration- sometimes only need to remind to breath even if apnic. • watch out for vomiting in to mask ...
... • Tox patients usually younger low likelihood of COPD so do not worry about decreased CO2 drive • Opioids-stimulate respiration- sometimes only need to remind to breath even if apnic. • watch out for vomiting in to mask ...
Chapter 6 and 17 notes
... which is a lower-energy compound than ATP. How is ATP made? During cellular respiration, food is broken down. The energy released in this process is used to attach a 3rd phosphate group to ADP, creating ATP. From the energy released from the breakdown of one Glucose molecule, 36 ATP molecules ...
... which is a lower-energy compound than ATP. How is ATP made? During cellular respiration, food is broken down. The energy released in this process is used to attach a 3rd phosphate group to ADP, creating ATP. From the energy released from the breakdown of one Glucose molecule, 36 ATP molecules ...
Browning - University of San Diego Home Pages
... 3. In crème brûlée (literally, “burned cream”), a baked custard of egg yolks and cream (usually flavored with vanilla) is topped with a hard, thin layer of caramel. The caramel is made by spreading ...
... 3. In crème brûlée (literally, “burned cream”), a baked custard of egg yolks and cream (usually flavored with vanilla) is topped with a hard, thin layer of caramel. The caramel is made by spreading ...
Nutrients are chemical substances in food that provide energy, form
... continuously or body temperature would rise steadily. The principal routes of heat loss include radiation, conduction, convection, and evaporation. If the amount of heat production equals the amount of heat loss, you maintain a constant body temperature near 37 degrees celsius or 98.6 degrees Fahren ...
... continuously or body temperature would rise steadily. The principal routes of heat loss include radiation, conduction, convection, and evaporation. If the amount of heat production equals the amount of heat loss, you maintain a constant body temperature near 37 degrees celsius or 98.6 degrees Fahren ...
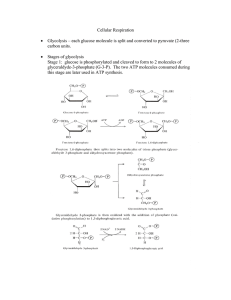
Cellular Respiration - Seattle Central College
... are produced. ATP are consumed in the formation of Glucose-6-phosphate from glucose and the conversion of Fructose-6-phosphate to Fructose-1,6-diphosphate. The net production of ATP per glucose is 2. ...
... are produced. ATP are consumed in the formation of Glucose-6-phosphate from glucose and the conversion of Fructose-6-phosphate to Fructose-1,6-diphosphate. The net production of ATP per glucose is 2. ...
Using enzymes in industrial processes
... Now the babies digestive system can cope with it better and they can get the amino acids they need from food ...
... Now the babies digestive system can cope with it better and they can get the amino acids they need from food ...
The Future of Biosensors Professor Brian Birch LIRANS University of Luton UK
... Reagents + glucose → ferrocyanide Ferrocyanide → ferricyanide → glucose ...
... Reagents + glucose → ferrocyanide Ferrocyanide → ferricyanide → glucose ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.