Document
... Go to Socrative on your cell phone. My room # is BRADYAPBIO 1. What leaf structure allows for gas exchange? a. chloroplast c. inner membrane b. stomata d. chlorophyll 2. What is the source of oxygen that is released from plant cells as a result of photosynthesis? a. carbon dioxide c. glucose b. ATP ...
... Go to Socrative on your cell phone. My room # is BRADYAPBIO 1. What leaf structure allows for gas exchange? a. chloroplast c. inner membrane b. stomata d. chlorophyll 2. What is the source of oxygen that is released from plant cells as a result of photosynthesis? a. carbon dioxide c. glucose b. ATP ...
Metabolism
... NADH and FADH enter ETC • Major source of energy! • Electrons held by NAD and FAD are “high energy” 9Transferred through a series of steps from one electron carrier to another ...
... NADH and FADH enter ETC • Major source of energy! • Electrons held by NAD and FAD are “high energy” 9Transferred through a series of steps from one electron carrier to another ...
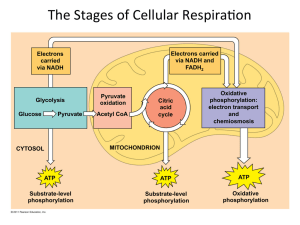
The Stages of Cellular RespiraWon
... Citric acid cycle and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on in mitochondria ...
... Citric acid cycle and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on in mitochondria ...
A2 Aerobic respiration Link reaction Glucose cannot cross the
... Acetyl coenzyme A (2C) combines with a 4C molecule to produce a 6 carbon molecule. The 6 C molecule loses carbon dioxide and some hydrogen in a series of reactions, eventually reforming the 4 C molecule. Hydrogen is accepted by 3 NAD to form 3 reduced NAD, and by one FAD to form reduced FAD. In addi ...
... Acetyl coenzyme A (2C) combines with a 4C molecule to produce a 6 carbon molecule. The 6 C molecule loses carbon dioxide and some hydrogen in a series of reactions, eventually reforming the 4 C molecule. Hydrogen is accepted by 3 NAD to form 3 reduced NAD, and by one FAD to form reduced FAD. In addi ...
Cellular Respiration
... Anaerobic respiration- without O2. Aerobic respiration- with O2. C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP) ...
... Anaerobic respiration- without O2. Aerobic respiration- with O2. C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP) ...
Bioenergetics, glycolysis, metabolism of monosaccharides and
... Where: ΔGo is the standard free energy change, R is the gas constant (1.987 cal/mol . degree), T is the absolute temperature (K), [A] and [B] are the actual concentrations of the reactant and product, ln represents the natural logarithm. Example: for non-equilibirium conditions (see the figure) gluc ...
... Where: ΔGo is the standard free energy change, R is the gas constant (1.987 cal/mol . degree), T is the absolute temperature (K), [A] and [B] are the actual concentrations of the reactant and product, ln represents the natural logarithm. Example: for non-equilibirium conditions (see the figure) gluc ...
Cellular respiration
... • Metabolism is all the chemical reactions of the body • some reactions produce the energy which is stored in ATP that other reactions consume • all molecules will eventually be broken down and recycled or excreted from the body ...
... • Metabolism is all the chemical reactions of the body • some reactions produce the energy which is stored in ATP that other reactions consume • all molecules will eventually be broken down and recycled or excreted from the body ...
peptides - WordPress.com
... release of cytokines in response to tumors and a number of other pathologic conditions, there is an increase in the rate of tissue protein catabolism, as well as a considerably increased metabolic rate, so they are in a state of advanced starvation. Again, death results when essential tissue protein ...
... release of cytokines in response to tumors and a number of other pathologic conditions, there is an increase in the rate of tissue protein catabolism, as well as a considerably increased metabolic rate, so they are in a state of advanced starvation. Again, death results when essential tissue protein ...
Photo Album
... Figure 3.9 Anaplerotic reactions are required for net synthesis of glutamate, glutamine, and aspartate and for normal synaptic transmission. (A) Net synthesis of TCA cycle-derived amino acids requires the ATP-dependent CO2 fixation reaction catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase to generate oxaloacetate ...
... Figure 3.9 Anaplerotic reactions are required for net synthesis of glutamate, glutamine, and aspartate and for normal synaptic transmission. (A) Net synthesis of TCA cycle-derived amino acids requires the ATP-dependent CO2 fixation reaction catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase to generate oxaloacetate ...
Problem Set #3 Key
... Name_____________________________ Chemistry 333 Principles of Biochemistry Homework #3 (30 points) Due Monday, November 23, 2009 (No later than 5pm!) ...
... Name_____________________________ Chemistry 333 Principles of Biochemistry Homework #3 (30 points) Due Monday, November 23, 2009 (No later than 5pm!) ...
BCH 3033 General Biochemistry EXAM 5 Name: Fall, 2012
... a. brain . b. kidney. c. liver. d. skeletal muscle. e. all of these. Written Answer Questions 1. For the average adult (70 kg or 154 lb), 15% of the body is fat. a. Calculate the energy reserve in terms of kJ. Assume 38 kJ/gram fat. (5points) ...
... a. brain . b. kidney. c. liver. d. skeletal muscle. e. all of these. Written Answer Questions 1. For the average adult (70 kg or 154 lb), 15% of the body is fat. a. Calculate the energy reserve in terms of kJ. Assume 38 kJ/gram fat. (5points) ...
Chapter 9 – Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... One catabolic process is called fermentation which is a partial oxidation of organic molecules, and it occurs without oxygen. Aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of organic compounds, like sugar, with the participation of oxygen in the process. Food provides the “fuel” for the cells, and m ...
... One catabolic process is called fermentation which is a partial oxidation of organic molecules, and it occurs without oxygen. Aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of organic compounds, like sugar, with the participation of oxygen in the process. Food provides the “fuel” for the cells, and m ...
Chapter 14- RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Living cells require a
... Living cells require a continuous supply of energy for maintaining various life activities. This energy is obtained by oxidizing the organic compounds (carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids) in the cells. This process of harvesting chemical energy for metabolic activities in the form of ATP by oxidisi ...
... Living cells require a continuous supply of energy for maintaining various life activities. This energy is obtained by oxidizing the organic compounds (carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids) in the cells. This process of harvesting chemical energy for metabolic activities in the form of ATP by oxidisi ...
CH395 G Exam 3 Fall 2004 - Multiple Choice 1. Which of the
... The patient develops vomiting and diarrhea shortly after milk ingestion. A lactose tolerance test is administered. The patient ingests a standard amount of lactose, and the glucose and galactose concentrations in blood plasma are measured at intervals. In lactose-tolerant individuals the levels incr ...
... The patient develops vomiting and diarrhea shortly after milk ingestion. A lactose tolerance test is administered. The patient ingests a standard amount of lactose, and the glucose and galactose concentrations in blood plasma are measured at intervals. In lactose-tolerant individuals the levels incr ...
Ch. 7.4: Cellular Respiration
... Oxygen is an excellent “electrongrabber”; electrons are pulled to O (electro-negative). (O is much better than N or H @ attracting electrons) ...
... Oxygen is an excellent “electrongrabber”; electrons are pulled to O (electro-negative). (O is much better than N or H @ attracting electrons) ...
enzymes - JonesHonorsBioGreen
... Citric Acid / Krebs Cycle – Page 97 ETC (Oxidative Phosphorylation)- Page 98 Fermentation – Page 101 Full sheet or Half sheet drawings – IN COLOR ...
... Citric Acid / Krebs Cycle – Page 97 ETC (Oxidative Phosphorylation)- Page 98 Fermentation – Page 101 Full sheet or Half sheet drawings – IN COLOR ...
PARMELIA PERLATA ALLOXAN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS Full Proceeding Paper
... and consequent increase in fasting blood glucose level in disease control animals (Group II) (Table: 1). Administration of test drug for 60 days (Group III& IV) was found to regenerate the pancreatic beta-cells which results in the normal secretion of insulin. Insulin, the potent hypoglycemic hormon ...
... and consequent increase in fasting blood glucose level in disease control animals (Group II) (Table: 1). Administration of test drug for 60 days (Group III& IV) was found to regenerate the pancreatic beta-cells which results in the normal secretion of insulin. Insulin, the potent hypoglycemic hormon ...
Cell ENERGY & ENZYMES
... Citric Acid / Krebs Cycle – Page 97 ETC (Oxidative Phosphorylation)- Page 98 Fermentation – Page 101 Full sheet or Half sheet drawings – IN COLOR ...
... Citric Acid / Krebs Cycle – Page 97 ETC (Oxidative Phosphorylation)- Page 98 Fermentation – Page 101 Full sheet or Half sheet drawings – IN COLOR ...
3.2 Carbohydrates, lipids and proteins – summary of previous mark
... lipids are insoluble in water less osmotic effect; lipids have more / twice the energy content per unit mass of carbohydrates; lipids / triglycerides used for long-term energy storage; triglycerides converted to fatty acids and glycerol (when energy is required); triglycerides broken down to yield a ...
... lipids are insoluble in water less osmotic effect; lipids have more / twice the energy content per unit mass of carbohydrates; lipids / triglycerides used for long-term energy storage; triglycerides converted to fatty acids and glycerol (when energy is required); triglycerides broken down to yield a ...
File
... 1. Plants carry out cellular respiration. (T or F) 2. Oxidative respiration must follow glycolysis if a cell is to maximize its ATP production. . (T or F) 3. Fermentation and oxidative respiration both take place in the absence of oxygen. . (T or F) 4. Lactic acid fermentation is a type of anaerobic ...
... 1. Plants carry out cellular respiration. (T or F) 2. Oxidative respiration must follow glycolysis if a cell is to maximize its ATP production. . (T or F) 3. Fermentation and oxidative respiration both take place in the absence of oxygen. . (T or F) 4. Lactic acid fermentation is a type of anaerobic ...
Successful Longevity - SENS Research Foundation
... Leptin fails to regulate body fat distribution, insulin action, and endocrine functions with aging ...
... Leptin fails to regulate body fat distribution, insulin action, and endocrine functions with aging ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General
... a. During glycolysis, 4 ATPs are produced but a net gain of only 2 ATPs (two are needed to start the process); also generate 2 NADHs b. During the transition rx, 2 NADHs are formed c. During each revolution of the citric acid cycle, one ATP, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2 d. Generate a total of 38 ATP (3 per each ...
... a. During glycolysis, 4 ATPs are produced but a net gain of only 2 ATPs (two are needed to start the process); also generate 2 NADHs b. During the transition rx, 2 NADHs are formed c. During each revolution of the citric acid cycle, one ATP, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2 d. Generate a total of 38 ATP (3 per each ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.