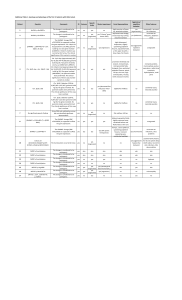
Additional Table 1. Genotype and phenotype of the
... kb, 45,265,479-45,828,359, genomic build hg 18). Two genes involved, one has an OMIM entry (PRKCE ). Chr. 20p21.1 del (approximately 218 kb, 14,823,878-15,041,954, genomic yes build hg 18). One gene involved (MACROD2 ). No parental studies were performed. The clinical significance of these copy numb ...
... kb, 45,265,479-45,828,359, genomic build hg 18). Two genes involved, one has an OMIM entry (PRKCE ). Chr. 20p21.1 del (approximately 218 kb, 14,823,878-15,041,954, genomic yes build hg 18). One gene involved (MACROD2 ). No parental studies were performed. The clinical significance of these copy numb ...
PDF
... hybridization. Expression was found not only in the central nervous system, as was expected from the expression pattern of the endogenous Ndn gene, but also to be comparatively widespread, suggesting that the promoter region did not contain all of the regulatory control sequences present in the endo ...
... hybridization. Expression was found not only in the central nervous system, as was expected from the expression pattern of the endogenous Ndn gene, but also to be comparatively widespread, suggesting that the promoter region did not contain all of the regulatory control sequences present in the endo ...
The Wnt code: cnidarians signal the way
... at the site of the blastopore during and after gastrulation of the embryo. They indicate an ancient function for Wnt signalling in gastrulation and axial patterning. An ancient function of Wnt signalling in axial patterning The expression domains for the Nematostella wnt genes have been determined b ...
... at the site of the blastopore during and after gastrulation of the embryo. They indicate an ancient function for Wnt signalling in gastrulation and axial patterning. An ancient function of Wnt signalling in axial patterning The expression domains for the Nematostella wnt genes have been determined b ...
Anterior boundaries of Hox gene expression in mesoderm
... developmental regulation [3,6,25, 31, 36,391. The homeotic genes of Drosophila determine the fate of individual body segments by specifying positional information during embryogenesis (for reviews see [l, 20-22,441. That mammalian homeobox-containing genes also are controlling factors required for t ...
... developmental regulation [3,6,25, 31, 36,391. The homeotic genes of Drosophila determine the fate of individual body segments by specifying positional information during embryogenesis (for reviews see [l, 20-22,441. That mammalian homeobox-containing genes also are controlling factors required for t ...
ABSTRACT Title of Document: PROGRAMMED
... The PTC is located at the bottom of the large cleft on the interface side of the large subunit underneath the central protuberance (Polacek & Mankin, 2005; Rodnina et al, 2006). The acceptor ends of the tRNAs meet at the bottom of the funnel-shaped active site above the entrance to the peptide exit ...
... The PTC is located at the bottom of the large cleft on the interface side of the large subunit underneath the central protuberance (Polacek & Mankin, 2005; Rodnina et al, 2006). The acceptor ends of the tRNAs meet at the bottom of the funnel-shaped active site above the entrance to the peptide exit ...
Warren, ST and Ashley, CT: Triplet repeat expansion mutations: The example of fragile X syndrome. Annual Review of Neuroscience 18:77-99 (1995).
... northern analysis, a 4.8-kb transcript was detected in RNA from human brain and placenta, which suggested that approximately 1 kb of sequence remained to be determined. A zoo blot containing genomic DNA from a number of eukaryotes, including lower organisms such as nematode and yeast, displayed band ...
... northern analysis, a 4.8-kb transcript was detected in RNA from human brain and placenta, which suggested that approximately 1 kb of sequence remained to be determined. A zoo blot containing genomic DNA from a number of eukaryotes, including lower organisms such as nematode and yeast, displayed band ...
Dickkopf1 Is Required for Embryonic Head Induction
... Localization of Dkk1 Function during Gastrulation Dkk1 may function in head formation by influencing the inductive properties of the extraembryonic AVE, the embryonic AME, or both. Recent data suggest that head induction in the mouse embryo requires not only a functional AVE but also the node and it ...
... Localization of Dkk1 Function during Gastrulation Dkk1 may function in head formation by influencing the inductive properties of the extraembryonic AVE, the embryonic AME, or both. Recent data suggest that head induction in the mouse embryo requires not only a functional AVE but also the node and it ...
Regulation of meiotic progression by the meiosis
... et al., 2002). In fact, most (if not all) yeast pachytene checkpoint proteins have homologs in other organisms (Roeder and Bailis, 2000). However, although the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe is a model organism widely used in checkpoint studies during the mitotic cell cycle (Murakami and Nu ...
... et al., 2002). In fact, most (if not all) yeast pachytene checkpoint proteins have homologs in other organisms (Roeder and Bailis, 2000). However, although the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe is a model organism widely used in checkpoint studies during the mitotic cell cycle (Murakami and Nu ...
Parallel Evolution of Copy-Number Variation across Continents in
... selection, confidence in the biological relevance of such differentiation can be increased by asking whether differentiation occurs in parallel across different geographic regions exhibiting similar ecological gradients (e.g., Jones et al. 2012). Therefore, for each differentiated CNV detected on on ...
... selection, confidence in the biological relevance of such differentiation can be increased by asking whether differentiation occurs in parallel across different geographic regions exhibiting similar ecological gradients (e.g., Jones et al. 2012). Therefore, for each differentiated CNV detected on on ...
Chromosomal translocations deregulated BCL6
... To gain further insight into the structure and pattern of expression of the various BCL6 mRNA species in NHL with t(3;14), we analyzed BCL6 mRNA in Ly8 cells using RNase protection assays. First, we tested whether Ly8 cells expressed a BCL6 RNA lacking exon 1 sequences, as predicted by the RACE prod ...
... To gain further insight into the structure and pattern of expression of the various BCL6 mRNA species in NHL with t(3;14), we analyzed BCL6 mRNA in Ly8 cells using RNase protection assays. First, we tested whether Ly8 cells expressed a BCL6 RNA lacking exon 1 sequences, as predicted by the RACE prod ...
PDF
... The sexual life cycle of E. siliculosus involves an alternation between two independent generations: the sporophyte and the gametophyte (Fig. 1). To compare the early development of these two generations, gametophytes were raised from meiospores of a heterozygous, field-isolated, sporophyte (strain ...
... The sexual life cycle of E. siliculosus involves an alternation between two independent generations: the sporophyte and the gametophyte (Fig. 1). To compare the early development of these two generations, gametophytes were raised from meiospores of a heterozygous, field-isolated, sporophyte (strain ...
PDF
... to the manufacturer’s instructions. The sequenced reads resulting from this run were separated into 12 libraries (representing three related but different projects) according to their indexes (demultiplexing) and stored as FASTQ files. The SiO2 NPs treated and control Hydra libraries yielded a total ...
... to the manufacturer’s instructions. The sequenced reads resulting from this run were separated into 12 libraries (representing three related but different projects) according to their indexes (demultiplexing) and stored as FASTQ files. The SiO2 NPs treated and control Hydra libraries yielded a total ...
The Histone Variant H2A.W Defines Heterochromatin and Promotes
... from gene bodies (Figure 1B). H2A.W was specifically enriched in pericentromeric heterochromatin, TEs, and islands of H3K9me2 (Figures 1A, 1C–1E, and S1C). The Pearson correlation between H3K9me2 and H2A.W within TEs across the genome was 0.7, indicating a very high degree of overlap between H2A.W a ...
... from gene bodies (Figure 1B). H2A.W was specifically enriched in pericentromeric heterochromatin, TEs, and islands of H3K9me2 (Figures 1A, 1C–1E, and S1C). The Pearson correlation between H3K9me2 and H2A.W within TEs across the genome was 0.7, indicating a very high degree of overlap between H2A.W a ...
Cerberus regulates left–right asymmetry of the embryonic head and
... later (stage 8–9) stages had little or no effect on the direction of heart looping or head turning compared with mocktransfected controls (Table 1). These results suggest that there is a narrow time window during which cCer can regulate left–right polarity. Does cCer act on the heart and the head to ...
... later (stage 8–9) stages had little or no effect on the direction of heart looping or head turning compared with mocktransfected controls (Table 1). These results suggest that there is a narrow time window during which cCer can regulate left–right polarity. Does cCer act on the heart and the head to ...
Wnt signaling
... translocation to the nucleus where it interacts with TCF/LEF family transcription factors. In the absence of signal, TCF/LEF factors bind DNA at Wnt-responsive genes and interact with other factors (e.g. Groucho, histone deacetylase) to repress transcription. β-catenin binding to TCF/LEF proteins pr ...
... translocation to the nucleus where it interacts with TCF/LEF family transcription factors. In the absence of signal, TCF/LEF factors bind DNA at Wnt-responsive genes and interact with other factors (e.g. Groucho, histone deacetylase) to repress transcription. β-catenin binding to TCF/LEF proteins pr ...
hemipterous Encodes a Novel Drosophila MAP
... of germ layers and the overall body organization in metazoan development. The cellular and mechanistic aspects of concerted cell movements have been described in several organisms, and a number of studies suggest an important role for cell communication in morphogenesis (for reviews, see Fristrom, ...
... of germ layers and the overall body organization in metazoan development. The cellular and mechanistic aspects of concerted cell movements have been described in several organisms, and a number of studies suggest an important role for cell communication in morphogenesis (for reviews, see Fristrom, ...
glo-3, a novel Caenorhabditis elegans gene, is required for lysosome
... glo-3 and glo-3short in embryos and L4 stage animals by amplifying their corresponding cDNAs from total RNA isolated using Trizol/chloroform extraction. cDNA was generated using a d(T)20 primer with Superscript III (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). In L4 stage animals the glo-3 cDNA was amplified using P4 ...
... glo-3 and glo-3short in embryos and L4 stage animals by amplifying their corresponding cDNAs from total RNA isolated using Trizol/chloroform extraction. cDNA was generated using a d(T)20 primer with Superscript III (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). In L4 stage animals the glo-3 cDNA was amplified using P4 ...
lilliputian - Development - The Company of Biologists
... embryos lacking zygotic lilli failed to hatch and subsequently died, although a small percentage hatched and died as first or second instar larvae. Cuticle from the late embryos was normal, with three thoracic and eight abdominal segments (Fig. 2A). Loss-of-function lilli mutations were found to be ...
... embryos lacking zygotic lilli failed to hatch and subsequently died, although a small percentage hatched and died as first or second instar larvae. Cuticle from the late embryos was normal, with three thoracic and eight abdominal segments (Fig. 2A). Loss-of-function lilli mutations were found to be ...
A NEW ALLELE OF THE lpr LOCUS, lpr"9, THAT COMPLEMENTS
... visible enlarged lymph nodes at 4 mo of age. Some mice were observed up to 1 yr of age for the survival, development of lymphadenopathy, and progress of the disease. Especially, CBA-m, C311-gld, C3H-Ipr, (CBA-m x C3H-Ipr)F,, and (CBA-m x C3H-gld)F, mice were killed by chloroform overdose for weight ...
... visible enlarged lymph nodes at 4 mo of age. Some mice were observed up to 1 yr of age for the survival, development of lymphadenopathy, and progress of the disease. Especially, CBA-m, C311-gld, C3H-Ipr, (CBA-m x C3H-Ipr)F,, and (CBA-m x C3H-gld)F, mice were killed by chloroform overdose for weight ...
hag expression in Bacillus subtilis is both negatively
... (Caldwell et al., 2001), which are mainly transcribed by the sD-dependent RNA polymerase (Ordal et al., 1993). This conclusion has been derived from the transcription profiling of scoC mutant cells (scoC4), which showed that most of the motility genes, including hag, are transcribed at lower levels ...
... (Caldwell et al., 2001), which are mainly transcribed by the sD-dependent RNA polymerase (Ordal et al., 1993). This conclusion has been derived from the transcription profiling of scoC mutant cells (scoC4), which showed that most of the motility genes, including hag, are transcribed at lower levels ...
Chromosomes Carrying Meiotic Avoidance Loci
... The LOSS OF APOMEIOSIS (LOA) locus is one of two dominant loci known to control apomixis in the eudicot Hieracium praealtum. LOA stimulates the differentiation of somatic aposporous initial cells after the initiation of meiosis in ovules. Aposporous initial cells undergo nuclear proliferation close ...
... The LOSS OF APOMEIOSIS (LOA) locus is one of two dominant loci known to control apomixis in the eudicot Hieracium praealtum. LOA stimulates the differentiation of somatic aposporous initial cells after the initiation of meiosis in ovules. Aposporous initial cells undergo nuclear proliferation close ...
Tetraploid rescue - Development
... lack or severe deficiency of the extraembryonic region as seen under a stereomicroscope (Fig. 1). The mean long axis of such embryos was 62.3% (range, 37-100%), that of normally growing littermates on day 6, whereas it was reduced to 39.5% (range, 28-55%) on day 7. Retarded and abnormal embryos havi ...
... lack or severe deficiency of the extraembryonic region as seen under a stereomicroscope (Fig. 1). The mean long axis of such embryos was 62.3% (range, 37-100%), that of normally growing littermates on day 6, whereas it was reduced to 39.5% (range, 28-55%) on day 7. Retarded and abnormal embryos havi ...
Direct control of shoot meristem activity by a cytokinin
... aerial organs, such as leaves, stems and flowers1. It has been assumed that the phytohormone cytokinin has a positive role in shoot meristem function2–4. A severe reduction in the size of meristems in a mutant that is defective in all of its cytokinin receptors has provided compelling evidence that ...
... aerial organs, such as leaves, stems and flowers1. It has been assumed that the phytohormone cytokinin has a positive role in shoot meristem function2–4. A severe reduction in the size of meristems in a mutant that is defective in all of its cytokinin receptors has provided compelling evidence that ...
The splanchnic mesodermal plate directs spleen and
... of the mesenchyme (Fig. 1F,G), indicating that this region will ultimately give rise to the spleen. By E11.5, the splenic rudiment, which continues to express Wt1 (Herzer et al., 1999), capsulin (Lu et al., 2000), Nkx2.5 and Hox11 (Dear et al., 1995; Kanzler and Dear, 2001; Roberts et al., 1994) (da ...
... of the mesenchyme (Fig. 1F,G), indicating that this region will ultimately give rise to the spleen. By E11.5, the splenic rudiment, which continues to express Wt1 (Herzer et al., 1999), capsulin (Lu et al., 2000), Nkx2.5 and Hox11 (Dear et al., 1995; Kanzler and Dear, 2001; Roberts et al., 1994) (da ...
The splanchnic mesodermal plate directs spleen and
... of the mesenchyme (Fig. 1F,G), indicating that this region will ultimately give rise to the spleen. By E11.5, the splenic rudiment, which continues to express Wt1 (Herzer et al., 1999), capsulin (Lu et al., 2000), Nkx2.5 and Hox11 (Dear et al., 1995; Kanzler and Dear, 2001; Roberts et al., 1994) (da ...
... of the mesenchyme (Fig. 1F,G), indicating that this region will ultimately give rise to the spleen. By E11.5, the splenic rudiment, which continues to express Wt1 (Herzer et al., 1999), capsulin (Lu et al., 2000), Nkx2.5 and Hox11 (Dear et al., 1995; Kanzler and Dear, 2001; Roberts et al., 1994) (da ...























