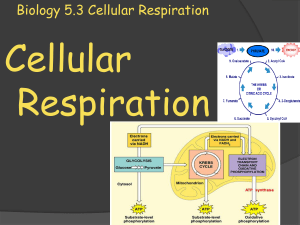
Biology 5.3 Cellular Respiration
... pyruvate during glycolysis. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process (no oxygen required), and it results in a gain of two ATP molecules. In the second stage of cellular respiration, the pyruvate passes through either aerobic respiration (requires oxygen) or fermentation. When oxygen is not present, ferme ...
... pyruvate during glycolysis. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process (no oxygen required), and it results in a gain of two ATP molecules. In the second stage of cellular respiration, the pyruvate passes through either aerobic respiration (requires oxygen) or fermentation. When oxygen is not present, ferme ...
Directed enzyme evolution: climbing fitness peaks one amino acid
... On rare occasions an enzyme with high specificity for a new substrate can be generated with a single amino acid substitution [39]. Activity on a new substrate, however, is usually achieved by broadening the substrate range (Figure 1), which indicates that these ‘generalist’ enzymes are the most acce ...
... On rare occasions an enzyme with high specificity for a new substrate can be generated with a single amino acid substitution [39]. Activity on a new substrate, however, is usually achieved by broadening the substrate range (Figure 1), which indicates that these ‘generalist’ enzymes are the most acce ...
Document
... • Over long periods of time a sequence will acquire random mutations. – These mutations may result in a new amino acid at a given position, the deletion of an amino acid, or the introduction of a new one. – Over VERY long periods of time two sequences may diverge so much that their relationship can ...
... • Over long periods of time a sequence will acquire random mutations. – These mutations may result in a new amino acid at a given position, the deletion of an amino acid, or the introduction of a new one. – Over VERY long periods of time two sequences may diverge so much that their relationship can ...
Function of Conserved Tryptophans in the Aspergillus niger
... yields of each SBD following purification from 1 L of SMM culture were greatly reduced when compared with that of the wild-type SBD: less than 1 mg for W615K and approximately 5 mg for W590K compared to more than 200 mg for the wild-type SBD. We obtained a better yield for W563K, 30-50 mg. The W615K ...
... yields of each SBD following purification from 1 L of SMM culture were greatly reduced when compared with that of the wild-type SBD: less than 1 mg for W615K and approximately 5 mg for W590K compared to more than 200 mg for the wild-type SBD. We obtained a better yield for W563K, 30-50 mg. The W615K ...
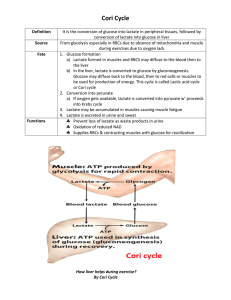
Cori Cycle - COFFEE BREAK CORNER
... conversion of lactate into glucose in liver From glycolysis especially in RBCs due to absence of mitochondria and muscle during exercises due to oxygen lack 1. Glucose formation a) Lactate formed i ...
... conversion of lactate into glucose in liver From glycolysis especially in RBCs due to absence of mitochondria and muscle during exercises due to oxygen lack 1. Glucose formation a) Lactate formed i ...
Lecture 39 - Amino Acid Metabolism 2
... Amino Acids as Metabolic Precursors Natural loss of hair color occurs as a result of aging when melanin production shuts down in human melanocytes located near the base of hair follicles and these defective cells are not replaced as they normally are in younger individuals. Gray hair can be colored ...
... Amino Acids as Metabolic Precursors Natural loss of hair color occurs as a result of aging when melanin production shuts down in human melanocytes located near the base of hair follicles and these defective cells are not replaced as they normally are in younger individuals. Gray hair can be colored ...
Defelipe, L.A, Dolghih E, Roitberg A.E., Nouzova M., Mayoral
... JHAMT. The substrate binding site was identified, as well as the residues that interact with the methyl donor (S-adenosylmethionine) and the carboxylic acid of the substrate methyl acceptors, farnesoic acid (FA) and juvenile hormone acid (JHA). To gain further insight we generated the structures of A ...
... JHAMT. The substrate binding site was identified, as well as the residues that interact with the methyl donor (S-adenosylmethionine) and the carboxylic acid of the substrate methyl acceptors, farnesoic acid (FA) and juvenile hormone acid (JHA). To gain further insight we generated the structures of A ...
Osteo Complex - Rocky Fork Formulas, Inc.
... journals, our biochemist has designed a formula that we believe you will find to be the finest supplements available for supporting your body in rebuilding and maintaining bone health. Many health care professionals have related to us their use of individual nutrients, both alone and in combination, ...
... journals, our biochemist has designed a formula that we believe you will find to be the finest supplements available for supporting your body in rebuilding and maintaining bone health. Many health care professionals have related to us their use of individual nutrients, both alone and in combination, ...
Atoms, Ions and Molecules
... 1. An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of any element disappears or is changed into an atom of another element. 3. Co ...
... 1. An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of any element disappears or is changed into an atom of another element. 3. Co ...
Instructor`s Guide - Ventura Educational Systems
... • Students will understand that families (up and down) have the same number of valence electrons, which means they have similar bonding characteristics. • Students will be able to make predictions about bonding and number of valence electrons ...
... • Students will understand that families (up and down) have the same number of valence electrons, which means they have similar bonding characteristics. • Students will be able to make predictions about bonding and number of valence electrons ...
One-dimensional Metallic Conductors
... orbitals (Fig. 3), or a combination of these orbitals, on adjacent metal atoms may overlap to form a d,2 band and, at higher energy, a p, band. In the case o€ nickel(II), palladium(I1) and platinum(I1) complexes, each d,2 orbital contains two electrons, while the p, orbital is empty, and therefore t ...
... orbitals (Fig. 3), or a combination of these orbitals, on adjacent metal atoms may overlap to form a d,2 band and, at higher energy, a p, band. In the case o€ nickel(II), palladium(I1) and platinum(I1) complexes, each d,2 orbital contains two electrons, while the p, orbital is empty, and therefore t ...
Biosynthesis of Nucleotides 1 - University of Alabama at Birmingham
... N-1 from aspartic acid N-3, N-9 from glutamine C-4, C-5, N-7 from glycine C-6 from CO2 C-2, C-8 from THF - one carbon units ...
... N-1 from aspartic acid N-3, N-9 from glutamine C-4, C-5, N-7 from glycine C-6 from CO2 C-2, C-8 from THF - one carbon units ...
MCB Lecture 2 – Protein Metabolism
... o The beginning and end of the protein is usually take off or modified What are signal sequences? o Signal sequences are areas at the beginning of a protein that can be cleaved off to create diversity. Which amino acids can be phosphorylated? o Ones with free –OH groups. o Examples: Serine, Threonin ...
... o The beginning and end of the protein is usually take off or modified What are signal sequences? o Signal sequences are areas at the beginning of a protein that can be cleaved off to create diversity. Which amino acids can be phosphorylated? o Ones with free –OH groups. o Examples: Serine, Threonin ...
Plants
... III. Photosystem I (make NADPH) A. How does it work? 1. sunlight is absorbed by pigments in the thylakoid 2. e- from photosystem II are transferred to reaction center of Photosystem I… 3. e- are sent to reaction center.. ...
... III. Photosystem I (make NADPH) A. How does it work? 1. sunlight is absorbed by pigments in the thylakoid 2. e- from photosystem II are transferred to reaction center of Photosystem I… 3. e- are sent to reaction center.. ...
full text - pdf 348 kB
... The links between residues have frequently been shown by peptide chemists as full points (periods, dots) and by carbohydrate chemists (generally) as short strokes (dashes, hyphens). At times, special symbols have been used (> or —*) to show the direction of what is in all cases an unsymmetrical link ...
... The links between residues have frequently been shown by peptide chemists as full points (periods, dots) and by carbohydrate chemists (generally) as short strokes (dashes, hyphens). At times, special symbols have been used (> or —*) to show the direction of what is in all cases an unsymmetrical link ...
Plants
... III. Photosystem I (make NADPH) A. How does it work? 1. sunlight is absorbed by pigments in the thylakoid 2. e- from photosystem II are transferred to reaction center of Photosystem I… 3. e- are sent to reaction center.. ...
... III. Photosystem I (make NADPH) A. How does it work? 1. sunlight is absorbed by pigments in the thylakoid 2. e- from photosystem II are transferred to reaction center of Photosystem I… 3. e- are sent to reaction center.. ...
Developmental Analysis of a Putative ATP/ADP Carrier Protein
... ATP/ADP carrier. We have been screening for PMP38 knockout mutants of A. thaliana and generating anti-sense transgenic plants to clarify whether PMP38 is responsible for the fatty acid >-oxidation cycle or not. Recently, we screened for ped mutants with defects in the fatty acid >-oxidation cycle (H ...
... ATP/ADP carrier. We have been screening for PMP38 knockout mutants of A. thaliana and generating anti-sense transgenic plants to clarify whether PMP38 is responsible for the fatty acid >-oxidation cycle or not. Recently, we screened for ped mutants with defects in the fatty acid >-oxidation cycle (H ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... At the end of this unit, I will: Know how to transcribe DNA to RNA and translate RNA to protein. Be able to find the amino acids represented on a codon table. Appreciate the fact that there can be some mutations in DNA that won’t show up in protein, but some mutations will. Know where in the ...
... At the end of this unit, I will: Know how to transcribe DNA to RNA and translate RNA to protein. Be able to find the amino acids represented on a codon table. Appreciate the fact that there can be some mutations in DNA that won’t show up in protein, but some mutations will. Know where in the ...
Sample Chapter - Chapter 4
... Water separates ions in a process that greatly reduces the electrostatic force of attraction between them. To see how it does this, let’s examine the water molecule closely. Water’s power as an ionizing solvent results from two features of the water molecule: the distribution of its bonding electron ...
... Water separates ions in a process that greatly reduces the electrostatic force of attraction between them. To see how it does this, let’s examine the water molecule closely. Water’s power as an ionizing solvent results from two features of the water molecule: the distribution of its bonding electron ...
Name - straubel
... 4. How many steps are involved in the entire cycle? _____ 5. How many CO2 molecules are produced per pyruvate? _____ per glucose? _____ 6. How many NADH2 molecules are produced per pyruvate? ______ 7. How many FADH2 molecules are produced per glucose? _______ 8. How many ATP are produced per glucose ...
... 4. How many steps are involved in the entire cycle? _____ 5. How many CO2 molecules are produced per pyruvate? _____ per glucose? _____ 6. How many NADH2 molecules are produced per pyruvate? ______ 7. How many FADH2 molecules are produced per glucose? _______ 8. How many ATP are produced per glucose ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.