GENE NOMENCLATURE OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF SPINOCEREBELLAR ATAXIA (SCA) AND
... distinct genetic causes of SCA are known and each of which could be considered a disease in its own right. The nomenclature of 36 types of Spinocerebellar ataxia and a computational work on Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1) are done in this study. SCA1 is a progressive, degenerative and often fat ...
... distinct genetic causes of SCA are known and each of which could be considered a disease in its own right. The nomenclature of 36 types of Spinocerebellar ataxia and a computational work on Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1) are done in this study. SCA1 is a progressive, degenerative and often fat ...
AQA A-level Biology
... is C6H12O6. This formula simply tells us how many atoms of each element there are in each glucose molecule. Now look at the structural formulae shown in Figure 1.4. They show a molecule of α-glucose and a molecule of β-glucose. Count each type of atom in diagram (a). There are 6 carbon atoms, 12 hyd ...
... is C6H12O6. This formula simply tells us how many atoms of each element there are in each glucose molecule. Now look at the structural formulae shown in Figure 1.4. They show a molecule of α-glucose and a molecule of β-glucose. Count each type of atom in diagram (a). There are 6 carbon atoms, 12 hyd ...
AP Biology
... 2. Use the following terms correctly in a sentence: redox reactions, oxidation, reduction, reducing agent and oxidizing agent. ...
... 2. Use the following terms correctly in a sentence: redox reactions, oxidation, reduction, reducing agent and oxidizing agent. ...
The Synthesis of Ferrocene
... Preparing Ferrocene via an alternate route; Miller et al noted: Compounds containing only carbon, hydrogen, and iron have not hitherto been described, and the direct replacement of hydrogen attached to carbon by iron would not have been expected to be feasible. It has now been found that reduced iro ...
... Preparing Ferrocene via an alternate route; Miller et al noted: Compounds containing only carbon, hydrogen, and iron have not hitherto been described, and the direct replacement of hydrogen attached to carbon by iron would not have been expected to be feasible. It has now been found that reduced iro ...
products of the dioxygenase reaction ... useful intermediates for natural-product syntheses ...
... oxygenase-catalyzed reactions that are relevant to biocatalysis. Oxygen is typically supplied as O2, and the required reduction equivalents are usually derived from NADH or NADPH via electron-transfer proteins (e.g. reductase). Collectively, the oxygenases catalyze highly regioselective and stereose ...
... oxygenase-catalyzed reactions that are relevant to biocatalysis. Oxygen is typically supplied as O2, and the required reduction equivalents are usually derived from NADH or NADPH via electron-transfer proteins (e.g. reductase). Collectively, the oxygenases catalyze highly regioselective and stereose ...
Rhodopsin
... possibly could interact with the C9 methyl on the retinylidene group Met-207, His-211, Phe-212, Tyr268, and Ala-269 surround the Bionone ring of the retinal Tyr-43, Met-44, Leu-47, Thr-94 and Phe-293 region surrounds the Schiff base Ala-169 may interact with the Bionone ring in the activated state w ...
... possibly could interact with the C9 methyl on the retinylidene group Met-207, His-211, Phe-212, Tyr268, and Ala-269 surround the Bionone ring of the retinal Tyr-43, Met-44, Leu-47, Thr-94 and Phe-293 region surrounds the Schiff base Ala-169 may interact with the Bionone ring in the activated state w ...
1 - AQA
... is C6H12O6. This formula simply tells us how many atoms of each element there are in each glucose molecule. Now look at the structural formulae shown in Figure 1.4. They show a molecule of α-glucose and a molecule of β-glucose. Count each type of atom in diagram (a). There are 6 carbon atoms, 12 hyd ...
... is C6H12O6. This formula simply tells us how many atoms of each element there are in each glucose molecule. Now look at the structural formulae shown in Figure 1.4. They show a molecule of α-glucose and a molecule of β-glucose. Count each type of atom in diagram (a). There are 6 carbon atoms, 12 hyd ...
General Amino Acid Metabolism
... The first step in the catabolism of most amino acids is the transfer of their α - amino group to α -ketoglutarate where the products are α - ketoacids and glutamate. This transfer of amino groups from one carbon skeleton to another is catalyzed by a family of transaminases which are also called amin ...
... The first step in the catabolism of most amino acids is the transfer of their α - amino group to α -ketoglutarate where the products are α - ketoacids and glutamate. This transfer of amino groups from one carbon skeleton to another is catalyzed by a family of transaminases which are also called amin ...
Part I - Punjabi University
... 1. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of reducing and total sugars by biochemical and biophysical techniques. 2. Determination of acid value of a fat/oil. 3. Determination of cholesterol-total, free and esterified. 4. Isolation, qualitative and quantitative analysis of lipids. 5. Qualitative and ...
... 1. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of reducing and total sugars by biochemical and biophysical techniques. 2. Determination of acid value of a fat/oil. 3. Determination of cholesterol-total, free and esterified. 4. Isolation, qualitative and quantitative analysis of lipids. 5. Qualitative and ...
AnaerobicAerobic CellResp
... Aerobic respiration is not able to give enough energy fast enough - so, anaerobic respiration gives a small amount of extra energy. Lactic acid is formed as byproduct in the process, building up slowly in the muscles. Muscles are in an oxygen debt – body must make up for it. ...
... Aerobic respiration is not able to give enough energy fast enough - so, anaerobic respiration gives a small amount of extra energy. Lactic acid is formed as byproduct in the process, building up slowly in the muscles. Muscles are in an oxygen debt – body must make up for it. ...
Oxypred: Prediction and Classification of Oxygen-Binding
... Moreover, these proteins have also been reported to be present in many prokaryotes and protozoans (2 ). The occurrence of oxygen-binding proteins in all kingdoms of organisms, though not in all organisms, shows their biological importance. Extensive studies on oxygen-binding proteins have categorize ...
... Moreover, these proteins have also been reported to be present in many prokaryotes and protozoans (2 ). The occurrence of oxygen-binding proteins in all kingdoms of organisms, though not in all organisms, shows their biological importance. Extensive studies on oxygen-binding proteins have categorize ...
File
... the H+ gradient was set-up by the ETC H+ diffuse back into the matrix (down their concentration gradient) through a channel protein called ATP Synthase the energy released from the exergonic flow of H+ ions activates the ATP Synthase (an enzyme) which catalyzes the phosphorylation of ADP ...
... the H+ gradient was set-up by the ETC H+ diffuse back into the matrix (down their concentration gradient) through a channel protein called ATP Synthase the energy released from the exergonic flow of H+ ions activates the ATP Synthase (an enzyme) which catalyzes the phosphorylation of ADP ...
Chem 100 Unit 5 Biochemistry
... Non polar ends of molecules at the center are attracted to the circular nonpolar material. The negativiely charged groups on the surface are attracted to the water ...
... Non polar ends of molecules at the center are attracted to the circular nonpolar material. The negativiely charged groups on the surface are attracted to the water ...
Cellular Metabolism
... – The electrons “power” the movement of H+ (protons) across the inner membrane space creating a proton motive gradient – This gradient is utilized along with oxygen that has entered the mitochondrial matrix to power a rotary ATP synthase transmembrane protein complex – The “spent” electrons are pick ...
... – The electrons “power” the movement of H+ (protons) across the inner membrane space creating a proton motive gradient – This gradient is utilized along with oxygen that has entered the mitochondrial matrix to power a rotary ATP synthase transmembrane protein complex – The “spent” electrons are pick ...
Tutorial for PyMOL
... a. Make sure you go back to the “sticks-‐mode” for IHEW. b. Now select only the tri-‐NAG by clicking on the grey “tri-‐NAG” bar on the right hand side of the window. (When atoms are selected th ...
... a. Make sure you go back to the “sticks-‐mode” for IHEW. b. Now select only the tri-‐NAG by clicking on the grey “tri-‐NAG” bar on the right hand side of the window. (When atoms are selected th ...
Photometry
... • The purpose of this step is to zero the detector with the shutter closed and no light hitting the detector. 4) Fill a clean cuvette (test tube) with appropriate volume (about 2/3 of the cuvette) of your blank solution. Wipe the cuvette with a Kimwipe to remove liquid droplets, dusts, and fingerpri ...
... • The purpose of this step is to zero the detector with the shutter closed and no light hitting the detector. 4) Fill a clean cuvette (test tube) with appropriate volume (about 2/3 of the cuvette) of your blank solution. Wipe the cuvette with a Kimwipe to remove liquid droplets, dusts, and fingerpri ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. • Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms. ...
... Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. • Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms. ...
Metabolism of fat File
... • The products of this reaction are acetyl-CoA and an acyl-CoA derivative containing two carbons less than the original acyl-CoA molecule that underwent this oxidation. • The acyl-CoA formed in the cleavage reaction renters the oxidative pathway at reaction 1. ...
... • The products of this reaction are acetyl-CoA and an acyl-CoA derivative containing two carbons less than the original acyl-CoA molecule that underwent this oxidation. • The acyl-CoA formed in the cleavage reaction renters the oxidative pathway at reaction 1. ...
Question paper - Unit A173/02 - Module C7 - Higher tier (PDF
... The sugar is fermented with yeast at a temperature of about 30 °C. (a) The sustainability of chemical processes depends on a number of factors. One of these factors is the renewability of raw materials. Consider this, and other factors, to compare the sustainability of making ethanol by these two me ...
... The sugar is fermented with yeast at a temperature of about 30 °C. (a) The sustainability of chemical processes depends on a number of factors. One of these factors is the renewability of raw materials. Consider this, and other factors, to compare the sustainability of making ethanol by these two me ...
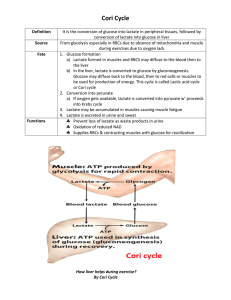
Cori Cycle - COFFEE BREAK CORNER
... conversion of lactate into glucose in liver From glycolysis especially in RBCs due to absence of mitochondria and muscle during exercises due to oxygen lack 1. Glucose formation a) Lactate formed i ...
... conversion of lactate into glucose in liver From glycolysis especially in RBCs due to absence of mitochondria and muscle during exercises due to oxygen lack 1. Glucose formation a) Lactate formed i ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.