essential amino acid
... Tryptophan Glycine Valine Ornithine * Proline * Selenocysteine * Serine * Taurine * Tyrosine * (*) Essential only in certain cases ...
... Tryptophan Glycine Valine Ornithine * Proline * Selenocysteine * Serine * Taurine * Tyrosine * (*) Essential only in certain cases ...
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts & Connections 4th Edition
... • An adenine (A) on one strand always hydrogen bonds to a thymine (T) on the other strand. • Also, a cytosine (C) on one strand always hydrogen bonds to a guanine (G) on the other strand. • These interactions give DNA its characteristic structure. ...
... • An adenine (A) on one strand always hydrogen bonds to a thymine (T) on the other strand. • Also, a cytosine (C) on one strand always hydrogen bonds to a guanine (G) on the other strand. • These interactions give DNA its characteristic structure. ...
Fatty oxidation, Amino acid degradation and energy metabolism
... 3. What are the ultimate catabolic products of Amino acids in mammalians? 4. What are the carriers of amino gp (ammonia) in blood? 5. During heavy exercise muscles produce excess of pyruvate due to accelerated glycolysis and lower oxygen availability. This pyruvate is used up for gluconeo genesis. H ...
... 3. What are the ultimate catabolic products of Amino acids in mammalians? 4. What are the carriers of amino gp (ammonia) in blood? 5. During heavy exercise muscles produce excess of pyruvate due to accelerated glycolysis and lower oxygen availability. This pyruvate is used up for gluconeo genesis. H ...
Basic Biochemistry Powerpoint
... The order or sequence of the amino acids determine the function of the protein ...
... The order or sequence of the amino acids determine the function of the protein ...
2. Explain how organic polymers contribute to
... - precursor to sex hormones and bile acids - common in cell membranes -atheriosclerosis ...
... - precursor to sex hormones and bile acids - common in cell membranes -atheriosclerosis ...
Energy Production
... coenzyme that catalyzes the process. Also, supply for the pathway substrate is limited to blood glucose or muscle glycogen. Liver glycogen contributes but is limited in amount. The amount of ATP synthesized is limited and only 30 % efficient, thus contributes energy lasting up to 60-120 seconds e.g. ...
... coenzyme that catalyzes the process. Also, supply for the pathway substrate is limited to blood glucose or muscle glycogen. Liver glycogen contributes but is limited in amount. The amount of ATP synthesized is limited and only 30 % efficient, thus contributes energy lasting up to 60-120 seconds e.g. ...
C14, C14:1
... Catalyzes first step of b-oxidation for C14C20 Defect leads to impaired energy production during times of fasting stress Accumulation of toxic long-chain acyl-CoA intermediates within mitochondria Steatosis (fatty accumulation/degeneration) seen in hepatic, cardiac and skeletal muscle ...
... Catalyzes first step of b-oxidation for C14C20 Defect leads to impaired energy production during times of fasting stress Accumulation of toxic long-chain acyl-CoA intermediates within mitochondria Steatosis (fatty accumulation/degeneration) seen in hepatic, cardiac and skeletal muscle ...
File
... • These drugs are effective in lowering plasma cholesterol levels in all types of hyperlipidemias. • All statins are metabolized in the liver, with some metabolites retaining activity. • Excretion takes place principally through bile and feces, but some urinary elimination also occurs. • Elevated ...
... • These drugs are effective in lowering plasma cholesterol levels in all types of hyperlipidemias. • All statins are metabolized in the liver, with some metabolites retaining activity. • Excretion takes place principally through bile and feces, but some urinary elimination also occurs. • Elevated ...
Nucleic Acids - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... information by determining what proteins a cell makes A. ...
... information by determining what proteins a cell makes A. ...
Tutorial Kit (Biochemistry-300 L)
... cofactors and they can be, for example, organic ions like mineral salts, or organic molecules. Inactive enzymes which are not bound to their cofactors are called apoenzymes. Active enzymes bound to their cofactors are called holoenzymes. 9. What is the relationship between vitamins and enzyme cofact ...
... cofactors and they can be, for example, organic ions like mineral salts, or organic molecules. Inactive enzymes which are not bound to their cofactors are called apoenzymes. Active enzymes bound to their cofactors are called holoenzymes. 9. What is the relationship between vitamins and enzyme cofact ...
SMU-DDE-Assignments-Scheme of Evaluation PROGRAM Bachelor
... produce acetoacetate and acetyl CoA. Acetoacetate can be reduced to form 3-hydroxybutyrate with NADH as the hydrogen donor. Acetoacetate can also spontaneously decarboxylate in the blood to form acetone- a volatile, biologically non-metabolized compound that can be released in the breath. The equili ...
... produce acetoacetate and acetyl CoA. Acetoacetate can be reduced to form 3-hydroxybutyrate with NADH as the hydrogen donor. Acetoacetate can also spontaneously decarboxylate in the blood to form acetone- a volatile, biologically non-metabolized compound that can be released in the breath. The equili ...
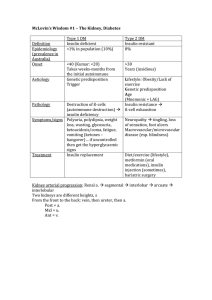
McLovin`s Wisdom #1 – The Kidney, Diabetes Type 1 DM Type 2
... At complex 4, 1/2O2 + 2H+ H2O (the H+s are reacted with oxygen to reduce it to water. Hence oxygen is needed). ATP synthase. 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membra ...
... At complex 4, 1/2O2 + 2H+ H2O (the H+s are reacted with oxygen to reduce it to water. Hence oxygen is needed). ATP synthase. 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membra ...
Macromolecules - Uplift Education
... • Used for energy storage in liver & muscles • Made of glucose molecules ...
... • Used for energy storage in liver & muscles • Made of glucose molecules ...
Chem331 Krebs Cycle
... TCA (tricarboxylic acid cycle) Citric acid cycle and Krebs cycle. Named after Sir Hans Krebs, Nobel Laureate. He worked as an assistant professor for Otto Warburg (Nobel Prize 1931) and his position terminated 1933 and at, Sir Fredrick Gowland Hopkin's (Nobel prize 1929) request he left Germany to h ...
... TCA (tricarboxylic acid cycle) Citric acid cycle and Krebs cycle. Named after Sir Hans Krebs, Nobel Laureate. He worked as an assistant professor for Otto Warburg (Nobel Prize 1931) and his position terminated 1933 and at, Sir Fredrick Gowland Hopkin's (Nobel prize 1929) request he left Germany to h ...
Lipids and Membranes
... made of fatty acids, glycerol, a phosphoryl group and an alcohol. Many also contain nitrogen – glycolipids (also known as glycosphingolipids): Lipids which have a spingosine and different backbone than the phospholipids ...
... made of fatty acids, glycerol, a phosphoryl group and an alcohol. Many also contain nitrogen – glycolipids (also known as glycosphingolipids): Lipids which have a spingosine and different backbone than the phospholipids ...
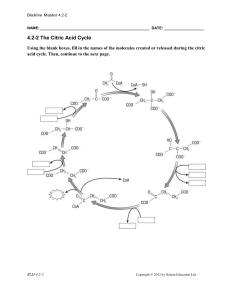
Blackline Master 4.2-2 NAME: DATE: 4.2
... ________________enters the cycle and then combines with ________________ to make the six-carbon compound ________________. During the eight steps of the citric cycle, ________________ undergoes a number of reactions, releasing _______ and ______ in a number of steps. ________________ is eventually c ...
... ________________enters the cycle and then combines with ________________ to make the six-carbon compound ________________. During the eight steps of the citric cycle, ________________ undergoes a number of reactions, releasing _______ and ______ in a number of steps. ________________ is eventually c ...
chapter3_part2
... coiled (helical) or sheetlike array held in place by hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) between different parts of the polypeptide chain. ...
... coiled (helical) or sheetlike array held in place by hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) between different parts of the polypeptide chain. ...
Macromolecules
... Notice the long chain hydrocarbon (fatty acid region) which is hydrophobic and the phosphate group which is hydrophilic . ...
... Notice the long chain hydrocarbon (fatty acid region) which is hydrophobic and the phosphate group which is hydrophilic . ...
Unit 2
... 8. To understand the self-ionization of water, that it always occurs in any aqueous solution, and that it has a specific equilibrium constant called Kw, the ion product of water. 9. To understand the definitions of pH and pOH, and review operations of common logarithms. 10. To convert among [H+], [O ...
... 8. To understand the self-ionization of water, that it always occurs in any aqueous solution, and that it has a specific equilibrium constant called Kw, the ion product of water. 9. To understand the definitions of pH and pOH, and review operations of common logarithms. 10. To convert among [H+], [O ...
3.2 Carbohydrates, lipids and proteins – summary of previous mark
... lipids are insoluble in water less osmotic effect; lipids have more / twice the energy content per unit mass of carbohydrates; lipids / triglycerides used for long-term energy storage; triglycerides converted to fatty acids and glycerol (when energy is required); triglycerides broken down to yield a ...
... lipids are insoluble in water less osmotic effect; lipids have more / twice the energy content per unit mass of carbohydrates; lipids / triglycerides used for long-term energy storage; triglycerides converted to fatty acids and glycerol (when energy is required); triglycerides broken down to yield a ...
9.6 Respiration 4 (Control and other metabolites)
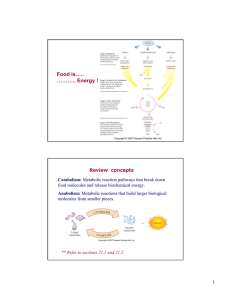
... – digestion • catabolism when organism needs energy or needs raw materials – synthesis • anabolism when organism has enough energy & a supply of raw materials – by regulating enzymes • feedback mechanisms • raw materials stimulate production • products inhibit further production ...
... – digestion • catabolism when organism needs energy or needs raw materials – synthesis • anabolism when organism has enough energy & a supply of raw materials – by regulating enzymes • feedback mechanisms • raw materials stimulate production • products inhibit further production ...
Energy
... Once this phosphate is formed, glucose is trapped within the cell because phosphorylated molecules cannot cross the cell membrane. Like the first step in many metabolic pathways, the formation of glucose-6-phosphate is highly exergonic and not reversible in the glycolytic pathway, thereby committing ...
... Once this phosphate is formed, glucose is trapped within the cell because phosphorylated molecules cannot cross the cell membrane. Like the first step in many metabolic pathways, the formation of glucose-6-phosphate is highly exergonic and not reversible in the glycolytic pathway, thereby committing ...
Metabolism 2010edit
... – digestion • catabolism when organism needs energy or needs raw materials – synthesis • anabolism when organism has enough energy & a supply of raw materials – by regulating enzymes • feedback mechanisms • raw materials stimulate production • products inhibit further production ...
... – digestion • catabolism when organism needs energy or needs raw materials – synthesis • anabolism when organism has enough energy & a supply of raw materials – by regulating enzymes • feedback mechanisms • raw materials stimulate production • products inhibit further production ...
Quick Quiz1
... will call on students randomly in class on 2/20 to read their answers to the class. Note: I will be calling on students who don’t normally speak up in class . ...
... will call on students randomly in class on 2/20 to read their answers to the class. Note: I will be calling on students who don’t normally speak up in class . ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.