Summary for Chapter 7 – Metabolism: Transformations
... Summary for Chapter 7 – Metabolism: Transformations and Interactions During digestion the energy-yielding nutrients—carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins—are broken down to glucose (and other monosaccharides), glycerol, fatty acids, and amino acids. Aided by enzymes and coenzymes, the cells use these ...
... Summary for Chapter 7 – Metabolism: Transformations and Interactions During digestion the energy-yielding nutrients—carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins—are broken down to glucose (and other monosaccharides), glycerol, fatty acids, and amino acids. Aided by enzymes and coenzymes, the cells use these ...
Lecture_11
... In tissues using ketone bodies, 3-hydroxybutyrate is oxidized to acetoacetate, which is ultimately metabolized to two molecules of acetyl CoA. ...
... In tissues using ketone bodies, 3-hydroxybutyrate is oxidized to acetoacetate, which is ultimately metabolized to two molecules of acetyl CoA. ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... greatest number of hydrogens to be attached to the carbon skeleton • Includes most animal fats • Solid at room temp ...
... greatest number of hydrogens to be attached to the carbon skeleton • Includes most animal fats • Solid at room temp ...
Inborn error in metabolism of amino acids
... is ketogenic while Isoleucine (Ile) (I) is both ketogenicand glucogenic. All the three are essential amino acids. Leucine is the major ketogenic amino acid.These amino acids serve as an alternate source of fuel for the brain especially under conditions of starvation.metabolism of these amino acid in ...
... is ketogenic while Isoleucine (Ile) (I) is both ketogenicand glucogenic. All the three are essential amino acids. Leucine is the major ketogenic amino acid.These amino acids serve as an alternate source of fuel for the brain especially under conditions of starvation.metabolism of these amino acid in ...
Amino Acids - Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC INTERNATIONAL
... of analyte that can be detected in a given matrix with no greater than 5% false-positive risk and 5% false-negative risk. Limit of quantitation (LOQ).—The minimum concentration or mass of analyte in a given matrix that can be reported as a quantitative result. Proteinogenic L-α-amino acids.—Amino ac ...
... of analyte that can be detected in a given matrix with no greater than 5% false-positive risk and 5% false-negative risk. Limit of quantitation (LOQ).—The minimum concentration or mass of analyte in a given matrix that can be reported as a quantitative result. Proteinogenic L-α-amino acids.—Amino ac ...
Secondary Metabolism Part 1: Introduction, Fatty Acids and
... acids) and their production via metabolic pathways are conserved among diverse organisms • Secondary Metabolites are more specialized molecules (e.g. toxins, volatile attractants, coloring agents) and many are organism-specific • Often referred to as natural products. Branch of organic chemistry = n ...
... acids) and their production via metabolic pathways are conserved among diverse organisms • Secondary Metabolites are more specialized molecules (e.g. toxins, volatile attractants, coloring agents) and many are organism-specific • Often referred to as natural products. Branch of organic chemistry = n ...
File
... 1. Contain even more C-H bonds than carbohydrates. 2. C-H bonds are non-polar and cannot form hydrogen bonds with water. 3. Hydrophobically excluded by water molecules – so they cluster together; insoluble and can be deposited at specific locations within the organisms. ...
... 1. Contain even more C-H bonds than carbohydrates. 2. C-H bonds are non-polar and cannot form hydrogen bonds with water. 3. Hydrophobically excluded by water molecules – so they cluster together; insoluble and can be deposited at specific locations within the organisms. ...
Ch 3 The Molecules of Cells
... Fat is now saturated Trans-fats created by heat (e.g. deep frying) & hydrogenation Double bonds fold in unnatural direction Enzymes that process fat are unable to process transfatty acids in a normal way Domino effect: Because trying to process trans-fatty acids, don’t process essential fatty acids ...
... Fat is now saturated Trans-fats created by heat (e.g. deep frying) & hydrogenation Double bonds fold in unnatural direction Enzymes that process fat are unable to process transfatty acids in a normal way Domino effect: Because trying to process trans-fatty acids, don’t process essential fatty acids ...
MACROMOLECULES - Savitha Sastry
... II) Lipids Lipids – are hydrophobic (mostly hydrocarbons) They are NOT polymers Important classes: FATS, PHOSPHOLIPIDS, and STEROIDS ...
... II) Lipids Lipids – are hydrophobic (mostly hydrocarbons) They are NOT polymers Important classes: FATS, PHOSPHOLIPIDS, and STEROIDS ...
Course Name:
... entropy. The central role of adenosine triphosphate. Glycolysis and alcohol fermentation. The energy yielding phase of Glycolysis, production of ATP. (3 hr) Glycogen metabolism. Inter-conversion of hexosemonophosphates. Biosynthetic role of Glycolysis. The phosphate pathway. (2 hr) The tricarbxylic ...
... entropy. The central role of adenosine triphosphate. Glycolysis and alcohol fermentation. The energy yielding phase of Glycolysis, production of ATP. (3 hr) Glycogen metabolism. Inter-conversion of hexosemonophosphates. Biosynthetic role of Glycolysis. The phosphate pathway. (2 hr) The tricarbxylic ...
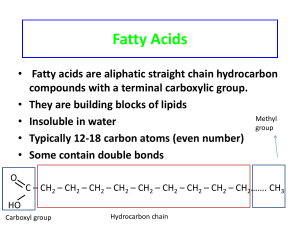
Fatty acid - thevignanam
... there are about 200 fatty acids Acetic acid (CH3COOH); Palmitic acid (C15H31COOH); Stearic acid (C17H35COOH); Oleic acid (C17H33COOH) they may or may not contain double bonds – fatty acids with double bonds are called as unsaturated fatty acids and fatty acids with double bonds are called as s ...
... there are about 200 fatty acids Acetic acid (CH3COOH); Palmitic acid (C15H31COOH); Stearic acid (C17H35COOH); Oleic acid (C17H33COOH) they may or may not contain double bonds – fatty acids with double bonds are called as unsaturated fatty acids and fatty acids with double bonds are called as s ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... A serious disease results from the inability to oxidize phenylalanine by a defective phenylalanine hydroxylase. This results in high levels of phenylpyruvate developing (phenylpyruvate is the result of transamination of phenylalanine with an amino acid). The disease is phenylketonuria (PKU), and res ...
... A serious disease results from the inability to oxidize phenylalanine by a defective phenylalanine hydroxylase. This results in high levels of phenylpyruvate developing (phenylpyruvate is the result of transamination of phenylalanine with an amino acid). The disease is phenylketonuria (PKU), and res ...
L10v02a_-_glycolysis.stamped_doc
... worth about three ATP each so we've made basically 10 molecules of ATP here although six will be coming later. [00:03:46.71] And then finally pyruvate is the molecule that will be shuttled into the mitochondria for the citric acid cycle. [00:03:53.52] I'd like to look at a detail of step three in g ...
... worth about three ATP each so we've made basically 10 molecules of ATP here although six will be coming later. [00:03:46.71] And then finally pyruvate is the molecule that will be shuttled into the mitochondria for the citric acid cycle. [00:03:53.52] I'd like to look at a detail of step three in g ...
Marvelous Macromolecules
... Animals can’t digest cellulose (passes through making digestion easier) Herbivores have special microbes in their stomachs that can digest cellulose (that’s why they can survive on only plants) ...
... Animals can’t digest cellulose (passes through making digestion easier) Herbivores have special microbes in their stomachs that can digest cellulose (that’s why they can survive on only plants) ...
1/23 Notes and Classwork
... three-carbon chain that connects the fatty acids together. A fatty acid is just a long chain of carbon atoms connected to each other. Saturated and Unsaturated There are two kinds of fats, saturated and unsaturated. Unsaturated fats have at least one double bond in one of the fatty acids. A double b ...
... three-carbon chain that connects the fatty acids together. A fatty acid is just a long chain of carbon atoms connected to each other. Saturated and Unsaturated There are two kinds of fats, saturated and unsaturated. Unsaturated fats have at least one double bond in one of the fatty acids. A double b ...
a sample task
... chains and two beta chains, each consisting of about 150 amino acids, for a total of 600 amino acids in the whole protein. The difference between a normal hemoglobin molecule and a sickle cell molecule—which dramatically decreases life expectancy—is just one amino acid out of the 600. So, why should ...
... chains and two beta chains, each consisting of about 150 amino acids, for a total of 600 amino acids in the whole protein. The difference between a normal hemoglobin molecule and a sickle cell molecule—which dramatically decreases life expectancy—is just one amino acid out of the 600. So, why should ...
CHAPTER 7 – COENZYMES AND VITAMINS CHAPTER SUMMARY
... 35. Ubiquinone (coenzyme ___) is lipid soluble and synthesized by almost all species. Its long hydrophobic chain allows it to dissolve into _______________, and its function is the transport of _______________ between membrane-embedded enzyme complexes. 36. Coenzyme Q is responsible for moving _____ ...
... 35. Ubiquinone (coenzyme ___) is lipid soluble and synthesized by almost all species. Its long hydrophobic chain allows it to dissolve into _______________, and its function is the transport of _______________ between membrane-embedded enzyme complexes. 36. Coenzyme Q is responsible for moving _____ ...
Structure of Proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats
... Fats are a sub-group of compounds known as lipids that are found in the body and have the general property of being hydrophobic (meaning they are insoluble in water). Fats are also known as triglycerides, molecules made from the combination of one molecule of glycerol with three fatty acids, as depi ...
... Fats are a sub-group of compounds known as lipids that are found in the body and have the general property of being hydrophobic (meaning they are insoluble in water). Fats are also known as triglycerides, molecules made from the combination of one molecule of glycerol with three fatty acids, as depi ...
Teacher`s Name: ___Julie
... x Using academic games x Using questioning techniques, probing incorrect answers; high expectations for all x Differentiating instruction x Checking for student understanding INCORPORATING the following: x Student technology use x Assessment – pre/form/sum/ ACT-like x Live-Scoring x Reading & writin ...
... x Using academic games x Using questioning techniques, probing incorrect answers; high expectations for all x Differentiating instruction x Checking for student understanding INCORPORATING the following: x Student technology use x Assessment – pre/form/sum/ ACT-like x Live-Scoring x Reading & writin ...
Cellular_Respiration_overviewap
... affinities. While being passed along the ETC, these high energy electrons are used by the ETC proteins to pump hydrogen ions across the inner membrane. This creates a high H+ concentration in the intermembrane space and a low H+ concentration in the matrix. The final acceptor of the electrons is oxy ...
... affinities. While being passed along the ETC, these high energy electrons are used by the ETC proteins to pump hydrogen ions across the inner membrane. This creates a high H+ concentration in the intermembrane space and a low H+ concentration in the matrix. The final acceptor of the electrons is oxy ...
Hans A. Krebs - Nobel Lecture
... between these amino acids and the citric acid cycle. It is thus evident that a substantial proportion of protein molecules pass through the citric acid cycle when undergoing oxidation. Since 1943 it has become evident that the citric acid cycle also comes into play in the later stages of the oxidati ...
... between these amino acids and the citric acid cycle. It is thus evident that a substantial proportion of protein molecules pass through the citric acid cycle when undergoing oxidation. Since 1943 it has become evident that the citric acid cycle also comes into play in the later stages of the oxidati ...
2.3 and 2.4 Notes
... How is a tulip bulb able to sprout in the spring and then come back again each year? ...
... How is a tulip bulb able to sprout in the spring and then come back again each year? ...
biomolecule ppt
... LIPIDS (fats) ● Functions: o Lipids can be used to store energy for later use o Phospholipids are important parts of biological membranes ...
... LIPIDS (fats) ● Functions: o Lipids can be used to store energy for later use o Phospholipids are important parts of biological membranes ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.