LAB 7
... found in living organisms. This lab deals with the important class of organic molecules known as proteins. They are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hair, muscle and blood. Other proteins serve in a regulatory capacity as enzymes or hormones. Proteins alway ...
... found in living organisms. This lab deals with the important class of organic molecules known as proteins. They are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hair, muscle and blood. Other proteins serve in a regulatory capacity as enzymes or hormones. Proteins alway ...
Biochemistry Objectives 43
... abundance of exogenous glucose; however, during the late post-absorptive state and early starvation, where protein catabolism for gluconeogenesis is necessary, cortisol synthesis and release is stimulated. Cortisol levels drop off during prolonged starvation in an effort to conserve proteins. ...
... abundance of exogenous glucose; however, during the late post-absorptive state and early starvation, where protein catabolism for gluconeogenesis is necessary, cortisol synthesis and release is stimulated. Cortisol levels drop off during prolonged starvation in an effort to conserve proteins. ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... 2. Draw two or three water molecules interacting with each other by accurately depicting where the hydrogen bonds would take place in your illustration. ...
... 2. Draw two or three water molecules interacting with each other by accurately depicting where the hydrogen bonds would take place in your illustration. ...
Chapter 2 Chemistry
... by hydrogen bonds iv. Contains a sugar-phosphate backbone b. Ribonucleic acid i. RNA is different from DNA in that: 1. Its sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose 2. It has the base uracil (U) instead of thymine (T) 3. It’s single stranded c. Some other nucleotides: i. ATP used for cellular work ii. ...
... by hydrogen bonds iv. Contains a sugar-phosphate backbone b. Ribonucleic acid i. RNA is different from DNA in that: 1. Its sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose 2. It has the base uracil (U) instead of thymine (T) 3. It’s single stranded c. Some other nucleotides: i. ATP used for cellular work ii. ...
Citric Acid Cycle Overview
... 5. Succinyl CoA Synthetase • Synthetase means ATP (or GTP) involved • High energy bond used to do substrate‐ level phosphorylation – Good leaving group to activate Pi – Covalent catalysis – GDP GTP ...
... 5. Succinyl CoA Synthetase • Synthetase means ATP (or GTP) involved • High energy bond used to do substrate‐ level phosphorylation – Good leaving group to activate Pi – Covalent catalysis – GDP GTP ...
METABOLISM FOUR CLASSES OF BIOMOLECULES (ALL
... amino acids are joined by a peptide bond…a type of covalent bond. ...
... amino acids are joined by a peptide bond…a type of covalent bond. ...
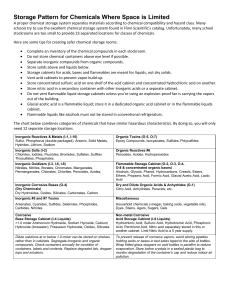
Storage Pattern for Chemicals Where Space is Limited
... Store concentrated sulfuric acid on one shelf of the acid cabinet and concentrated hydrochloric acid on another. Store nitric acid in a secondary container with other inorganic acids or a separate cabinet. Do not vent flammable liquid storage cabinets unless you’re using an explosion-proof fan is ca ...
... Store concentrated sulfuric acid on one shelf of the acid cabinet and concentrated hydrochloric acid on another. Store nitric acid in a secondary container with other inorganic acids or a separate cabinet. Do not vent flammable liquid storage cabinets unless you’re using an explosion-proof fan is ca ...
Contents - Garland Science
... tricarboxylic acid cycle The tricarboxylic acid cycle is regulated at several steps Recent research into a thioredoxin/NADPH redox system for regulating tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes and other mitochondrial proteins ...
... tricarboxylic acid cycle The tricarboxylic acid cycle is regulated at several steps Recent research into a thioredoxin/NADPH redox system for regulating tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes and other mitochondrial proteins ...
Lecture 9. Treatments
... metabolism. These compounds normally accumulate during exercise or ischemia, but are also elevated in patients with disorders of pyruvate metabolism or mitochondrial disorders. Ammonia is an end product of amino acid metabolism and is converted in the liver to urea through a series of enzymatic reac ...
... metabolism. These compounds normally accumulate during exercise or ischemia, but are also elevated in patients with disorders of pyruvate metabolism or mitochondrial disorders. Ammonia is an end product of amino acid metabolism and is converted in the liver to urea through a series of enzymatic reac ...
Lipids MCAS Practice Name: Date: 1. All living things contain which
... The brown paper test for lipids is positive when food is placed on the paper and a spot forms which will allow light to pass through it. Which food would give the most positive test for lipids? ...
... The brown paper test for lipids is positive when food is placed on the paper and a spot forms which will allow light to pass through it. Which food would give the most positive test for lipids? ...
BOTANY DEPARTMENT - university of nairobi staff profiles
... 2. To describe and emphasize functional and regulatory aspects with illustrations of pathways and structural features of carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids. 3. To describe the importance of cellular respiration and energy metabolism. Expected Learning Outcome By the end of the course unit the lea ...
... 2. To describe and emphasize functional and regulatory aspects with illustrations of pathways and structural features of carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids. 3. To describe the importance of cellular respiration and energy metabolism. Expected Learning Outcome By the end of the course unit the lea ...
Carbs and Lipids Review
... acids have at least one double bond between carbons in the chain. They are generally from plants and liquid at room temperature. 22. What are the two types of fatty acids? a. ______________________________________________ b. ______________________________________________ 23. What does an unsaturated ...
... acids have at least one double bond between carbons in the chain. They are generally from plants and liquid at room temperature. 22. What are the two types of fatty acids? a. ______________________________________________ b. ______________________________________________ 23. What does an unsaturated ...
Biomolecule exam review
... acids have at least one double bond between carbons in the chain. They are generally from plants and liquid at room temperature. 22. What are the two types of fatty acids? a. ______________________________________________ b. ______________________________________________ 23. What does an unsaturated ...
... acids have at least one double bond between carbons in the chain. They are generally from plants and liquid at room temperature. 22. What are the two types of fatty acids? a. ______________________________________________ b. ______________________________________________ 23. What does an unsaturated ...
Amino Acid Catabolism
... • Transfer of an amino group from an α-amino acid to an α-keto acid • In amino acid biosynthesis, the amino group of glutamate is transferred to various α-keto acids generating α-amino acids • In amino acid catabolism, transamination reactions generate glutamate or aspartate ...
... • Transfer of an amino group from an α-amino acid to an α-keto acid • In amino acid biosynthesis, the amino group of glutamate is transferred to various α-keto acids generating α-amino acids • In amino acid catabolism, transamination reactions generate glutamate or aspartate ...
C - Eric Hamber Secondary
... - heavy metals (mercury, lead etc.) bind preferentially with specific R group bonds (the S in Cystine), breaking the tertiary structure. C11. FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS - polymers of amino acids - have 2 major functions I) Structural - large proteins are important - muscle, tendon, cartilage, hair etc. K ...
... - heavy metals (mercury, lead etc.) bind preferentially with specific R group bonds (the S in Cystine), breaking the tertiary structure. C11. FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS - polymers of amino acids - have 2 major functions I) Structural - large proteins are important - muscle, tendon, cartilage, hair etc. K ...
Biological Molecules - Parkland Secondary School
... The glycocalyx also help cells adhere to each other. Structure All carbohydrates have approximately 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom (ie. water) for each carbon atom hence the name ‘hydrates of carbon’. Usually, the formula for carbohydrates is given as the molecular formula which gives clue ...
... The glycocalyx also help cells adhere to each other. Structure All carbohydrates have approximately 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom (ie. water) for each carbon atom hence the name ‘hydrates of carbon’. Usually, the formula for carbohydrates is given as the molecular formula which gives clue ...
acetyl-CoA - Winona State University
... positive value if there is “No Membrane In Between”. This is why Delta G from the reactions in the mitochondria cannot help to drive the reactions of glycolysis in the cytosol. Although molecules such as pyruvate can “carry” the energy between different compartments. ...
... positive value if there is “No Membrane In Between”. This is why Delta G from the reactions in the mitochondria cannot help to drive the reactions of glycolysis in the cytosol. Although molecules such as pyruvate can “carry” the energy between different compartments. ...
Reading Guide
... 19. Amino acids are not completely catabolized in the liver. Rather, the nitrogen is removed through ________________ reactions, then the carbon skeletons are transformed into compounds such as ____________ and ____________ for fuel storage.. 20. Two catabolic classifications for amino acids are ___ ...
... 19. Amino acids are not completely catabolized in the liver. Rather, the nitrogen is removed through ________________ reactions, then the carbon skeletons are transformed into compounds such as ____________ and ____________ for fuel storage.. 20. Two catabolic classifications for amino acids are ___ ...
Basic Strategies of Cell Metabolism
... convert substrate into the desired product. For the biotechnological evaluation of the usefulness of a microbial process, for example, the stoichiometry of microbial metabolism together with its regulatory mechanisms can be a very useful tool, since stoichiometric equations describing the consumptio ...
... convert substrate into the desired product. For the biotechnological evaluation of the usefulness of a microbial process, for example, the stoichiometry of microbial metabolism together with its regulatory mechanisms can be a very useful tool, since stoichiometric equations describing the consumptio ...
b-Oxidation of fatty acids
... Cytochrome c has a dual function in the cell. Electron transport for ATP production AND the major cause of most programmed cell death (apoptosis) is initiated by the release of cytochrome c into the cytosol! ...
... Cytochrome c has a dual function in the cell. Electron transport for ATP production AND the major cause of most programmed cell death (apoptosis) is initiated by the release of cytochrome c into the cytosol! ...
A2 Module 2814: Chains, Rings and Spectroscopy
... the proteins found in living organisms. They are all α-amino acids, i.e. the NH2 and the COOH groups are attached to the same carbon atom. Their general formula is RCH(NH 2)COOH, where R represents a side-chain (not just an alkyl group). Three examples are given below: ...
... the proteins found in living organisms. They are all α-amino acids, i.e. the NH2 and the COOH groups are attached to the same carbon atom. Their general formula is RCH(NH 2)COOH, where R represents a side-chain (not just an alkyl group). Three examples are given below: ...
Amino Acid Sidechains
... Relationship of pK and pH to charge Every acidic or basic group on a molecule has a different “pK” (K is the dissociation constant) value. The relationship between the pH of the solution it is in and the pK of the ionizable group will determine the predominant form of the ionizable group. Every aci ...
... Relationship of pK and pH to charge Every acidic or basic group on a molecule has a different “pK” (K is the dissociation constant) value. The relationship between the pH of the solution it is in and the pK of the ionizable group will determine the predominant form of the ionizable group. Every aci ...
Lipid Biosynthesis
... Mammalian liver smooth ER contains four desaturase enzymes. There are Δ4, Δ5, Δ6, and Δ9 Fatty AcylCoA Desaturases that introduce double bonds into newly synthesized fatty acids with a wide variety of chain lengths. The Fatty Acyl-CoA Desaturases are mix-function oxidases, they oxidize two substrat ...
... Mammalian liver smooth ER contains four desaturase enzymes. There are Δ4, Δ5, Δ6, and Δ9 Fatty AcylCoA Desaturases that introduce double bonds into newly synthesized fatty acids with a wide variety of chain lengths. The Fatty Acyl-CoA Desaturases are mix-function oxidases, they oxidize two substrat ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.