The Mechanics of Life
... • Living things (organisms) are self-‐replica$ng machines. • All organisms are composed of cells. • Most organisms consist of single cells. • Mul$cellular organisms are the most complex and integrated machine ...
... • Living things (organisms) are self-‐replica$ng machines. • All organisms are composed of cells. • Most organisms consist of single cells. • Mul$cellular organisms are the most complex and integrated machine ...
Development of drug targets for bone diseases.
... regulation of bone growth in our body is controlled by various enzymes and other genetic factors. We are just beginning to understand the cause and molecular pathways of many bone diseases and looking to develop novel drug targets for such diseases. Here, we focus our attention on the Atm-cAbl-p53 p ...
... regulation of bone growth in our body is controlled by various enzymes and other genetic factors. We are just beginning to understand the cause and molecular pathways of many bone diseases and looking to develop novel drug targets for such diseases. Here, we focus our attention on the Atm-cAbl-p53 p ...
Representation of and Reasoning with signal networks
... – a process whereby certain molecules are attracted (recruited) by another molecule to a particular site within the cell, often to form a complex which is a component of a pathway. For example the T-cell receptor (TCR) is a membrane associated receptor with extracellular portion which binds antigen ...
... – a process whereby certain molecules are attracted (recruited) by another molecule to a particular site within the cell, often to form a complex which is a component of a pathway. For example the T-cell receptor (TCR) is a membrane associated receptor with extracellular portion which binds antigen ...
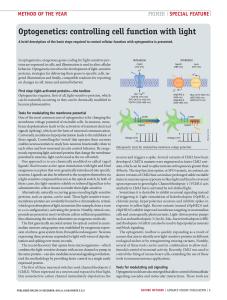
Optogenetics: controlling cell function with light
... Fusions of PIF with upstream activators of the Rho-family GTPases allowed light-dependent recruitment to the plasma membrane where PhyB was anchored, leading to localized activation of the actin cytoskeleton and formation of cellular extensions. Unlike the retinaland flavin-based systems described a ...
... Fusions of PIF with upstream activators of the Rho-family GTPases allowed light-dependent recruitment to the plasma membrane where PhyB was anchored, leading to localized activation of the actin cytoskeleton and formation of cellular extensions. Unlike the retinaland flavin-based systems described a ...
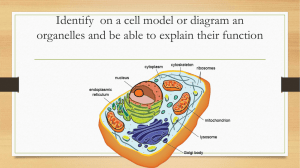
Identify on a cell model or diagram an organelles and be able to
... Identify on a cell model or diagram an organelles and be able to explain their function ...
... Identify on a cell model or diagram an organelles and be able to explain their function ...
IMMUNE DEFENCE - ASAB-NUST
... In man it consists of set of over 20 soluble glycoproteins, many of which are produced by hepatocytes and monocytes. They are constitutively present in blood and other body fluids and may be present in quite large amounts. For example C3, the pivotal molecule of the complement system, is present at ...
... In man it consists of set of over 20 soluble glycoproteins, many of which are produced by hepatocytes and monocytes. They are constitutively present in blood and other body fluids and may be present in quite large amounts. For example C3, the pivotal molecule of the complement system, is present at ...
Table S2. Functional classification of differentially expressed genes
... Transcriptional regulators ...
... Transcriptional regulators ...
Why do cells need a stable environment?
... inside the body. The environment influencing cells is the tissue fluid which surrounds them. • The internal environment may change due to the products of metabolism diffusing into the tissue fluid. E.g. CO2 is a waste product of respiration. If allowed to build up it changes the pH of the environmen ...
... inside the body. The environment influencing cells is the tissue fluid which surrounds them. • The internal environment may change due to the products of metabolism diffusing into the tissue fluid. E.g. CO2 is a waste product of respiration. If allowed to build up it changes the pH of the environmen ...
OptoXR control - Mike DeSalvio
... Test in Neural Tissue • Used a Lentiviral vector with Synapsin-I promotor to deliver optoXR gene – Targets biochemical modulation to local neurons only – Excludes Gs/Gq responsive cells such as glia and endothelial cells • Stereotactically injected into nucleus accumbens of adult mice – Targeting b ...
... Test in Neural Tissue • Used a Lentiviral vector with Synapsin-I promotor to deliver optoXR gene – Targets biochemical modulation to local neurons only – Excludes Gs/Gq responsive cells such as glia and endothelial cells • Stereotactically injected into nucleus accumbens of adult mice – Targeting b ...
cell signalling
... Why the need for receptors? • Cells need to be able to sense and respond to changes in their internal and external environment • cells need to communicate information between each other by the process of cell signalling ...
... Why the need for receptors? • Cells need to be able to sense and respond to changes in their internal and external environment • cells need to communicate information between each other by the process of cell signalling ...
Gene Section DAB2 (disabled homolog 2, mitogen-responsive phosphoprotein (Drosophila))
... Angiogenesis: DAB2 can bind to Shc3 domain of Src and this interaction results in Src inactivation. DAB2 is expressed in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). By modulating the activation of Src-FAK signaling and MAPK phosphorylation, DAB2 controls endothelial cell migration and differenti ...
... Angiogenesis: DAB2 can bind to Shc3 domain of Src and this interaction results in Src inactivation. DAB2 is expressed in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). By modulating the activation of Src-FAK signaling and MAPK phosphorylation, DAB2 controls endothelial cell migration and differenti ...
Cell Communication
... Gillman et al were able to select another S49 cell variant (cyc-) that appeared to have normal receptors and adenylyl cyclase but that failed to generate a cyclic AMP signal in response to appropriate hormones (b-adrenergic agonists or prostaglandins). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 2016 – 2020 ...
... Gillman et al were able to select another S49 cell variant (cyc-) that appeared to have normal receptors and adenylyl cyclase but that failed to generate a cyclic AMP signal in response to appropriate hormones (b-adrenergic agonists or prostaglandins). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 2016 – 2020 ...
Lecture 6 POWERPOINT here
... An average cell has both general reactions which it needs to perform to sustain life, as well as specialized ones that make that cell type unique, i.e. pancreatic cell. The general reactions are called housekeeping reactions These can be many in number and their interactions are pretty comple ...
... An average cell has both general reactions which it needs to perform to sustain life, as well as specialized ones that make that cell type unique, i.e. pancreatic cell. The general reactions are called housekeeping reactions These can be many in number and their interactions are pretty comple ...
Molecular mechanism of bradykinin action in neuronal differentiation
... and ionotropic receptors are crucial for neuronal function as well as for the differentiation of stem and progenitor cells into neurons. We have used the murine embryonal carcimoma P19 cell line as an in vitro model for studying the function of metabotropic kinin-B2 receptors (B2R) during early neur ...
... and ionotropic receptors are crucial for neuronal function as well as for the differentiation of stem and progenitor cells into neurons. We have used the murine embryonal carcimoma P19 cell line as an in vitro model for studying the function of metabotropic kinin-B2 receptors (B2R) during early neur ...
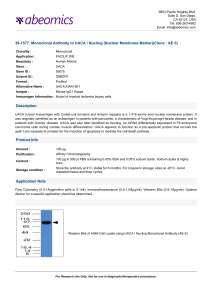
36-1577: Monoclonal Antibody to UACA / Nucling (Nuclear
... UACA (Uveal Autoantigen with Coiled-coil domains and Ankyrin repeats) is a 1,416 amino acid nuclear membrane protein. It was originally identified as an autoantigen in patients with panuveitis, a characteristic of Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease, and in patients with Graves' disease. UACA was also late ...
... UACA (Uveal Autoantigen with Coiled-coil domains and Ankyrin repeats) is a 1,416 amino acid nuclear membrane protein. It was originally identified as an autoantigen in patients with panuveitis, a characteristic of Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease, and in patients with Graves' disease. UACA was also late ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 16. Explain Substrate level phosphorylation. 17. What is an irreversible inhibitor? 18. Write about UAS. 19. Define Metabolic Control theory. 20. Explain Gene shuffling. SECTION B Answer any five, each answer within 350 words only. ...
... 16. Explain Substrate level phosphorylation. 17. What is an irreversible inhibitor? 18. Write about UAS. 19. Define Metabolic Control theory. 20. Explain Gene shuffling. SECTION B Answer any five, each answer within 350 words only. ...
Introduction to Metabolism
... Metabolic pathways consist of sequential steps. There are more than 2,000 metabolic reactions, each catalyzed by a distinct enzyme. The enzymes may be physically separate requiring the intermediate metabolites to diffuse from one active site to the next or enzymes may form a multienzyme complex whe ...
... Metabolic pathways consist of sequential steps. There are more than 2,000 metabolic reactions, each catalyzed by a distinct enzyme. The enzymes may be physically separate requiring the intermediate metabolites to diffuse from one active site to the next or enzymes may form a multienzyme complex whe ...
ExPlain: Causal Analysis of Gene Expression Data from Promoter
... usage of a rather limited set of signaling molecules and pathways. These combinatorics must be mirrored by the structure of gene promoters as combinations of transcription factor binding sites (composite modules). Different signal transduction pathways leading to the activation of transcription fact ...
... usage of a rather limited set of signaling molecules and pathways. These combinatorics must be mirrored by the structure of gene promoters as combinations of transcription factor binding sites (composite modules). Different signal transduction pathways leading to the activation of transcription fact ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... Binding of C1q to immune complex auto-catalytic splitting of proenzyme C1r for active enzyme C1r conversion of C1s for active serine protease C1s splitting of C2 na C2a a C2b and C4 na C4a a C4b C4b2a = C3 convertase – split C3 for C3a a C3b C4b2a3b = C5 convertase – split C5 C5a a C5b ...
... Binding of C1q to immune complex auto-catalytic splitting of proenzyme C1r for active enzyme C1r conversion of C1s for active serine protease C1s splitting of C2 na C2a a C2b and C4 na C4a a C4b C4b2a = C3 convertase – split C3 for C3a a C3b C4b2a3b = C5 convertase – split C5 C5a a C5b ...
experimental oncology
... 2. What is the ‘Warburg Effect’ ? (in which cells it occurs ? what is the functional consequence ?) 3. What are the main signalling pathways (driven by oncogenes and oncosuppressors) involved in the Warburg Effect ? 4. How is the Warburg Effect linked to the Fatty acid synthesis ? 5. Which aminoacid ...
... 2. What is the ‘Warburg Effect’ ? (in which cells it occurs ? what is the functional consequence ?) 3. What are the main signalling pathways (driven by oncogenes and oncosuppressors) involved in the Warburg Effect ? 4. How is the Warburg Effect linked to the Fatty acid synthesis ? 5. Which aminoacid ...
presentation
... Effects of abnormal gene expression • Roughly 90% of human cancers are epithelial in origin and exhibit a large number of changes in the structure and function of the genome. • Abnormal expression levels can be observed for a a large number of genes. • This complexity might be the reason for the cl ...
... Effects of abnormal gene expression • Roughly 90% of human cancers are epithelial in origin and exhibit a large number of changes in the structure and function of the genome. • Abnormal expression levels can be observed for a a large number of genes. • This complexity might be the reason for the cl ...
PDF
... formation in a 3-dimensional collagen matrix requires the Src-family nonreceptor tyrosine kinases (SFKs) Src and Yes, which regulate the actin cytoskeleton and cell migration, as well as PKCε, which activates SFKs. SFKs regulate Rho GTPase activity in many contexts, and the authors report that, duri ...
... formation in a 3-dimensional collagen matrix requires the Src-family nonreceptor tyrosine kinases (SFKs) Src and Yes, which regulate the actin cytoskeleton and cell migration, as well as PKCε, which activates SFKs. SFKs regulate Rho GTPase activity in many contexts, and the authors report that, duri ...
PDF
... formation in a 3-dimensional collagen matrix requires the Src-family nonreceptor tyrosine kinases (SFKs) Src and Yes, which regulate the actin cytoskeleton and cell migration, as well as PKCε, which activates SFKs. SFKs regulate Rho GTPase activity in many contexts, and the authors report that, duri ...
... formation in a 3-dimensional collagen matrix requires the Src-family nonreceptor tyrosine kinases (SFKs) Src and Yes, which regulate the actin cytoskeleton and cell migration, as well as PKCε, which activates SFKs. SFKs regulate Rho GTPase activity in many contexts, and the authors report that, duri ...