Slide 1
... A set of physiological reactions to damage of tissue integrity, leading to protection against infection, localization and restriction of the damaged site and finally to healing. ...
... A set of physiological reactions to damage of tissue integrity, leading to protection against infection, localization and restriction of the damaged site and finally to healing. ...
Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
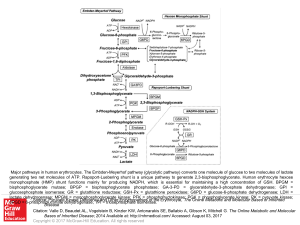
... Major pathways in human erythrocytes. The Embden-Meyerhof pathway (glycolytic pathway) converts one molecule of glucose to two molecules of lactate generating two net molecules of ATP. Rapoport-Luebering shunt is a unique pathway to generate 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate. Human erythrocyte hexose monophos ...
... Major pathways in human erythrocytes. The Embden-Meyerhof pathway (glycolytic pathway) converts one molecule of glucose to two molecules of lactate generating two net molecules of ATP. Rapoport-Luebering shunt is a unique pathway to generate 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate. Human erythrocyte hexose monophos ...
Supplementary table 2: Description of the gene pathways
... Genes related to muscle myosin Genes involved in glucose processing Genes involved in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis Genes involved in bile acid biosynthesis Reactive oxidative species related genes The protein phosphatase Cdc25 is phosphorylated by Chk1 and activates Cdc2 to stimulate eukaryotic ce ...
... Genes related to muscle myosin Genes involved in glucose processing Genes involved in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis Genes involved in bile acid biosynthesis Reactive oxidative species related genes The protein phosphatase Cdc25 is phosphorylated by Chk1 and activates Cdc2 to stimulate eukaryotic ce ...
Module code SB-2243 Module Title Introduction to Biochemistry
... and function of biologically important macromolecules and assemblies. It will also provide them with the concept of energy conservation and conversion processes in a living cell and thus lay a foundation in understanding the reactions of metabolism. Learning Outcomes ...
... and function of biologically important macromolecules and assemblies. It will also provide them with the concept of energy conservation and conversion processes in a living cell and thus lay a foundation in understanding the reactions of metabolism. Learning Outcomes ...
Workshop IV Signal Transduction Chair: Miguel Peñalva 100
... exposed to a highly variable environment with significant changes affecting, temperature, pH, oxygen, andwater and nutrient availability. Many of these changes occur during Trichoderma life cycle, triggering specific stress responses to external factors. In some cases, stress-related responses can a ...
... exposed to a highly variable environment with significant changes affecting, temperature, pH, oxygen, andwater and nutrient availability. Many of these changes occur during Trichoderma life cycle, triggering specific stress responses to external factors. In some cases, stress-related responses can a ...
MS Word File
... Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Responses • Ultimately, a signal transduction pathway leads to regulation of one or more cellular activities • The response may occur in the cytoplasm or may involve action in the nucleus • Many signaling pathways regulate the synthesis of enzymes or other proteins, usually b ...
... Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Responses • Ultimately, a signal transduction pathway leads to regulation of one or more cellular activities • The response may occur in the cytoplasm or may involve action in the nucleus • Many signaling pathways regulate the synthesis of enzymes or other proteins, usually b ...
Cell Cycle
... Specific Signal Transduction Pathways: be aware of the overall processes discussed below. Do not worry about the specific steps or the names of specific molecules, as these will be given to you on the test. o G-Protein Pathway What is a G-Protein Linked Receptor? What is a G-Protein? What does ...
... Specific Signal Transduction Pathways: be aware of the overall processes discussed below. Do not worry about the specific steps or the names of specific molecules, as these will be given to you on the test. o G-Protein Pathway What is a G-Protein Linked Receptor? What is a G-Protein? What does ...
Cell Signaling Study Sheet
... • Quorum sensing in bacteria • Morphogens in embryonic development ~Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another cell type. • Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances ...
... • Quorum sensing in bacteria • Morphogens in embryonic development ~Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another cell type. • Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances ...
Recombinant Human Neuregulin-1 (rh NRG-1)
... Introduction: Neuregulin/Heregulin is a family of structurally related polypeptide growth factors derived from alternatively spliced genes (NRG-1, NRG-2, NRG-3 and NRG-4). To date, there are over 14 soluble and transmembrane proteins derived from the NRG-1 gene. Proteolytic processing of the extrace ...
... Introduction: Neuregulin/Heregulin is a family of structurally related polypeptide growth factors derived from alternatively spliced genes (NRG-1, NRG-2, NRG-3 and NRG-4). To date, there are over 14 soluble and transmembrane proteins derived from the NRG-1 gene. Proteolytic processing of the extrace ...
Presentation (PowerPoint File) - IPAM
... Ligand binding activates the receptor, which activates the G protein, which activates an effector enzyme to generate an intracellular second messenger – e.g. adenylyl cyclase – converts ATP to cAMP depending on regulation at the effector enzyme – this pathway can be either activated or inhibited – b ...
... Ligand binding activates the receptor, which activates the G protein, which activates an effector enzyme to generate an intracellular second messenger – e.g. adenylyl cyclase – converts ATP to cAMP depending on regulation at the effector enzyme – this pathway can be either activated or inhibited – b ...
OverallQuiz2Ch5-8.doc
... 3. Two types of connections between cells called "gap junctions" and "plasmodesmata" are specialized to __________. a. prevent the movement of molecules between cells that are tightly joined along ribbons of cell membrane b. tightly hold one cell against another at focal points, almost like a spot w ...
... 3. Two types of connections between cells called "gap junctions" and "plasmodesmata" are specialized to __________. a. prevent the movement of molecules between cells that are tightly joined along ribbons of cell membrane b. tightly hold one cell against another at focal points, almost like a spot w ...
Chapter 34-4B: Second Messengers
... are not transmembrane proteins. Steroid hormones can pass freely through cell membrane, and bind the specific receptor protein in cytosol. The receptor activated by the steroid hormone moves into the nucleus. The active receptor binds a specific region of DNA and activates or inactivates the replica ...
... are not transmembrane proteins. Steroid hormones can pass freely through cell membrane, and bind the specific receptor protein in cytosol. The receptor activated by the steroid hormone moves into the nucleus. The active receptor binds a specific region of DNA and activates or inactivates the replica ...
Signalling and transcriptional regulation in biology and disease
... on dissecting out signalling pathways from the cell membrane to the nucleus and also to other parts of the cell, and on how the ultimate cellular response will be determined by the signalling pathways activated. Many signalling pathways regulate cell growth, cell survival, cell differentiation, cell ...
... on dissecting out signalling pathways from the cell membrane to the nucleus and also to other parts of the cell, and on how the ultimate cellular response will be determined by the signalling pathways activated. Many signalling pathways regulate cell growth, cell survival, cell differentiation, cell ...
Cell signaling
... intracellular proteins, which are able to recognize and bind to corresponding ligand molecules, Receptor when activated by ligand ,the receptor causes a change in the target cell in which lt is expressed. Glycoprotein or Lipoprotein ...
... intracellular proteins, which are able to recognize and bind to corresponding ligand molecules, Receptor when activated by ligand ,the receptor causes a change in the target cell in which lt is expressed. Glycoprotein or Lipoprotein ...
No Slide Title
... Understanding the dynamical behavior of these systems necessitates the understanding of their interconnections. An abstract representation of interaction networks and theoretical modeling can give general insights into system-level behavior. ...
... Understanding the dynamical behavior of these systems necessitates the understanding of their interconnections. An abstract representation of interaction networks and theoretical modeling can give general insights into system-level behavior. ...
'Receptor-ligand interactions - cell signaling, adhesion
... Ligand binding activates the receptor, which activates the G protein, which activates an effector enzyme to generate an intracellular second messenger – e.g. adenylyl cyclase – converts ATP to cAMP depending on regulation at the effector enzyme – this pathway can be either activated or inhibited – b ...
... Ligand binding activates the receptor, which activates the G protein, which activates an effector enzyme to generate an intracellular second messenger – e.g. adenylyl cyclase – converts ATP to cAMP depending on regulation at the effector enzyme – this pathway can be either activated or inhibited – b ...
Modification of the K-Ras Signaling Pathway
... • Active only in GTP-bound form • Activation through facilitated nucleotide exchange from GDP GTP via GEF (SOS) • Self-regulates via hydrolysis of GTP GDP – partially dependent on GAP (RASA1) ...
... • Active only in GTP-bound form • Activation through facilitated nucleotide exchange from GDP GTP via GEF (SOS) • Self-regulates via hydrolysis of GTP GDP – partially dependent on GAP (RASA1) ...
Chapter 34
... A model for their activity • Binding of hormone, etc., to receptor protein in the membrane triggers dissociation of GDP and binding of GTP to -subunit of G protein • G-GTP complex dissociates from G and migrates to effector sites, activating or inhibiting • But it is now clear that G also func ...
... A model for their activity • Binding of hormone, etc., to receptor protein in the membrane triggers dissociation of GDP and binding of GTP to -subunit of G protein • G-GTP complex dissociates from G and migrates to effector sites, activating or inhibiting • But it is now clear that G also func ...
A new blueprint for plant pathogen resistance
... ideal intracellular mediators of information, because they shuttle between cytoplasm and nucleus, and among their targets are several classes of transcription factors. Thus, MAPKs represent the mechanistic link between information transfer through the interior of the cell and the transcriptional res ...
... ideal intracellular mediators of information, because they shuttle between cytoplasm and nucleus, and among their targets are several classes of transcription factors. Thus, MAPKs represent the mechanistic link between information transfer through the interior of the cell and the transcriptional res ...
Fact Sheet
... In the case of cancer, the tumor microenvironment includes tumor cells, cells surrounding a tumor, cells inside of a tumor, and various molecules that are secreted by or exposed outside of those cells. Interactions among these players are involved in disease progression and therefore of interest to ...
... In the case of cancer, the tumor microenvironment includes tumor cells, cells surrounding a tumor, cells inside of a tumor, and various molecules that are secreted by or exposed outside of those cells. Interactions among these players are involved in disease progression and therefore of interest to ...