Chapter 2 SWBATS Content Standards Cell Biology 1. The
... What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Give an example of each. Why are water molecules polar? What are acidic solutions? What are basic solutions? Give an example of each. What are the functions of each group of organic compounds? What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? Ho ...
... What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Give an example of each. Why are water molecules polar? What are acidic solutions? What are basic solutions? Give an example of each. What are the functions of each group of organic compounds? What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? Ho ...
Document
... • A bi-product of the glycolytic pathway is lactic acid – this lowers the extracellular pH so that it favours tumour cell proliferation AND it is toxic to normal cells. ...
... • A bi-product of the glycolytic pathway is lactic acid – this lowers the extracellular pH so that it favours tumour cell proliferation AND it is toxic to normal cells. ...
NK cells
... • Recruits SHP-1/SHP-2 phosphatases • Linked to inhibition of function in lymphocytes ...
... • Recruits SHP-1/SHP-2 phosphatases • Linked to inhibition of function in lymphocytes ...
- TCYonline.com
... o increased free Ca2+ initiates many events, including contraction, secretion, enzyme activation and membrane hyperpolarisation o DAG activates protein kinase C, which controls many cellular functions by phosphorylating a variety of proteins. phospholipase A2 (and thus the formation of arachidonic ...
... o increased free Ca2+ initiates many events, including contraction, secretion, enzyme activation and membrane hyperpolarisation o DAG activates protein kinase C, which controls many cellular functions by phosphorylating a variety of proteins. phospholipase A2 (and thus the formation of arachidonic ...
Lecture 7: Signaling Through Lymphocyte Receptors
... Nucleus Activates Genes There are multiple pathways that transduce the ...
... Nucleus Activates Genes There are multiple pathways that transduce the ...
II Sensory - Washington State University
... Taste transduction has mainly been studied in animals like catfish and rats… • Many differences exist in the taste capabilities and mechanisms of different vertebrates – for instance, rats can taste pure water – whether or not the information is relevant to human gustation is unclear. ...
... Taste transduction has mainly been studied in animals like catfish and rats… • Many differences exist in the taste capabilities and mechanisms of different vertebrates – for instance, rats can taste pure water – whether or not the information is relevant to human gustation is unclear. ...
Chapter 1 Notes - Social Circle City Schools
... activates adenlyl cyclase, which in turn can synthesize many molecules of cAMP ...
... activates adenlyl cyclase, which in turn can synthesize many molecules of cAMP ...
APChapter11 2014 - Auburn School District
... Signal reception: The signal binds to a specific cellular protein called a receptor, which is often located on the surface of the cell. Signal transduction: The binding of the signal changes the receptor in some way, usually a change in conformation or shape, The change in the receptor initiates a p ...
... Signal reception: The signal binds to a specific cellular protein called a receptor, which is often located on the surface of the cell. Signal transduction: The binding of the signal changes the receptor in some way, usually a change in conformation or shape, The change in the receptor initiates a p ...
Bio 201, Fall 2010 Test 3 Study Guide Questions to be able to
... 3. What is pectin, what are its chemical properties and how do they contribute to the function of the middle lamella? 4. Why are there cations in the middle lamella? 5. Why do fruits and vegetables get mushy? 6. What is the series of connections between the molecules involved in the extracellular ma ...
... 3. What is pectin, what are its chemical properties and how do they contribute to the function of the middle lamella? 4. Why are there cations in the middle lamella? 5. Why do fruits and vegetables get mushy? 6. What is the series of connections between the molecules involved in the extracellular ma ...
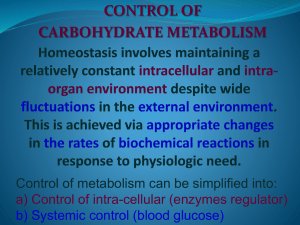
Control of intra-cellular (enzyme regulator)
... Fatty acid biosynthesis occurs in the cytosol, whereas fatty acid oxidation takes place within mitochondria Segregation of certain metabolic pathways within specialized cell types can provide further physical compartmentation. ...
... Fatty acid biosynthesis occurs in the cytosol, whereas fatty acid oxidation takes place within mitochondria Segregation of certain metabolic pathways within specialized cell types can provide further physical compartmentation. ...
IMMUNITY MEDIATED BY B LYMPHOCYTES AND ANTIBODIES
... * Rolling adhesion * Slowing down leukocytes (margination) * Weibel-Palade bodies in vascular endothelial cells secreting P and E selectins ...
... * Rolling adhesion * Slowing down leukocytes (margination) * Weibel-Palade bodies in vascular endothelial cells secreting P and E selectins ...
Celularni imunski odgovor Aktivacija T limfocita
... 2. Signal transduction in T cells is mediated by ...
... 2. Signal transduction in T cells is mediated by ...
The Quantification of Multiple Signalling Pathway Proteins in Intact
... an important role in drug R&D; by enabling the accurate quantification of multiple proteins on a per-cell basis in intact tissue, a new technology platform will help researchers to better understand the signalling pathways implicated in a given disease. In order to obtain an improved determination o ...
... an important role in drug R&D; by enabling the accurate quantification of multiple proteins on a per-cell basis in intact tissue, a new technology platform will help researchers to better understand the signalling pathways implicated in a given disease. In order to obtain an improved determination o ...
PDF
... development. During embryogenesis, cranial neural crest (CNC) cells give rise to the facial bones, cartilage and connective tissues. Neural crest development involves an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) that converts epithelial cells into migratory mesenchymal cells, which delaminate from the ...
... development. During embryogenesis, cranial neural crest (CNC) cells give rise to the facial bones, cartilage and connective tissues. Neural crest development involves an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) that converts epithelial cells into migratory mesenchymal cells, which delaminate from the ...
Cell Communication
... • Second messengers are small, non-protein, watersoluble molecules or ions that spread throughout a cell by diffusion • Second messengers participate in pathways initiated by G protein-coupled receptors • Cyclic AMP and calcium ions are common second messengers ...
... • Second messengers are small, non-protein, watersoluble molecules or ions that spread throughout a cell by diffusion • Second messengers participate in pathways initiated by G protein-coupled receptors • Cyclic AMP and calcium ions are common second messengers ...
Apoptosis-associtated pathways are induced vy Phytophthora
... –To build an intelligent and generic system for new hypothesis formulation from complex biochemical pathway databases. ...
... –To build an intelligent and generic system for new hypothesis formulation from complex biochemical pathway databases. ...
cell longevity pathways govern vascular and inflammatory
... member FoxO3a and blocks the trafficking of FoxO3a to the cell nucleus to prevent apoptosis. Intimately linked to this pathway is the sirtuin SIRT1. During elevated Dglucose exposure, SIRT1 is sequestered in the cytoplasm of ECs, but specific activation of SIRT1 shuttles the protein to the nucleus t ...
... member FoxO3a and blocks the trafficking of FoxO3a to the cell nucleus to prevent apoptosis. Intimately linked to this pathway is the sirtuin SIRT1. During elevated Dglucose exposure, SIRT1 is sequestered in the cytoplasm of ECs, but specific activation of SIRT1 shuttles the protein to the nucleus t ...
Document
... suggests that oxidative stress is linked, more or less directly, to either primary or secondary pathophysiologic mechanisms of several acute and chronic human diseases. cancer cells develop an enhanced constitutive oxidative stress that sustains tumor growth and shields these cells against pro-apo ...
... suggests that oxidative stress is linked, more or less directly, to either primary or secondary pathophysiologic mechanisms of several acute and chronic human diseases. cancer cells develop an enhanced constitutive oxidative stress that sustains tumor growth and shields these cells against pro-apo ...
ABSTRACT Mast cells are critical component of the immune system
... Mast cells are critical component of the immune system. In pathological situations, they are activated and are responsible for allergic reaction. Therefore, detail understanding of mast cell activation at molecular level is important for design of new therapies of allergic diseases. Principal transm ...
... Mast cells are critical component of the immune system. In pathological situations, they are activated and are responsible for allergic reaction. Therefore, detail understanding of mast cell activation at molecular level is important for design of new therapies of allergic diseases. Principal transm ...
ppt
... • We demonstrate a requirement for Wnt signaling during the earliest steps of mesendodermal differentiation of ES cells • How Wnt signaling regulates gene expression – Wnt pathway activation could act autonomously and directly to induce target gene expression through the b-catenindependent conversi ...
... • We demonstrate a requirement for Wnt signaling during the earliest steps of mesendodermal differentiation of ES cells • How Wnt signaling regulates gene expression – Wnt pathway activation could act autonomously and directly to induce target gene expression through the b-catenindependent conversi ...
General Principles
... in which hormones secreted by endocrine cells are carried in the blood to target cells throughout the body, and by synaptic signaling, in which neurotransmitters secreted by nerve cells act locally on the postsynaptic cells that their axons contact. Cell signaling requires both extracellular signali ...
... in which hormones secreted by endocrine cells are carried in the blood to target cells throughout the body, and by synaptic signaling, in which neurotransmitters secreted by nerve cells act locally on the postsynaptic cells that their axons contact. Cell signaling requires both extracellular signali ...
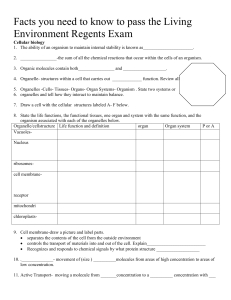
Facts you need to know to pass the Living Environment
... Cellular biology 1. The ability of an organism to maintain internal stability is known as______________________. 2. ________________-the sum of all the chemical reactions that occur within the cells of an organism. 3. Organic molecules contain both________________ and ___________________. 4. Organel ...
... Cellular biology 1. The ability of an organism to maintain internal stability is known as______________________. 2. ________________-the sum of all the chemical reactions that occur within the cells of an organism. 3. Organic molecules contain both________________ and ___________________. 4. Organel ...
Name: Date: 1. The is the source of most of the cellular energy. A
... 28. Which of the following factors will decrease the function of most enzyme? A) ...
... 28. Which of the following factors will decrease the function of most enzyme? A) ...
Signal Receptors 4 types
... WHAT??? molecules interact with each other and pass information into the nucleus ...
... WHAT??? molecules interact with each other and pass information into the nucleus ...
Molecular Cell Biology course 1BL320 Spring
... progression and why a transient burst of Erk activation fails to do so. (2p) c) Signaling pathways often lead to changes in gene expression. Describe two ways to regulate the activity/function of a transcription factor. (1p) d) Two types of post-translational modifications found in proteins involved ...
... progression and why a transient burst of Erk activation fails to do so. (2p) c) Signaling pathways often lead to changes in gene expression. Describe two ways to regulate the activity/function of a transcription factor. (1p) d) Two types of post-translational modifications found in proteins involved ...