Introduction
... •Cells use Ca2+ as a second messenger in both Gprotein pathways and tyrosine-kinase pathways. ...
... •Cells use Ca2+ as a second messenger in both Gprotein pathways and tyrosine-kinase pathways. ...
Cell Signaling - Erlenbeck`s Science Room
... receptor to change shape and attracts the G protein to attach and activate (GTP). That G protein then binds to an enzyme which triggers the next steps to a cellular response. The G protein is then deactivated (GDP) meaning the pathway can be shut down. ...
... receptor to change shape and attracts the G protein to attach and activate (GTP). That G protein then binds to an enzyme which triggers the next steps to a cellular response. The G protein is then deactivated (GDP) meaning the pathway can be shut down. ...
No Slide Title
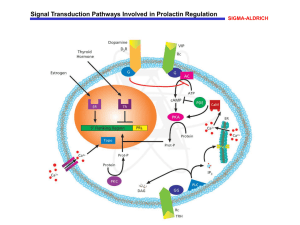
... regulators of PRL release include vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), estrogen, and thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), while negative regulators include dopamine and thyroid hormone. VIP exerts its effects by the G-protein-mediated activation of adenyl cyclase (AC) and its downstream effector ...
... regulators of PRL release include vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), estrogen, and thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), while negative regulators include dopamine and thyroid hormone. VIP exerts its effects by the G-protein-mediated activation of adenyl cyclase (AC) and its downstream effector ...
Unit Five
... A class of proteins that bind phosphotyrosines Do not participate in signal transduction, but act as a link between receptors and downstream events RAS ...
... A class of proteins that bind phosphotyrosines Do not participate in signal transduction, but act as a link between receptors and downstream events RAS ...
lecture-2-hhd - WordPress.com
... A change in cellular metabolism, function or development triggered by the receptorsignal complex Removal of the signal, which often terminate the cellular response ...
... A change in cellular metabolism, function or development triggered by the receptorsignal complex Removal of the signal, which often terminate the cellular response ...
Cell signaling
... activate the substrate of the kinase, but can also target the substrate for degradation •Kinases are often themselves activated by other kinases via phosphorylation and can organize into phosphorylation cascades •One important class of phosphorylation cascade is called a mitogen activated protein ki ...
... activate the substrate of the kinase, but can also target the substrate for degradation •Kinases are often themselves activated by other kinases via phosphorylation and can organize into phosphorylation cascades •One important class of phosphorylation cascade is called a mitogen activated protein ki ...
No Slide Title
... Two bacterial toxins act via Gs,Gi: - cholera: a subunit of Gs altered, can’t hydrolyze GTP - pertussis: a subunit of Gi altered, can’t exchange GDP ...
... Two bacterial toxins act via Gs,Gi: - cholera: a subunit of Gs altered, can’t hydrolyze GTP - pertussis: a subunit of Gi altered, can’t exchange GDP ...
arsenic trioxide causes cell cycle arrest and induces intrinsic
... arrests cell cycle progression of HL-60 cells at S – phase and leading to cell death by intrinsic pathway of apoptotic signaling. To test the hypothesis, we used western blotting, confocal imaging and spectrofluoremetric techniques to identify detailed cellular and molecular mechanisms of ATO action ...
... arrests cell cycle progression of HL-60 cells at S – phase and leading to cell death by intrinsic pathway of apoptotic signaling. To test the hypothesis, we used western blotting, confocal imaging and spectrofluoremetric techniques to identify detailed cellular and molecular mechanisms of ATO action ...
Hydrophobic signal molecules
... Cells do not work in isolation but continually ‘talk’ to each other by sending and receiving chemical signals to each other. This process is known as cell signaling Cell signaling has a number of important steps A signaling cell produces a signal molecule The signal molecule is recognised by a tar ...
... Cells do not work in isolation but continually ‘talk’ to each other by sending and receiving chemical signals to each other. This process is known as cell signaling Cell signaling has a number of important steps A signaling cell produces a signal molecule The signal molecule is recognised by a tar ...
Ch 11 PP - medmood.com
... 1. Different receptors recognize different chemical messengers, which can be peptides, small chemicals or proteins, in a specific one-to-one relationship. ...
... 1. Different receptors recognize different chemical messengers, which can be peptides, small chemicals or proteins, in a specific one-to-one relationship. ...
Dr. Laurent Sabbagh
... Tumour necrosis factor receptors (TNFRs) are a family of receptors involved in transmitting survival and death signals in lymphocytes and play a critical role in determining the outcome of an immune response and the maintenance of memory T cells. The role of TRAF1, an adaptor protein involved in lin ...
... Tumour necrosis factor receptors (TNFRs) are a family of receptors involved in transmitting survival and death signals in lymphocytes and play a critical role in determining the outcome of an immune response and the maintenance of memory T cells. The role of TRAF1, an adaptor protein involved in lin ...
Slides - Brown Computer Science
... Activation of signalling occurs when a cytokine binds to its receptor at the cell surface, leading to dimerisation of the receptor and activation of receptor-associated JAKs. Activated JAK proteins transphosphorylate one another as well as the C-terminal tails of the receptor. The resulting phosphot ...
... Activation of signalling occurs when a cytokine binds to its receptor at the cell surface, leading to dimerisation of the receptor and activation of receptor-associated JAKs. Activated JAK proteins transphosphorylate one another as well as the C-terminal tails of the receptor. The resulting phosphot ...
1 Table S1. Pathway/Function Gene Symbol Fold Change Function
... apoptosis characterized by a rapid and robust release of cytochrome C from the mitochondria and activation of BAX and caspases 2, 3, 6, 8 and 9 ...
... apoptosis characterized by a rapid and robust release of cytochrome C from the mitochondria and activation of BAX and caspases 2, 3, 6, 8 and 9 ...
Tyrosine kinases can be cytosolic or integral membrane
... The pocket of the SH2 domain is highly specific for phospho-tyrosine because of the bulky size of the tyrosine. ...
... The pocket of the SH2 domain is highly specific for phospho-tyrosine because of the bulky size of the tyrosine. ...
邵吉民_Signal_and_dis
... Insulin receptor (IR): heterotetramer (2, 2) Insulin binding leads to change in conformation Activates IR -subunit (PTK activity) IR-subunit phosphorylates Tyr residues on cytoplasmic domains as well as downstream substrates (IRS) ...
... Insulin receptor (IR): heterotetramer (2, 2) Insulin binding leads to change in conformation Activates IR -subunit (PTK activity) IR-subunit phosphorylates Tyr residues on cytoplasmic domains as well as downstream substrates (IRS) ...
Cell Communication
... contact or they may operate over very short distances. Ex: Immune cells interact by cell-to-cell contact, antigen-presenting cells (APCs), helper T-cells, and killer T-cells. Question: Why do we need such a complex system to combat infection? ...
... contact or they may operate over very short distances. Ex: Immune cells interact by cell-to-cell contact, antigen-presenting cells (APCs), helper T-cells, and killer T-cells. Question: Why do we need such a complex system to combat infection? ...
Cell Communication Study Guide
... 9. Fill-in the chart below regarding the 3 types of membrane receptors: Receptor ...
... 9. Fill-in the chart below regarding the 3 types of membrane receptors: Receptor ...
CELL SIGNALING How do cells receive and respond to signals from
... •calcium transport (carried out by the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump) •nitric oxide pathway •regulation of cytoskeletal proteins Most of these systems are evolutionarily conserved, with counterparts in vertebrates as well as non-vertebrate species. The conservation of the ...
... •calcium transport (carried out by the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump) •nitric oxide pathway •regulation of cytoskeletal proteins Most of these systems are evolutionarily conserved, with counterparts in vertebrates as well as non-vertebrate species. The conservation of the ...
Chapter 11
... 3 Stages of Cell Signaling: 1. Reception: Detection of a signal molecule (ligand) coming from outside the cell 2. Transduction: Convert signal to a form that can bring about a cellular response ...
... 3 Stages of Cell Signaling: 1. Reception: Detection of a signal molecule (ligand) coming from outside the cell 2. Transduction: Convert signal to a form that can bring about a cellular response ...
G protein
... Signal transduction pathways act like falling dominoes. • The signal-activated receptor activates another protein, which activates another and so on, until the protein that produces the final cellular response is activated. ...
... Signal transduction pathways act like falling dominoes. • The signal-activated receptor activates another protein, which activates another and so on, until the protein that produces the final cellular response is activated. ...
Game 1
... proteins involved in the photosystems responsible for reducing DPIP or disrupt the structure of the pigments involved. ...
... proteins involved in the photosystems responsible for reducing DPIP or disrupt the structure of the pigments involved. ...
Cell Signaling - Scott County Schools
... • There are many types of receptor proteins! • Different receptors recognize different chemical messengers, which can be peptides, small chemicals or proteins, in a specific one-to-one relationship. • Example of on type of receptor protein: Receptor tyrosine kinases. • A kinase is an enzyme that cat ...
... • There are many types of receptor proteins! • Different receptors recognize different chemical messengers, which can be peptides, small chemicals or proteins, in a specific one-to-one relationship. • Example of on type of receptor protein: Receptor tyrosine kinases. • A kinase is an enzyme that cat ...