Communication in living systems is normally not covered in the 10th
... o Essential Knowledge 2.D.4 Plants and animals have a variety of chemical defenses against infections that affect dynamic homeostasis Plants, invertebrates and vertebrates have multiple, nonspecific immune responses Invertebrate – nonspecific lacking pathogen-specific responses Plant – recogni ...
... o Essential Knowledge 2.D.4 Plants and animals have a variety of chemical defenses against infections that affect dynamic homeostasis Plants, invertebrates and vertebrates have multiple, nonspecific immune responses Invertebrate – nonspecific lacking pathogen-specific responses Plant – recogni ...
Models and Theory in Molecular Cell Biology
... supramolecular processes taking place within individual cells. These processes are generally organised in the form of reaction networks, such as metabolic pathways, signal transduction networks and gene regulatory networks. In contrast to chemical reactions of inanimate nature the biochemical proces ...
... supramolecular processes taking place within individual cells. These processes are generally organised in the form of reaction networks, such as metabolic pathways, signal transduction networks and gene regulatory networks. In contrast to chemical reactions of inanimate nature the biochemical proces ...
COMPLEMENT activation - Akademik Ciamik 2010
... a system comprised of a groups of plasma and cell membrane proteins that play an important role in host defense process. Components: More than 30 proteins Synthesized in the liver, macrophages and other cells ...
... a system comprised of a groups of plasma and cell membrane proteins that play an important role in host defense process. Components: More than 30 proteins Synthesized in the liver, macrophages and other cells ...
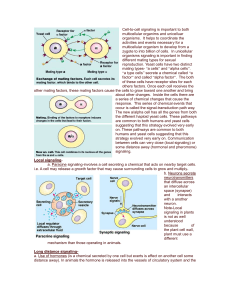
1 OVERVIEW OF EXTRACELLULAR SIGNALING A. Steps of
... A. Steps of extracellular communication 1. synthesis of signaling molecule 2. Release of signaling molecule 3. Transport of the signal to the target cell 4. Detection of the signal by a specific receptor protein 5. Change in cellular metabolism or gene expression triggered by the receptorsignaling m ...
... A. Steps of extracellular communication 1. synthesis of signaling molecule 2. Release of signaling molecule 3. Transport of the signal to the target cell 4. Detection of the signal by a specific receptor protein 5. Change in cellular metabolism or gene expression triggered by the receptorsignaling m ...
Cell Communication
... with other cellular molecules – G- protein is a common type of protein receptor for cell signaling found in the membrane. ...
... with other cellular molecules – G- protein is a common type of protein receptor for cell signaling found in the membrane. ...
receptor proteins
... Growth factors and their trans‐membrane receptor tyrosine kinases play important roles in cell proliferation, survival, migration and differentiation. One group of growth factors, comprising epidermal growth factor (EGF)‐like proteins and neuregulins, stimulates cells ...
... Growth factors and their trans‐membrane receptor tyrosine kinases play important roles in cell proliferation, survival, migration and differentiation. One group of growth factors, comprising epidermal growth factor (EGF)‐like proteins and neuregulins, stimulates cells ...
Cell Communication
... release of calcium from ER • Causes muscle cell contraction, cell division, secretion of substances • Used by neurotransmitters, growth factors and some hormones ...
... release of calcium from ER • Causes muscle cell contraction, cell division, secretion of substances • Used by neurotransmitters, growth factors and some hormones ...
Supplementary Figure Legends (doc 60K)
... and in turn the small GTP-binding protein, RAS. Recruitment of RAF-1 to the plasma membrane by RAS leads to its activation triggering the MAPK cascade and cell proliferation. Binding of an ...
... and in turn the small GTP-binding protein, RAS. Recruitment of RAF-1 to the plasma membrane by RAS leads to its activation triggering the MAPK cascade and cell proliferation. Binding of an ...
ReliaTech GmbH Recombinant Human p16
... p16-INK4a is a nuclear protein that regulates the cell cycle by inhibiting cyclin dependent kinase-4 (CDK4) and CDK6. p16-INK4a inhibits CDK activity by binding to the CDK molecules in a manner that interferes with their ability to interact with cyclin D. This activity has the effect of suppressing ...
... p16-INK4a is a nuclear protein that regulates the cell cycle by inhibiting cyclin dependent kinase-4 (CDK4) and CDK6. p16-INK4a inhibits CDK activity by binding to the CDK molecules in a manner that interferes with their ability to interact with cyclin D. This activity has the effect of suppressing ...
Abstract
... (Nox) isozymes can be activated by toll-like receptors (TLRs), which are key regulators of innate immunity. TLRs recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) on the surface of pathogens as well as altered host proteins and lipoproteins and stimulate inflammatory signaling pathways. We sh ...
... (Nox) isozymes can be activated by toll-like receptors (TLRs), which are key regulators of innate immunity. TLRs recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) on the surface of pathogens as well as altered host proteins and lipoproteins and stimulate inflammatory signaling pathways. We sh ...
Meili, R and R.A. Firtel (2002). Leading the way. Nature Cell Biol. 4
... of chemical signals, is a feature of a wide variety of eukaryotic cells. Chemotaxis is important for many biological responses, from the movement of leukocytes towards sites of infection or inflammation to the aggregation of Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae to form a multicellular organism. Recent w ...
... of chemical signals, is a feature of a wide variety of eukaryotic cells. Chemotaxis is important for many biological responses, from the movement of leukocytes towards sites of infection or inflammation to the aggregation of Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae to form a multicellular organism. Recent w ...
{alpha}-Lipoic Acid Inhibits Adipocyte Differentiation by Regulating
... of the insulin receptor/Akt signaling pathway. These findings suggest that LA inhibits insulin or the hormonal mixture-induced differentiation of 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes by modulating activity and/or expression of pro- or anti-adipogenic transcription factors mainly through activating the MAPK pathway ...
... of the insulin receptor/Akt signaling pathway. These findings suggest that LA inhibits insulin or the hormonal mixture-induced differentiation of 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes by modulating activity and/or expression of pro- or anti-adipogenic transcription factors mainly through activating the MAPK pathway ...
AP Biology - AdamsAPBiostars
... outside the cell. • IP3 (inositol triphosphate) is the ligand for a gated calcium channel in the membrane of the ER, which stores Ca2+ at high concentrations. • When IP3 binds, Ca2+ flows into the cytosol, where it activates proteins of many signaling pathways. • Increasing cytosolic concentration o ...
... outside the cell. • IP3 (inositol triphosphate) is the ligand for a gated calcium channel in the membrane of the ER, which stores Ca2+ at high concentrations. • When IP3 binds, Ca2+ flows into the cytosol, where it activates proteins of many signaling pathways. • Increasing cytosolic concentration o ...
1. Categorize chemical signals in terms of the
... cyclase which is associated with the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP to cAMP cAMP binds to and activates a cytoplasmic enzyme protein kinase A Protein kinase A propagates the message by phosphorylating various other proteins that lead to the cellular response ...
... cyclase which is associated with the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP to cAMP cAMP binds to and activates a cytoplasmic enzyme protein kinase A Protein kinase A propagates the message by phosphorylating various other proteins that lead to the cellular response ...
model questions for SCT
... Both have a non-covalently associated signaling subunit. Both have a transmembrane domain. Both consist of heavy and light chains. They recognize epitopes. Generation of several millions of different variable domains is possible. ...
... Both have a non-covalently associated signaling subunit. Both have a transmembrane domain. Both consist of heavy and light chains. They recognize epitopes. Generation of several millions of different variable domains is possible. ...
How do cells communicate?
... • Many signal molecules increase cytosolic concentration of Ca2+ – contraction of muscle cells, secretion of substances, and cell division – In plant cells, trigger responses for coping with ...
... • Many signal molecules increase cytosolic concentration of Ca2+ – contraction of muscle cells, secretion of substances, and cell division – In plant cells, trigger responses for coping with ...
L04 - Extracellular Signal Receptors II
... • The CrkL adaptor protein may regulate downstream integrin signaling. • Growth factor signaling pathways and the caveolin receptor exhibit important cross talk with integrin receptors in cellular responses like activation of map kinase, proliferation and motility. ...
... • The CrkL adaptor protein may regulate downstream integrin signaling. • Growth factor signaling pathways and the caveolin receptor exhibit important cross talk with integrin receptors in cellular responses like activation of map kinase, proliferation and motility. ...
pathway_cell_models_2006
... – Inter/intra-cellular – Metabolic networks – Gene networks – Signal transduction networks ...
... – Inter/intra-cellular – Metabolic networks – Gene networks – Signal transduction networks ...
Cell-to-cell signaling is important to both multicellular organims and
... perception in vision and smell. NoteBacteria that often cause disease by secreting toxins. These toxins may interfere with G-protein functions. 60% of all medicines exert their effect by influencing G-protein pathways. b. Tyrosine-Kinase receptors-are receptors that when activated can activate more ...
... perception in vision and smell. NoteBacteria that often cause disease by secreting toxins. These toxins may interfere with G-protein functions. 60% of all medicines exert their effect by influencing G-protein pathways. b. Tyrosine-Kinase receptors-are receptors that when activated can activate more ...
Cellular Communication
... messenger, a ligand, by a receptor protein – Different receptors recognize different chemical messengers, which can bee peptides, small chemicals or proteins, in a specific one to one relationship – A receptor protein recognizes signal molecules, causing the receptor protein’s shape to change, which ...
... messenger, a ligand, by a receptor protein – Different receptors recognize different chemical messengers, which can bee peptides, small chemicals or proteins, in a specific one to one relationship – A receptor protein recognizes signal molecules, causing the receptor protein’s shape to change, which ...
Time course of immune response
... • Produced in response to an activating stimulus • Function by binding to a specific receptor • Usually soluble, but can be membrane associated • Can work locally or at a distance ...
... • Produced in response to an activating stimulus • Function by binding to a specific receptor • Usually soluble, but can be membrane associated • Can work locally or at a distance ...











![Notes [, 802 KB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016170823_1-0ccab870903f643deda3e881641da50b-300x300.png)