Chapter 2-ROLE OF ENZYMES
... 12. What happens to the active site of an enzyme at high temperatures? 13. What pH does pepsin enzyme work best at in the stomach? 14. What word is used to describe the best set of conditions that an enzyme can work at? 15. What happens to the rate of reaction if the concentration of either enzyme o ...
... 12. What happens to the active site of an enzyme at high temperatures? 13. What pH does pepsin enzyme work best at in the stomach? 14. What word is used to describe the best set of conditions that an enzyme can work at? 15. What happens to the rate of reaction if the concentration of either enzyme o ...
Pentose Phosphate Pathway - Berkeley MCB
... How is this pentose phosphate pathway regulated? NADPH which is generated in the oxidative branch of the pathway can feed back and inhibit the pathway. Glucose 6-phosphate can still be utilized by glycolysis. ...
... How is this pentose phosphate pathway regulated? NADPH which is generated in the oxidative branch of the pathway can feed back and inhibit the pathway. Glucose 6-phosphate can still be utilized by glycolysis. ...
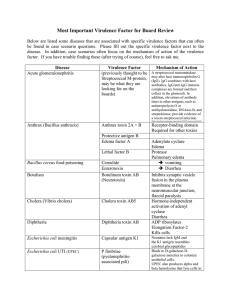
Most important VF Table for Board Review
... Below are listed some diseases that are associated with specific virulence factors that can often be found in case scenario questions. Please fill out the specific virulence factor next to the disease. In addition, case scenarios often focus on the mechanism of action of the virulence factor. If you ...
... Below are listed some diseases that are associated with specific virulence factors that can often be found in case scenario questions. Please fill out the specific virulence factor next to the disease. In addition, case scenarios often focus on the mechanism of action of the virulence factor. If you ...
Introduction
... Connecting reactions: select initial reaction (in either pane) ===> red and green reactions select a green reaction Useful Commands: choose main compounds for reaction disconnect all reactions In circular pathways, specify which compound should be at the top Add links to other pathways, reac ...
... Connecting reactions: select initial reaction (in either pane) ===> red and green reactions select a green reaction Useful Commands: choose main compounds for reaction disconnect all reactions In circular pathways, specify which compound should be at the top Add links to other pathways, reac ...
Biochemistry
... Regulation by Thioredoxin • Activates biosynthetic pathways by reducing regulatory enzymes of that pathway. • Ferridoxin reduces thioredoxin which reduces regulatory enzymes in pathway. ...
... Regulation by Thioredoxin • Activates biosynthetic pathways by reducing regulatory enzymes of that pathway. • Ferridoxin reduces thioredoxin which reduces regulatory enzymes in pathway. ...
Studies of vacuolar trafficking pathways regulated by RAB5 and
... transformed with these markers revealed that the increase in cell layers in mutant roots was caused by periclinal divisions of endodermal cells (Figure 3g,h). The outer daughter cells of divided endodermal cells also gradually lost endodermal identity, acquiring cortical identity (Figure 3i,j). The ...
... transformed with these markers revealed that the increase in cell layers in mutant roots was caused by periclinal divisions of endodermal cells (Figure 3g,h). The outer daughter cells of divided endodermal cells also gradually lost endodermal identity, acquiring cortical identity (Figure 3i,j). The ...
Electrontransfer proteins
... - In the case of cytochrome a and b the hem is bound strongly but not covalently to the protein. In the case of cytochrome c the hem and the protein bind covalently. Most of the cytochromes are 1:1 units (1 hem + 1 protein), but there are cytochromes with multiple hem units. - The cytochromes always ...
... - In the case of cytochrome a and b the hem is bound strongly but not covalently to the protein. In the case of cytochrome c the hem and the protein bind covalently. Most of the cytochromes are 1:1 units (1 hem + 1 protein), but there are cytochromes with multiple hem units. - The cytochromes always ...
Review Session One
... 10. Compare/contrast plant vs. animal cells. List ALL key organelles and describe their general function. Provide specific examples of cells with “specialized organelles” or an abundance of certain organelles. Trace the organelle pathway of protein synthesis to secretion. ...
... 10. Compare/contrast plant vs. animal cells. List ALL key organelles and describe their general function. Provide specific examples of cells with “specialized organelles” or an abundance of certain organelles. Trace the organelle pathway of protein synthesis to secretion. ...
Lecture
... Internal Fertilization • sperm deposited in or near the female reproductive tract – male copulatory organ deposits sperm – female can have a seminal receptacle for receipt and storage of sperm – then delivers it to the egg when needed – e.g. sharks – modified pelvic fins called claspers that are in ...
... Internal Fertilization • sperm deposited in or near the female reproductive tract – male copulatory organ deposits sperm – female can have a seminal receptacle for receipt and storage of sperm – then delivers it to the egg when needed – e.g. sharks – modified pelvic fins called claspers that are in ...
Lab Test 2009 - The University of Auckland
... 34. Which of the following is NOT a potentially useful target for drugs that affect peptidemediated transmission? (a) Presynaptic reuptake of peptides (b) Peptide synthesis and post-translational modification (c) Peptide transport and storage (d) Post-synaptic actions of peptides (e) Peptide release ...
... 34. Which of the following is NOT a potentially useful target for drugs that affect peptidemediated transmission? (a) Presynaptic reuptake of peptides (b) Peptide synthesis and post-translational modification (c) Peptide transport and storage (d) Post-synaptic actions of peptides (e) Peptide release ...
Protein kinase Protein kinases are enzymes that add a phosphate
... other family of human enzymes except proteases. Workers have identified 478 typical and 40 atypical protein kinase genes in humans (total 518) that correspond to about 2% of all human genes (Table). Protein kinases have a similar overall three-dimensional structure and chemical mechanism. Protein-se ...
... other family of human enzymes except proteases. Workers have identified 478 typical and 40 atypical protein kinase genes in humans (total 518) that correspond to about 2% of all human genes (Table). Protein kinases have a similar overall three-dimensional structure and chemical mechanism. Protein-se ...
UAB DIVISION of Molecular and Cellular Pathology
... The metabolites overlaid onto the core metabolic map offered for humans. Red points = serum, blue points = urine, and orange points = feces. Green points represent metabolites that were found to be diet-responsive in two or more biofluids. Particularly rich coverage is provided in amino acid metabo ...
... The metabolites overlaid onto the core metabolic map offered for humans. Red points = serum, blue points = urine, and orange points = feces. Green points represent metabolites that were found to be diet-responsive in two or more biofluids. Particularly rich coverage is provided in amino acid metabo ...
Answer Key - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... i. (10 points) What is its role, metabolically speaking? Which hormones regulate its expression and why? PEPCK is an essential enzyme in gluconeogenesis which catalyzes the conversion of oxaloacetate into phosphoenolpyruvate. It is one of the enzymes that circumvents the irreversible steps of glycol ...
... i. (10 points) What is its role, metabolically speaking? Which hormones regulate its expression and why? PEPCK is an essential enzyme in gluconeogenesis which catalyzes the conversion of oxaloacetate into phosphoenolpyruvate. It is one of the enzymes that circumvents the irreversible steps of glycol ...
Fill in blank notes - Cathkin High School
... is because most of their genes are still __________ ____ (or expressed). Adult stem cells Adult (or tissue) stem cells are involved in the growth and repair and renewal of the cells found in that tissue. Unlike embryonic stem cells, they can only produce a limited range of cell types. For example, t ...
... is because most of their genes are still __________ ____ (or expressed). Adult stem cells Adult (or tissue) stem cells are involved in the growth and repair and renewal of the cells found in that tissue. Unlike embryonic stem cells, they can only produce a limited range of cell types. For example, t ...
Lecture #11 – 9/28 – Dr. Hirsh
... PEP carboxylase has a higher affinity for CO2; no oxygenase activity. It’s found in sugar cane and crab grass. Note sugar cane is one of the most efficient plants known; captures approximately 8% of the energy of the sun’s light as chemical bonds. The C4 pathway is a very recent evolutionary develop ...
... PEP carboxylase has a higher affinity for CO2; no oxygenase activity. It’s found in sugar cane and crab grass. Note sugar cane is one of the most efficient plants known; captures approximately 8% of the energy of the sun’s light as chemical bonds. The C4 pathway is a very recent evolutionary develop ...
Amino Acid Regulation of RNA Synthesis
... The driving force in this type of transportation is the concentration gradient in the case of non-electrolytes or in the case of ions the difference in electrical charge across the membrane between the internal of the cell and the outside. Yeasts take up sugar by this method. However, few comp ...
... The driving force in this type of transportation is the concentration gradient in the case of non-electrolytes or in the case of ions the difference in electrical charge across the membrane between the internal of the cell and the outside. Yeasts take up sugar by this method. However, few comp ...
Student notes in ppt
... liver and pancreas cells when blood glucose levels are high. Unlike hexokinase I, glucokinase as a very low affinity for glucose and is not inhibited by glucose6P. Therefore after a meal, the liver accumulates glucose for glycogen synthesis, and the insulin secretion pathway is activated in pancreat ...
... liver and pancreas cells when blood glucose levels are high. Unlike hexokinase I, glucokinase as a very low affinity for glucose and is not inhibited by glucose6P. Therefore after a meal, the liver accumulates glucose for glycogen synthesis, and the insulin secretion pathway is activated in pancreat ...
Lecture 26 - Glycolysis 2
... liver and pancreas cells when blood glucose levels are high. Unlike hexokinase I, glucokinase as a very low affinity for glucose and is not inhibited by glucose6P. Therefore after a meal, the liver accumulates glucose for glycogen synthesis, and the insulin secretion pathway is activated in pancreat ...
... liver and pancreas cells when blood glucose levels are high. Unlike hexokinase I, glucokinase as a very low affinity for glucose and is not inhibited by glucose6P. Therefore after a meal, the liver accumulates glucose for glycogen synthesis, and the insulin secretion pathway is activated in pancreat ...
Metabolism of erythrocytes
... • no ATP production in oxidative phosphorylation • no ability to replace damaged lipids and proteins (low metabolic activities, with no ability to synthesize new proteins or lipids) ...
... • no ATP production in oxidative phosphorylation • no ability to replace damaged lipids and proteins (low metabolic activities, with no ability to synthesize new proteins or lipids) ...
Genome-Scale Modeling of the Protein Secretory Machinery
... Secretory proteins first need to enter to the ER in order to be properly folded, get posttranscriptional modifications and be directed to its final location in the cell[1, 2]. Translocation enters the target protein to the ER[3]. Figure 2, represents the translocation steps to the ER. The first 7 te ...
... Secretory proteins first need to enter to the ER in order to be properly folded, get posttranscriptional modifications and be directed to its final location in the cell[1, 2]. Translocation enters the target protein to the ER[3]. Figure 2, represents the translocation steps to the ER. The first 7 te ...
Alternative isoleucine synthesis pathway in
... this gene from the Cyanothece 51142 genome by BLAST analysis (Table 2). In contrast, BLAST search results indicate the presence of a complete citramalate pathway for isoleucine synthesis and the gene for CimA is identified as cce_0248, which has 53 % identity to the reported citramalate synthase gen ...
... this gene from the Cyanothece 51142 genome by BLAST analysis (Table 2). In contrast, BLAST search results indicate the presence of a complete citramalate pathway for isoleucine synthesis and the gene for CimA is identified as cce_0248, which has 53 % identity to the reported citramalate synthase gen ...
24,7 Loctic Fermentotion
... (synthetic) pathway. Like most anabolic pathways, it requires the expenditure of ATP Six molecules of ATP are required to convert two molecules of lactate to one molecule of glucose.However,only two molecules of ATP were gained by converting one molecule of glucose to two molecules of lactate in lac ...
... (synthetic) pathway. Like most anabolic pathways, it requires the expenditure of ATP Six molecules of ATP are required to convert two molecules of lactate to one molecule of glucose.However,only two molecules of ATP were gained by converting one molecule of glucose to two molecules of lactate in lac ...